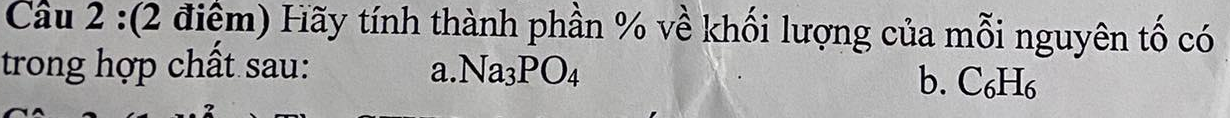
giúp mình câu a với ạ !!!
giúp mình bài 6 với ạ trừ câu a còn các câu b,c,d, giúp mình với ạ
\(b,N=\left(2x-1\right)^2-4\ge-4\\ N_{min}=-4\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\ c,P=\left(2x-5\right)^2+6\left(2x-5\right)+9-4\\ P=\left(2x-5+3\right)^2-4=\left(2x-2\right)^2-4\ge-4\\ P_{min}=-4\Leftrightarrow x=1\\ d,Q=\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+\left(y^2+4y+4\right)+1\\ Q=\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y+2\right)^2+1\ge1\\ Q_{min}=1\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
6a.
$M=x^2-x+1=(x^2-x+\frac{1}{4})+\frac{3}{4}$
$=(x-\frac{1}{2})^2+\frac{3}{4}\geq \frac{3}{4}$
Vậy $M_{\min}=\frac{3}{4}$ khi $x-\frac{1}{2}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{2}$
giúp mình cái này với ạ!:< ở câu b ý ạ câu a em giải rồi ạ!
Mong các bạn giải giúp mình câu b với ạ! ( câu b mình làm không đúng đâu )
Còn câu a là thầy giáo mình đã chữa.
Cảm ơn các bạn nhiều ạ !!!


 giúp mình câu a, b với ạ
giúp mình câu a, b với ạ
b) Thay y=0 vào (d1), ta được:
\(\dfrac{1}{2}x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}=-2\)
hay x=-4
Vậy: A(-4;0)
Thay y=0 vào (d2), ta được:
\(2-x=0\)
hay x=2
Vậy: B(2;0)
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của (d1) và (d2) là:
\(\dfrac{1}{2}x+2=-x+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Thay x=0 vào (d2), ta được:
\(y=-0+2=2\)
Vậy: C(0;2)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(-4-2\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=6\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(-4-0\right)^2+\left(0-2\right)^2}=2\sqrt{5}\)
\(BC=\sqrt{\left(2-0\right)^2+\left(0-2\right)^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
c) Chu vi tam giác ABC là:
\(C_{ABC}=AB+AC+BC=6+2\sqrt{5}+2\sqrt{2}\left(cm\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P_{ABC}=\dfrac{C_{ABC}}{2}=3+\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2}\)
Diện tích tam giác ABC là:
\(S_{ABC}=\sqrt{P\cdot\left(P-AB\right)\left(P-AC\right)\left(P-BC\right)}\)
\(=\sqrt{\left(3+\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2}\right)\left(-3+\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2}\right)\left(3-\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2}\right)\left(3+\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{2}\right)}\)
\(=6\left(cm^2\right)\)
Giúp mình câu a, b với ạ!

a:Thay x=1 và y=-1 vào (d), ta được:
2a-4=-1
hay \(a=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
a) Ta có: \(A\left(1;-1\right)\in\left(d\right)\Rightarrow y_A=\left(2a-1\right)x_A-3\)
\(\Rightarrow-1=\left(2a-1\right).1-3\Rightarrow2a-1=2\)
Vậy \(\left(d\right):y=2x-3\)
b) Ta có: \(\left(d'\right)\perp\left(d\right)\Leftrightarrow a.a'=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a'.2=-1\Leftrightarrow a'=-\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow\left(d'\right):y=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+b\)
Ta có: \(\left(d'\right)\) cắt trục tung tại điểm B có tung độ là \(\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow b=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
Vậy \(\left(d'\right):y=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{4}{3}\)
a, Vì (d) đi qua A(1;-1) nên \(x=1;y=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a-1-3=-1\\ \Leftrightarrow a=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Vậy \(\left(d\right):y=\left(2\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}-1\right)x-3=2x-3\)
\(b,\) Gọi \(\left(d'\right):y=cx+d\left(c\ne0\right)\) là đt cần tìm
\(\left(d'\right)\perp\left(d\right)\Leftrightarrow2c=-1\Leftrightarrow c=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\left(d'\right)\) cắt trục tung tại điểm B có tung độ \(\dfrac{4}{3}\Leftrightarrow x=0;y=\dfrac{4}{3}\Leftrightarrow d=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
Vậy \(\left(d'\right):y=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{4}{3}\)
c, PTHDGD của \(\left(d\right)\) và \(\left(d'\right)\) là \(-\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{4}{3}=2x-3\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{2}x=\dfrac{13}{3}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{26}{15}\\ \Leftrightarrow y=\dfrac{7}{15}\Leftrightarrow C\left(\dfrac{26}{15};\dfrac{7}{15}\right)\)
d, Ta có \(B\left(0;\dfrac{4}{3}\right)\Leftrightarrow BC=\sqrt{\left(\dfrac{26}{15}-0\right)^2+\left(\dfrac{7}{15}-\dfrac{4}{3}\right)^2}=\dfrac{13\sqrt{5}}{15}\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(\dfrac{26}{15}-1\right)^2+\left(\dfrac{7}{15}+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{11\sqrt{5}}{15}\)
Vì \(\Delta ABC\) vuông tại C nên \(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{1}{2}AC\cdot BC=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{13\sqrt{5}}{15}\cdot\dfrac{11\sqrt{5}}{15}=\dfrac{143}{90}\left(đvdt\right)\)
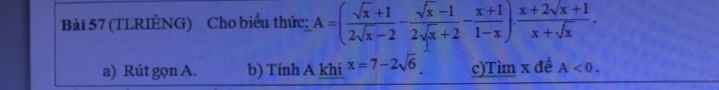
mọi người giúp mình giải hết các câu a,b,c với ạ
mình đang cần gấp mình cám ơn ạ
giúp mình với ạ (nếu được giải chi tiết câu a cho mình với mình cảm ơn)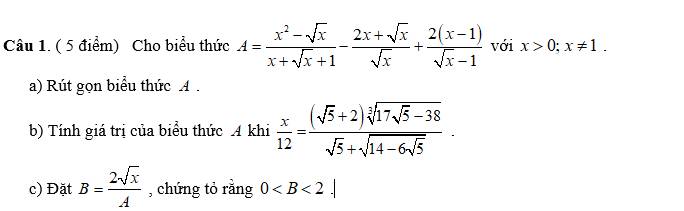
a: \(A=\dfrac{x^2-\sqrt{x}}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}-\dfrac{2x+\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(x\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(2\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(x+\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}-2\sqrt{x}-1+2\sqrt{x}+2\)
\(=\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)+1=x-\sqrt{x}+1\)
b:
\(\dfrac{x}{12}=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{5}+2\right)\sqrt[3]{17\sqrt{5}-38}}{\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{14-6\sqrt{5}}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\cdot\dfrac{1}{12}=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{5}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{5}-2\right)}{\sqrt{5}+3-\sqrt{5}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{12}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
=>x=36
Khi x=36 thì \(A=36-6+1=37-6=31\)
c: \(B=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{A}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{x-\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(B-2=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-2x+2\sqrt{x}-2}{x-\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2x+4\sqrt{x}-2}{x-\sqrt{x}+1}=\dfrac{-2\left(x-2\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{x-\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}}< 0\)
=>B<2
\(2\sqrt{x}>0;x-\sqrt{x}+1=\left(\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}>0\)
=>B>0
=>0<B<2
Làm giúp mình câu a,b với ạ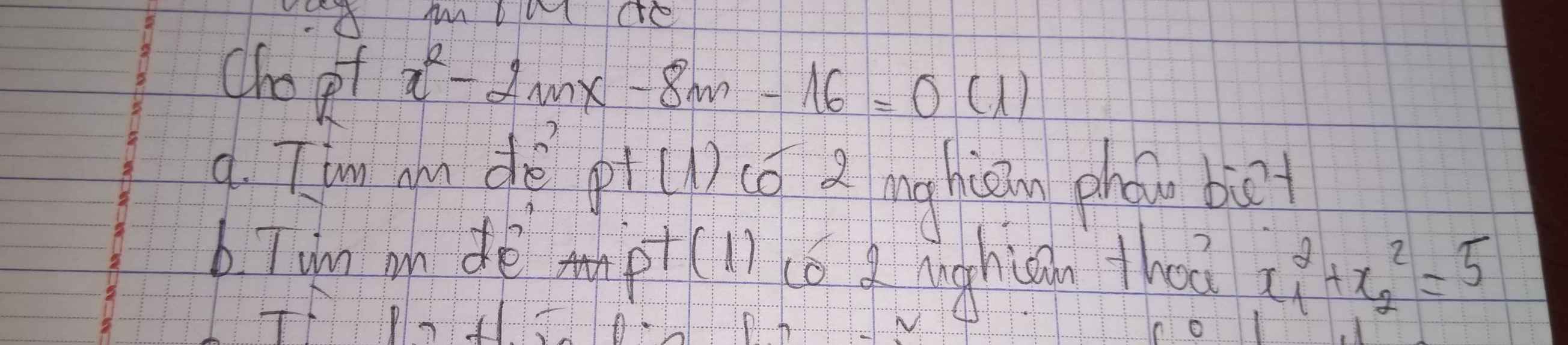
a/ Pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
\(\to\Delta'=(-m)^2-1.(-8m-16)=m^2+8m+16=(m+4)^2>0\\\to m+4>0\quad or\quad m+4<0\\\to m>-4\quad or\quad m<-4\)
b/ Theo Vi-ét:
\(\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=2m\\x_1x_2=-8m-16\end{cases}\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=5\\\leftrightarrow x_1^2+2x_1x_2+x_2^2-2x_1x_2=5\\\leftrightarrow (x_1+x_2)^2-2x_1x_2=5\\\leftrightarrow (2m)^2-2.(-8m-16)=5\\\leftrightarrow 4m^2+16m+32=5\\\leftrightarrow 4(m^2+4m+8)=5\\\leftrightarrow 4(m+2)^2+16=5\\\leftrightarrow 4(m+2)^2+11=0(\text{vô lý})\\\to m\in\varnothing\)
Vậy không có giá trị m thỏa mãn
giúp mình bài 1 câu a với ạ

1a.
\(2x^2+7xy+5y^2-5y-2x\)
\(=2x^2+5xy+2xy+5y^2-5y-2x\)
\(=x\left(2x+5y\right)+y\left(2x+5y\right)-\left(2x+5y\right)\)
\(=\left(2x+5y\right)\left(x+y-1\right)\)