Hàm số f x = 2 s i n x + s i n 2 x trên đoạn 0 ; 3 π 2 có giá trị lớn nhất là M, giá trị nhỏ nhất là m Khi đó M+m bằng:
A. − 3 3
B. 3 3
C. − 3 3 4
D. 3 3 2
Cho hai hàm số y = f(x) và y = g(x) xác định trên R. Đặt S(x) = f(x) + g(x) và P(x) = f(x) g(x).
Xét các mệnh đề:
i) Nếu y = f(x) và y = g(x) là những hàm số chẵn thì y = S(x) và y = P(x) cũng là những hàm số chẵn
ii) Nếu y = f(x) và y = g(x) là những hàm số lẻ thì y = S(x) là hàm số lẻ và y = P(x) là hàm số chẵn
iii) Nếu y = f(x) là hàm số chẵn, y = g(x) là hàm số lẻ thì y = P(x) là hàm số lẻ
Số mệnh đề đúng là:
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. Tất cả đều sai
tìm 10 số
s/e/s/e/v/e/n/t/y
n/i/t/e/n/r/t/a/h
t/w/e/n/t/y/l/y/x/u
e/t/h/i/r/t/y/s/n
f/v/u/n/g/c/a/i/d
i/y/c/e/a/h/i/x/r
f/o/r/t/y/a/t/t/e
t/bo/x/s/z/i/y/d
y/r/a/y/i/t/v/ra
seven
twenty
forty
ten
thirty
còn lại chịu
câu trả lời của các bạn ko đc lay ví dụ;
-seve,seventy
Áp dụng quy tắc I, hãy tìm các điểm cực trị của hàm s f(x) = x(x^2 – 3).
1. TXĐ: D = R
2. f’(x) = 3x^2 – 3. Cho f’(x) = 0 ⇔ x = 1 hoặc x = -1.
3. Ta có bảng biến thiên:
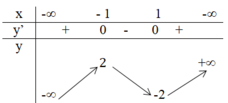
Hàm số đạt cực đại tại x = -1 và giá trị cực đại là 2
Hàm số đạt cực tiểu tại x = 1 và giá trị cực tiểu là -2.
ĐÁP ÁN VÒNG 2 CUỘC THI TIN HỌC:
* ĐỀ 1:
Câu 1:
CÂU 1:
const fi='uc.inp'
fo='uc.out'
var f: text;
a,b,c : integer;
function uc(x,y): integer;
var z: integer;
begin
while y<>0 do
begin
z:=x mod y;
x:=y;
y:=z;
end;
uc:=x;
end;
procedure ip;
begin
assign(f,fi);
reset(f);
read(f,a,b,c);
close(f);
end;
procedure out;
begin
assign(f,fo);
rewrite(f);
write(f,uc(uc(a,b),c);
close(f);
end;
begin
ip;
out;
end.
Câu 2:
const fi='SN.inp'
fo='SN.out'
var
f:text;
i,n:integer;
s:real;
procedure ip;
begin
assign(f,fi);
reset(f);
read(f,n);
close(f);
end;
procedure out;
begin
assign(f,fo);
rewrite(f);
s:=0;
for i:= 1 to n do
begin
if i mod 2 <> 0 then
s:=s+(i/(i+1));
if i mod 2 = 0 then
s:=s-(i/(i+1));
end;
write(f,s:0:2);
close(f);
end;
BEGIN
ip;
out;
END.
Câu 3:
const fi='SSNT.inp'
fo='SSNT.out'
var
f:text;
n,i,max,j:integer;
s:string;
a:array[1..32000] of integer;
function nt(x:integer):boolean;
var
i:integer;
begin
nt:=false;
if x < 2 then exit;
for i:= 2 to trunc(sqrt(x)) do
if x mod i = 0 then exit;
nt:=true;
end;
function snt(x:integer):boolean;
begin
snt:=false;
if x= 0 then exit;
while nt(x) = true do
x := x div 10;
if x = 0 then snt:=true;
end;
procedure ip;
begin
assign(f,fi);
reset(f);
max:=a[1];
readln(f,n);
for i:= 1 to n do
begin
read(f,a[i]);
if( a[i] < max ) and (nt(a[i]) = true) then
max:=a[i];
end;
close(f);
end;
procedure out;
begin
assign(f,fo);
rewrite(f);
writeln(f,max);
max:=0;
for i:= 1 to n do
begin
if snt(a[i]) = true then
begin
str(a[i],s);
if length(s) = 2 then
max:=max+a[i];
s:=''
end
else
a[i]:=-32000;
end;
writeln(f,max);
for i:= 1 to n-1 do
for j :=i+1 to n do
if a[i] > a[j] then
begin
max:=a[i];
a[i]:=a[j];
a[j]:=max;
end;
for i:= 1 to n do
if (a[i] > 0) and (a[i] <> a[i-1]) then write(f,a[i],' ');
close(f);
end;
BEGIN
ip;
out;
END.
CÂU 4:
const fi='TUOI.INP'
fo='TUOI.OUT'
var f: text;
a,b: byte;
procedure ip;
begin
assign(f,fi);
reset(f);
read(f,a,b);
close(f);
end;
procedure out;
begin
assign(f,fo);
rewrite(f);
if (x=y*2) and (x>18) and (x-y>=18) then write(f,'CO') else write(f,x-y*2);
close(f);
end;
begin
ip;
out;
end.
const fi='CM.INP'
fo='CM.OUT'
var f: text;
a,n,b,k: integer;
a1: array[1..32000] of integer;
function nt(x: integer): boolean;
var i: integer;
begin
nt:=false;
if x<2 then exit;
for i:=2 to trunc(sqrt(x)) do if x mod i=0 then exit;
nt:=true;
end;
procedure ip;
begin
assign(f,fi);
reset(f);
read(f,n);
close(f);
end;
procedure out;
begin
assign(f,fo);
rewrite(f);
d:=0;
for a:=1 to k do
if nt(a) then
begin
inc(d);
a1[d]:=a;
end;
for a:=1 to d do
for b:=x to d do
if a1[a]+a1[b]=k then writeln(f,a1[a],'+',a1[b]);
end;
close(f);
end;
begin
ip;
out;
end.
*ĐỀ 2 :
BÀI LÀM CỦA BẠN LÊ HOÀNG THẮNG:
//----------------------------CAU 1--------------------------------
var s,d,n,i,u:longint;
a:array[0..32001] of longint;
f:text;
function ucln(x,y:longint):longint;
begin
if y=0 then exit(x) else exit(ucln(y,x mod y));
end;
begin
assign(f,'ucln.inp');reset(f);
readln(f,n);
for i:=1 to n do read(f,a[i]); close(f);
u:=a[1];
for i:=2 to n do u:=ucln(u,a[i]);
assign(f,'ucln.out');rewrite(f);
write(f,'UCLN: ',u,' UC: ');
for i:=1 to u do if u mod i=0 then
begin
if i<>u then write(f,i,',') else write(f,i);
if i<10 then inc(d) else inc(s,i);
end;
writeln(f);
writeln(f,d); write(f,s);
close(f);
end.
//----------------------------CAU 2--------------------------------
var n,i:longint;
s:real;
f:text;
begin
assign(f,'sn.inp');reset(f);
readln(f,n); close(f);
for i:=1 to n do if odd(i) then s:=s-i/(i+1) else s:=s+i/(i+1);
assign(f,'sn.out');rewrite(f);
write(f,s:0:2);
close(f);
end.
//----------------------------CAU 3--------------------------------
var a:array[0..1000000] of boolean;
b:array[0..1000000] of longint;
i,j,k,n,d:longint;
f:text;
procedure taosang(n:longint);
var i,j:longint;
begin
for i:=2 to trunc(sqrt(n)) do if not(a[i]) then
begin
j:=i*i;
while j<=n do begin a[j]:=true; inc(j,i); end;
end;
end;
begin
assign(f,'boso.inp');reset(f);
readln(f,n); taosang(n); close(f);
assign(f,'boso.out');rewrite(f);
for i:=2 to n do if not(a[i]) then
begin
inc(d);
b[d]:=i;
end;
for i:=1 to d do
for j:=i to d do
if (n-b[i]-b[j]>=b[j]) and not(a[n-b[i]-b[j]]) then
writeln(f,b[i],' ',b[j],' ',n-b[i]-b[j]);
close(f);
end.
//----------------------------CAU 4--------------------------------
THAM KHẢO ĐỀ 1.
//----------------------------CAU 5--------------------------------
var n,i,s,t:longint;
f:text;
begin
assign(f,'u.inp');reset(f);
readln(f,n); t:=n; close(f);
assign(f,'u.out');rewrite(f);
for i:=2 to trunc(sqrt(n)) do
begin
if n mod i=0 then
begin
write(f,i,' ');
repeat n:=n div i until n mod i>0;
end;
if t mod (i*i)=0 then inc(s,i*i);
end;
writeln(f);
write(f,s+1);
close(f);
end.
*ĐỀ CHUNG:
BÀI LÀM CỦA BẠN ĐÀO XUÂN SƠN :
Câu 1:
const fi='TCS.inp'
fo='TCS.out'
var
f:text;
x:char;
tg:byte;
s:integer;
CODE:integer;
procedure ip;
begin
assign(f,fi);
reset(f);
s:=0;
while not(eof(f)) do
begin
read(f,x);
if x in ['0'..'9'] then
begin
val(x,tg,CODE);
s:=s+tg;
end;
end;
close(f);
end;
procedure out;
begin
assign(f,fo);
rewrite(f);
write(f,s);
close(f);
end;
BEGIN
ip;
out;
END.
Câu 2:
const fi='t.inp'
fo='t.out'
var
f:text;
s:string;
i:byte;
procedure ip;
begin
assign(f,fi);
reset(f);
read(f,s);
close(f);
end;
procedure out;
begin
assign(f,fo);
rewrite(f);
s[1]:=upcase(s[1]);
for i:= 2 to length(s) do
if s[i-1] <> #32 then
s[i]:=lowercase(s[i]) else
s[i]:=upcase(s[i]);
write(f,s);
close(f);
end;
BEGIN
ip;
out;
END.
Em dốt tin lắm cô ơi, cô tạo khóa học nào đi, cô còn kèm em học ![]()
Cho hàm số f(x) liên tục trên R và thỏa mãn f ( x ) + f π 3 - x = 1 3 sin x cos x ( 8 cos 3 x + 1 ) . Biết tích phân I = ∫ 0 π 3 f ( x ) d x được biểu diễn dưới dạng I = a b ln c d và các phân số là các phân số tối giản. Tính S = a 3 + a b - c + d
A. S=6
B. S=3
C. S=5
D. S=7
Cho hàm số y=f(x) liên tục trên R và hàm số y = g ( x ) = x f ( x 2 ) có đồ thị trên đoạn [0; 2] như hình vẽ bên. Biết diện tích S của miền được tô đậm bằng 5/2, tính tích phân I = ∫ 1 4 f ( x ) d x
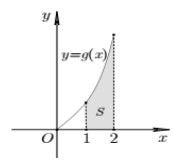
A. 5/4
B. 5/2
C. 5
D. 10
Cho hàm số y = f(x) liên tục trên R và hàm số y = g ( x ) = x f ( x 2 ) có đồ thị trên đoạn [1;2] như hình vẽ bên. Biết phần diện tích miền được tô màu là S = 5/2 , tính tích phân I = ∫ 1 4 f ( x ) d x
A. I = 7
B. I = 6
C. I = 10
D. I = 5
Cho hàm số y = f(x) liên tục trên R và hàm số y = g(x) = x.f(x2) có đồ thị trên đoạn [0;2] như hình vẽ bên. Biết diện tích S của miền được tô đậm bằng 5/2 tính tích phân I = ∫ 1 4 f ( x ) d x
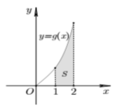
A. I = 5/4
B. I = 5/2
C. I = 5
D. I = 10
Cho hàm số y=f(x) có đạo hàm f'(x) = ( x 2 - 1 ) ( x - 2 ) . Gọi S là tập tất cả các giá trị nguyên của tham số m để hàm số f ( x 2 + m ) có 5 điểm cực trị. Số phần tử của tập S là.
A. 4
B. 1
C. 3
D. 2
cho hàm số f(x)=\(\frac{2x+1}{x^2\left(x+1\right)^2}\).Tìm x,y thuộc N sao cho
S=f(1)+f(2)+...+f(x)=\(\frac{2y\left(x+1\right)^3-1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)-19+x
Ta có:
f(x)=\(\frac{x^2+2x+1-x^2}{x^2\left(x+1\right)^2}=\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2-x^2}{x^2\left(x+1\right)^2}=\frac{1}{x^2}-\frac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(1\right)=1-\frac{1}{2^2};f\left(2\right)=\frac{1}{2^2}-\frac{1}{3^2};...;f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x^2}-\frac{1}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
=> \(S=1-\frac{1}{2^2}+\frac{1}{2^2}-\frac{1}{3^2}+\frac{1}{3^2}-\frac{1}{4^2}+...+\frac{1}{x^2}-\frac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=1-\frac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
Theo bài ra ta có :
\(1-\frac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=\frac{2y\left(x+1\right)^3-1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}-19+x\)
<=> \(1-\frac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=2y\left(x+1\right)-\frac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}-19+x\)
<=> 1=2y(x+1)-19+x
<=> (2y+1)(x+1)=21
x, y thuộc N => 2y+1, x+1 thuộc N
Ta có bảng
| x+1 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 21 |
| 2y+1 | 7 | 21 | 3 | 1 |
| x | 2 | 0 | 6 | 20 |
| y | 3 | 10 | 1 | 0 |
Vậy....
Cô Linh Chi:
phần bảng x không có giá trị bằng 0
Nếu x = 0 thì hàm số f (x) có giá trị bằng 0
Thứ nhất: Không phải phần bảng không có giá trị bằng 0. Mà là kết luận thì phải loại trường hợp x=0. :)
Thứ 2: Nếu x=0 thì hàm số f(x) không xác định chứ ko phải bằng 0 em nhé :)