Giải các phương trình: 5 x 2 - 3 x + 1 = 2 x + 11

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Bài 1. Giải các phương trình sau
(x+1)(x+9)=(x+3)(x+5)
(x-1)^3 -x(x+1)^2=5x(2-x)-11(x+2)
Bài 1:
(x+1)(x+9)=(x+3)(x+5)
⇔x2+10x+9=x2+8x+15
⇔2x-6=0
⇔x=3
(x-1)3-x(x+1)2=5x(2-x)-11(x+2)
⇔x3-3x2+3x-1-x3-2x2-x=10x-5x2-11x-22
⇔-5x2+2x-1=-5x2-x-22
⇔3x+21=0
⇔x=-7
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
2
(
x
+
5
)
3
+
x
+
12
2
-
5
(
x
-
2
)
6
x
3
+
11
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau: 2 ( x + 5 ) 3 + x + 12 2 - 5 ( x - 2 ) 6 = x 3 + 11
Ta có:
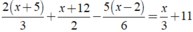
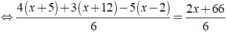
⇔ 4x + 20 + 3x + 36 - 5x + 10 = 2x + 66
⇔ 0x = 0
⇒ Phương trình đã cho vô số nghiệm.
Vậy phương trình đã cho vô số nghiệm.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau: a) 11x+4=-3/2 b) x^2-9+2(x-3) =0 c) x-3/5+1+2x/3=6 d) 2/x+1-1/x-2=3x-11/(x+1) (x-2)
a: 11x+4=-3/2
=>\(11x=-\dfrac{3}{2}-4=-\dfrac{11}{2}\)
=>\(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
b: \(x^2-9+2\left(x-3\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)+2\left(x-3\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3+2\right)=0\)
=>(x-3)(x+5)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: \(\dfrac{x-3}{5}+\dfrac{1+2x}{3}=6\)
=>\(\dfrac{3\left(x-3\right)+5\left(2x+1\right)}{15}=6\)
=>\(3x-9+10x+5=90\)
=>13x-4=90
=>13x=94
=>\(x=\dfrac{94}{13}\)
d: \(\dfrac{2}{x+1}-\dfrac{1}{x-2}=\dfrac{3x-11}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)(ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-1;2\right\}\))
=>\(\dfrac{2\left(x-2\right)-\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{3x-11}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
=>3x-11=2x-4-x-1
=>3x-11=x-5
=>2x=6
=>x=3(nhận)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
bài 2 giải các phương trình sau
b,2(x+3)-4=0
d,5(x-3)=3x-5
f,7(5-x)=11-5x
h,2(3x-1)-3x=10
j,3-2x=3.(x+1)-x-2
m,4(2x-3)-5=6(3-x)-7
b)x+3=4:2
=> x=-1
d)5x-15=3x-5
<=> 5x-3x=15-5
<=> 2x=10
<=> x=5
f) 35-7x=11-5x
<=> 35-11=-5x+7x
<=> 24=2x
<=> x=12
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
h) 6x-2-3x=10
<=> 3x=10+2
<=> x=4
j)3-2x=3x+3-x-2
<=> 3-2x=2x+1
<=>-4x=-2
<=> x=1/2
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình sau:
a)\(\dfrac{x-3}{5}+\dfrac{1+2x}{3}=6\)
b)\(\dfrac{2}{x+1}-\dfrac{1}{x-2}=\dfrac{3x-11}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
a: =>3x-9+5+10x=90
=>13x-4=90
=>13x=94
hay x=94/13
b: \(\Leftrightarrow2x-4-x-1=3x-11\)
=>3x-11=x-5
=>2x=6
hay x=3(nhận)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x-11}}+\sqrt{x-\sqrt{x-11}}=4\).
b) \(\sqrt{x+2+3\sqrt{2x-5}}+\sqrt{x-2-\sqrt{2x-5}}=2\sqrt{2}\)
a, ĐK: \(x\ge11\)
\(\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x-11}}+\sqrt{x-\sqrt{x-11}}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\sqrt{x-11}+x-\sqrt{x-11}+2\sqrt{x^2-x+11}=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+2\sqrt{x^2-x+11}=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\sqrt{x^2-x+11}=8\)
Ta thấy \(x+\sqrt{x^2-x+11}>11>\text{}8\)
\(\Rightarrow\) phương trình vô nghiệm.
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(a,\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x-11}}+\sqrt{x-\sqrt{x-11}}=4\left(x\ge11\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x+\sqrt{x-11}+x-\sqrt{x-11}+2\sqrt{\left(x+\sqrt{x-11}\right)\left(x-\sqrt{x-11}\right)}=16\\ \Leftrightarrow2x+2\sqrt{x^2-x+11}=16\\ \Leftrightarrow x+\sqrt{x^2-x+11}=8\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2-x+11}=8-x\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-x+11=x^2-16x+64\\ \Leftrightarrow15x=53\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{53}{15}\left(ktm\right)\)
\(b,\sqrt{x+2+3\sqrt{2x-5}}+\sqrt{x-2-\sqrt{2x-5}}=2\sqrt{2}\left(x\ge\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x-5+6\sqrt{2x-5}+9}+\sqrt{2x-5-2\sqrt{2x-5}+1}=4\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{2x-5}+3\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{2x-5}-1\right)^2}=4\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x-5}+3+\left|\sqrt{2x-5}-1\right|=4\\ \Leftrightarrow\left|\sqrt{2x-5}-1\right|=1-\sqrt{2x-5}\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x-5}-1\le0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x-5}\le1\\ \Leftrightarrow2x-5\le1\Leftrightarrow x\le\dfrac{5}{2}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
b, ĐK: \(x\ge\dfrac{5}{2}\)
\(\sqrt{x+2+3\sqrt{2x-5}}+\sqrt{x-2-\sqrt{2x-5}}=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x+4+6\sqrt{2x-5}}+\sqrt{2x-4-\sqrt{2x-5}}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{2x-5}+3\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{2x-5}-1\right)^2}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|\sqrt{2x-5}+3\right|+\left|\sqrt{2x-5}-1\right|=4\)
Áp dụng BĐT \(\left|a\right|+\left|b\right|\ge\left|a+b\right|\):
\(\left|\sqrt{2x-5}+3\right|+\left|\sqrt{2x-5}-1\right|\)
\(=\left|\sqrt{2x-5}+3\right|+\left|1-\sqrt{2x-5}\right|\)
\(\ge\left|\sqrt{2x-5}+3+1-\sqrt{2x-5}\right|\)
\(=4\)
Đẳng thức xảy ra khi:
\(\left(\sqrt{2x-5}+3\right)\left(1-\sqrt{2x-5}\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-\sqrt{2x-5}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x-5}\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0\le2x-5\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{2}\le x\le3\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
giải các phương trình sau:
a. x2-25=8(5-x)
b.x-2/ x+2 - 2(x-11)/x2-4 =3/x-2
a.\(x^2-25=8\left(5-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)-8\left(5-x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)+8\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x+13\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-13\end{matrix}\right.\)
b.\(\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}-\dfrac{2\left(x-11\right)}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{3}{x-2}\) ; \(ĐK:x\ne\pm2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-2\right)-2\left(x-11\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{3\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2-2\left(x-11\right)=3\left(x+2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+4-2x+22=3x+6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9x+20=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\left(tm\right)\\x=4\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) \(\sqrt {11{x^2} - 14x - 12} = \sqrt {3{x^2} + 4x - 7} \)
b) \(\sqrt {{x^2} + x - 42} = \sqrt {2x - 30} \)
c) \(2\sqrt {{x^2} - x - 1} = \sqrt {{x^2} + 2x + 5} \)
d) \(3\sqrt {{x^2} + x - 1} - \sqrt {7{x^2} + 2x - 5} = 0\)
a) \(\sqrt {11{x^2} - 14x - 12} = \sqrt {3{x^2} + 4x - 7} \)
\(\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 11{x^2} - 14x - 12 = 3{x^2} + 4x - 7\\ \Rightarrow 8{x^2} - 18x - 5 = 0\end{array}\)
\( \Rightarrow x = - \frac{1}{4}\) và \(x = \frac{5}{2}\)
Thay nghiệm vừa tìm được vào phương trình \(\sqrt {11{x^2} - 14x - 12} = \sqrt {3{x^2} + 4x - 7} \) ta thấy chỉ có nghiệm \(x = \frac{5}{2}\) thảo mãn phương trình
Vậy nhiệm của phương trình đã cho là \(x = \frac{5}{2}\)
b) \(\sqrt {{x^2} + x - 42} = \sqrt {2x - 30} \)
\(\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow {x^2} + x - 42 = 2x - 3\\ \Rightarrow {x^2} - x - 12 = 0\end{array}\)
\( \Rightarrow x = - 3\) và \(x = 4\)
Thay vào phương trình \(\sqrt {{x^2} + x - 42} = \sqrt {2x - 30} \) ta thấy không có nghiệm nào thỏa mãn
Vậy phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm
c) \(2\sqrt {{x^2} - x - 1} = \sqrt {{x^2} + 2x + 5} \)
\(\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 4.\left( {{x^2} - x - 1} \right) = {x^2} + 2x + 5\\ \Rightarrow 3{x^2} - 6x - 9 = 0\end{array}\)
\( \Rightarrow x = - 1\) và \(x = 3\)
Thay hai nghiệm trên vào phương trình \(2\sqrt {{x^2} - x - 1} = \sqrt {{x^2} + 2x + 5} \) ta thấy cả hai nghiệm đếu thỏa mãn phương trình
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình \(2\sqrt {{x^2} - x - 1} = \sqrt {{x^2} + 2x + 5} \) là \(x = - 1\) và \(x = 3\)
d) \(3\sqrt {{x^2} + x - 1} - \sqrt {7{x^2} + 2x - 5} = 0\)
\(\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 3\sqrt {{x^2} + x - 1} = \sqrt {7{x^2} + 2x - 5} \\ \Rightarrow 9.\left( {{x^2} + x - 1} \right) = 7{x^2} + 2x - 5\\ \Rightarrow 2{x^2} + 7x - 4 = 0\end{array}\)
\( \Rightarrow x = - 4\) và \(x = \frac{1}{2}\)
Thay hai nghiệm trên vào phương trình \(3\sqrt {{x^2} + x - 1} - \sqrt {7{x^2} + 2x - 5} = 0\) ta thấy chỉ có nghiệm \(x = - 4\) thỏa mãn phương trình
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình trên là \(x = - 4\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
\(e.\dfrac{12}{1-9x^2}=\dfrac{1-3x}{1+3x}-\dfrac{1+3x}{1-3x}\)
\(f.\dfrac{6x+1}{x^2-7x+10}+\dfrac{5}{x-2}=\dfrac{3}{x-5}\)
\(g.\dfrac{2}{x+2}-\dfrac{2x^2+16}{x^3+8}=\dfrac{5}{x^2-2x+4}\)
\(h.\dfrac{8}{x-8}+\dfrac{11}{x-11}=\dfrac{9}{x-9}+\dfrac{10}{x-10}\)
e) ĐK : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}1+3x\ne0\\1-3x\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x\ne-1\\3x\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{-1}{3}\\x\ne\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{12}{\left(1-3x\right)\left(1+3x\right)}=\dfrac{\left(1-3x\right)^2-\left(1+3x\right)^2}{\left(1+3x\right)\left(1-3x\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12\left(1+3x\right)\left(1-3x\right)=\left(1-3x\right)\left(1+3x\right)\left(1-3x-1-3x\right)\left(1-3x+1+3x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12=\left(-6x\right).2\Leftrightarrow6=-6x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\left(TM\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
giải các phương trình sau
Xem chi tiết
e,x-2/2+x-3/x-2=2(x-11)/x^2-4
f,x+1/x-1-x-1/x+1=4/x^2-1




























