giải phương trình:
x4+2x3+5x2+4x+4=0
Giải phương trình sau bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích: 2x3 + 5x2 – 3x = 0
2x3 + 5x2 – 3x = 0
⇔ x(2x2 + 5x – 3) = 0
⇔ x.(2x2 + 6x – x – 3) = 0
⇔ x. [2x(x + 3) – (x + 3)] = 0
⇔ x.(2x – 1)(x + 3) = 0
⇔ x = 0 hoặc 2x – 1 = 0 hoặc x + 3 = 0
+ 2x – 1 = 0 ⇔ 2x = 1 ⇔ x = 1/2.
+ x + 3 = 0 ⇔ x = -3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 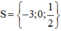
Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử bằng phương pháp đặt ẩn phụ
x4+2x3+5x2+4x-12
`x^4+2x^3+5x^2+4x-12`
`=x^4-x^3+3x^3-3x^2+8x^2-8x+12x-12`
`=x^3(x-1)+3x^2(x-1)+8x(x-1)+12(x-1)`
`=(x-1)(x^3+3x^2+8x+12)`
`=(x-1)(x^3+2x^2+2x^2+4x+6x+12)`
`=(x-1)[x^2(x+2)+2x(x+2)+6(x+2)]`
`=(x-1)(x+2)(x^2+2x+6)`
\(x^4+2x^3+5x^2+4x-12\)
\(=x^4-x^3+3x^3-3x^2+8x^2-8x+12x-12\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^3+3x^2+8x+12\right)\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+2x^2+x^2+2x+6x+12\right)\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2+x+6\right)\)
Giải phương trình:
a) x4 - 2x3 + x2 - 4x +4 = 0
b) x4 + 2x3 - 3 = 0
c) 2x4 - 100x + 98 = 0
d) (x + 1)(x + 2)(x + 3)(x + 4) = 24
d: Ta có: \(\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)=24\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+5x+4\right)\left(x^2+5x+6\right)-24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải Phương trình
5x2 + 4x + 2x3 + x4 - 12 = 0
\(5x^2+4x+2x^3+x^4-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+2x^3+5x^2+4x-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^3+3x^3-3x^2+8x^2-8x+12x-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x-1\right)+3x^2\left(x-1\right)+8x\left(x-1\right)+12\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^3+3x^2+8x+12\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[x^3+2x^2+x^2+2x+6x+12\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[x^2\left(x+2\right)+x\left(x+2\right)+6\left(x+2\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2+x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left[x^2+2\times\dfrac{1}{2}x+\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2-\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+6\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left[\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{23}{4}\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x+2=0\\\left(x^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{23}{4}=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vì \(\left(x^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\Rightarrow\left(x^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{23}{4}\ge\dfrac{23}{4}\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{23}{4}\) vô nghiệm
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là\(S=\left\{1;-2\right\}\)
Chứng minh rằng phương trình sau có ít nhất hai nghiệm: 2 x 3 - 5 x 2 + x + 1 = 0
Chứng minh rằng phương trình sau có ít nhất hai nghiệm :
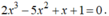
- Xét hàm số: f ( x ) = 2 x 3 - 5 x 2 + x + 1 là hàm đa thức.
⇒ Hàm số f liên tục trên R.
- Ta có:
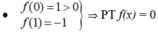 có ít nhất một nghiệm c1 ∈ (0;1).
có ít nhất một nghiệm c1 ∈ (0;1).
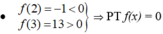 có ít nhất một nghiệm c2 ∈ (2;3).
có ít nhất một nghiệm c2 ∈ (2;3).
- Mà c ≠ c 2 nên PT f(x) = 0 có ít nhất 2 nghiệm.
Tìm bậc của mỗi đa thức sau
a) f (x) = 3x2 + 2x3 - 6x - 2
b) g(x) = 5x2 + 9 - 2x3 - 3x2 - 4x + 2x3 - 2
f (x) = 3x2 + 2x3 - 6x - 2
bậc của đa thức là: 3
g(x) = 5x2 + 9 - 2x3 - 3x2 - 4x + 2x3 - 2
g(x) = ( 5x2 - 3x2 ) + ( 9 -2) + ( - 2x3 + 2x3 ) - 4x
g(x) = 2x2 + 7 - 4x
bậc của đa thức là : 2
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 5 x − 1 5 x + 1 = 0 ; b) x − 1 2 3 x − 1 = 0 ;
c) 2 x 3 + 4 x + 3 x 2 − 1 = 0 ; d) x 2 − 4 x 4 − 4 x + 5 3 = 0 .
Bài 5:
1) a) Cho hai đa thức:
P (x) = 5x2 + 3x3 - 5x2 + 2x3 – 2 +4x – 4x2 + x3
Q(x) = 6x – x3 + 5 – 4x3 + 6 – 3x2 – 7x2
Tính M(x) = P(x) + Q(x)
b) Tìm C(x) biết: (5x2 + 9x – 3x4 + 7x3 -12) + C(x) = -2x3 + 9 – 6x + 7x4 -2x3
2) Tìm nghiệm của các đa thức sau
a) 4x - ![]() b) x2 – 4x +3
b) x2 – 4x +3
a: P(x)=6x^3-4x^2+4x-2
Q(x)=-5x^3-10x^2+6x+11
M(x)=x^3-14x^2+10x+9
b: \(C\left(x\right)=7x^4-4x^3-6x+9+3x^4-7x^3-5x^2-9x+12\)
=10x^4-11x^3-5x^2-15x+21
Bài 1. Giải các phương trình sau:
a) x2 - 6x + 5 = 0 b) 2x2 + 4x – 8 = 0
c) 4y2 – 4y + 1 = 0 d) 5x2 - x + 2 = 0
\(a,x^2-6x+5=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x^2-5x\right)-\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow x\left(x-5\right)-\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,2x^2+4x-8=0\\ \Rightarrow x^2+2x-4=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x^2+2x+1\right)-5=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2-\sqrt{5^2}=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x+1+\sqrt{5}\right)\left(x+1-\sqrt{5}\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1-\sqrt{5}\\x=-1+\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,4y^2-4y+1=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(2y-1\right)^2=0\\ \Rightarrow2y-1=0\\ \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(d,5x^2-x+2=0\)
Ta có:\(\Delta=\left(-1\right)^2-4.5.2=1-40=-39\)
Vì \(\Delta< 0\Rightarrow\) pt vô nghiệm
Phân tích
a,(x2 + x + 2)3 - (x+1)3 = x6 +1 b,(x2 + 10x + 8)2 - (8x + 4)(x2 + 8x+7)
c, A= x4 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 2x+4 d,B= x4 + 4x3 + +8x2 + 8x + 4
e, C= x4 - 2x3 + 5x2 - 4x + 4