Làm hộ mik bài VIII. Mik cảm ơn!
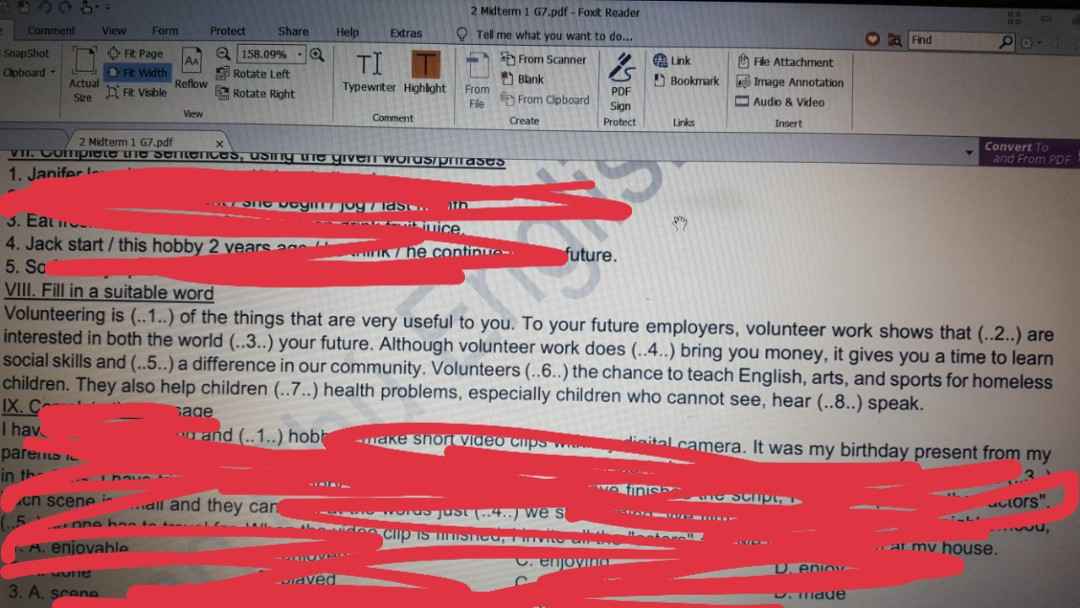

Bạn nào biết làm hộ mik được ko ạ! Mik cảm ơn! Bạn nào làm hộ mik, mik tick hết chứ ko phải mỗi bn đầu! Bạn nào biết bài nào thì làm hộ mik bài đó nha!
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
double a,b,c,p,s;
int main()
{
cin>>a>>b>>c;
p=(a+b+c)/2;
s=sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c));
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<p;
return 0;
}
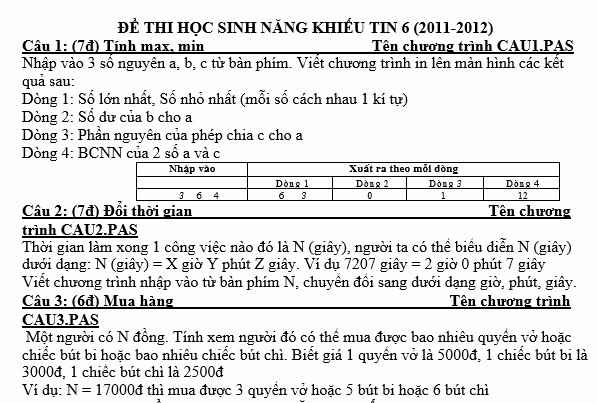
Bạn nào biết làm hộ mik được ko ạ! Mik cảm ơn! Bạn nào làm hộ mik, mik tick hết chứ ko phải mỗi bn đầu! Bạn nào biết bài nào thì làm hộ mik bài đó nha!
1:
uses crt;
var a,b,c,max,min:longint;
begin
clrscr;
readln(a,b,c);
max=a;
if max<b then max:=b;
if max<c then max:=c;
min:=a;
if min>c then min:=c;
if min>b then min:=b;
writeln(max,' ',min);
readln;
end.
Làm hộ mik bài này ạ,mik cảm ơn
Lời giải:
a.
Nếu $m=3$ thì pt trở thành:
$x^2+4x-5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(x+5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$ hoặc $x=-5$
b.
Để pt có 2 nghiệm pb $x_1,x_2$ thì:
$\Delta'=4+m^2-4>0\Leftrightarrow m^2>0\Leftrightarrow m\neq 0$
PT có 2 nghiệm $(-2+m, -2-m)$
Khi đó:
\(x_2=x_1^3+4x_2^2\Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} -2+m=(-2-m)^3+4(-2+m)^2\\ -2-m=(-2+m)^3+4(-2-m)^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} -m^3+2m^2-29m+10=0\\ m^3-2m^2+29m+10=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Nghiệm khá xấu, cảm giác đề cứ sai sai bạn ạ.
 làm hộ mik bài 5 ạ,mik cảm ơn ạ
làm hộ mik bài 5 ạ,mik cảm ơn ạ
Làm hộ mik bài 2 câu b) và cả bài 3 ạ,mik cảm ơn
Làm lại hộ mik bài VIII (Ex1) với ạ
1 What have you done?
2 has eaten
3 have been writing
4 has been cooking
5 have seen
6 have scored
làm hộ mik b1.2, 2.2, 3.2
bài 2.2 lm bằng pp chặn giúp mik ạ
mik cảm ơn
Bài 1.2
\(A=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+7}{\sqrt{x}+2}=2+\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
C1:Bạn dùng pp chặn như bài 2.2
C2: (Gợi ý)\(\sqrt{x}+2\ge2\) và \(\sqrt{x}+2\inƯ\left(3\right)\)\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}+2=3\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Vậy x=1 thì A nguyên
Bài 2.2
\(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+7}{\sqrt{x}+2}=1+\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
Do \(\sqrt{x}\ge0;\forall x\)\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}+2\ge2\) \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\le\dfrac{5}{2}\)\(\Rightarrow A\le\dfrac{7}{2}\) (1)
mà \(\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}>0;\forall x\Rightarrow A>1\) (2)
Từ (1) (2) \(\Rightarrow1< A\le\dfrac{7}{2}\) mà A nguyên
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}A=2\\A=3\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}1+\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}=2\\1+\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}=3\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}+2=5\\\sqrt{x}+2=\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}=3\\\sqrt{x}=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=9\\x=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...
Bài 3.2
\(A=\dfrac{-x-2\sqrt{x}-5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)\(=\dfrac{-\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)-5}{\sqrt{x}+2}=-\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
\(=2-\left(\sqrt{x}+2+\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\right)\)
Áp dụng bđt cosi: \(\sqrt{x}+2+\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\ge2\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right).\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}}=2\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow A\le2-2\sqrt{5}\)
Dấu = xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+2=\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}\Leftrightarrow x=9-4\sqrt{5}\)
làm hộ mik bài này ạ.mik cảm ơn ạ
làm hộ mik bài 2 với, cảm ơn mọi người.
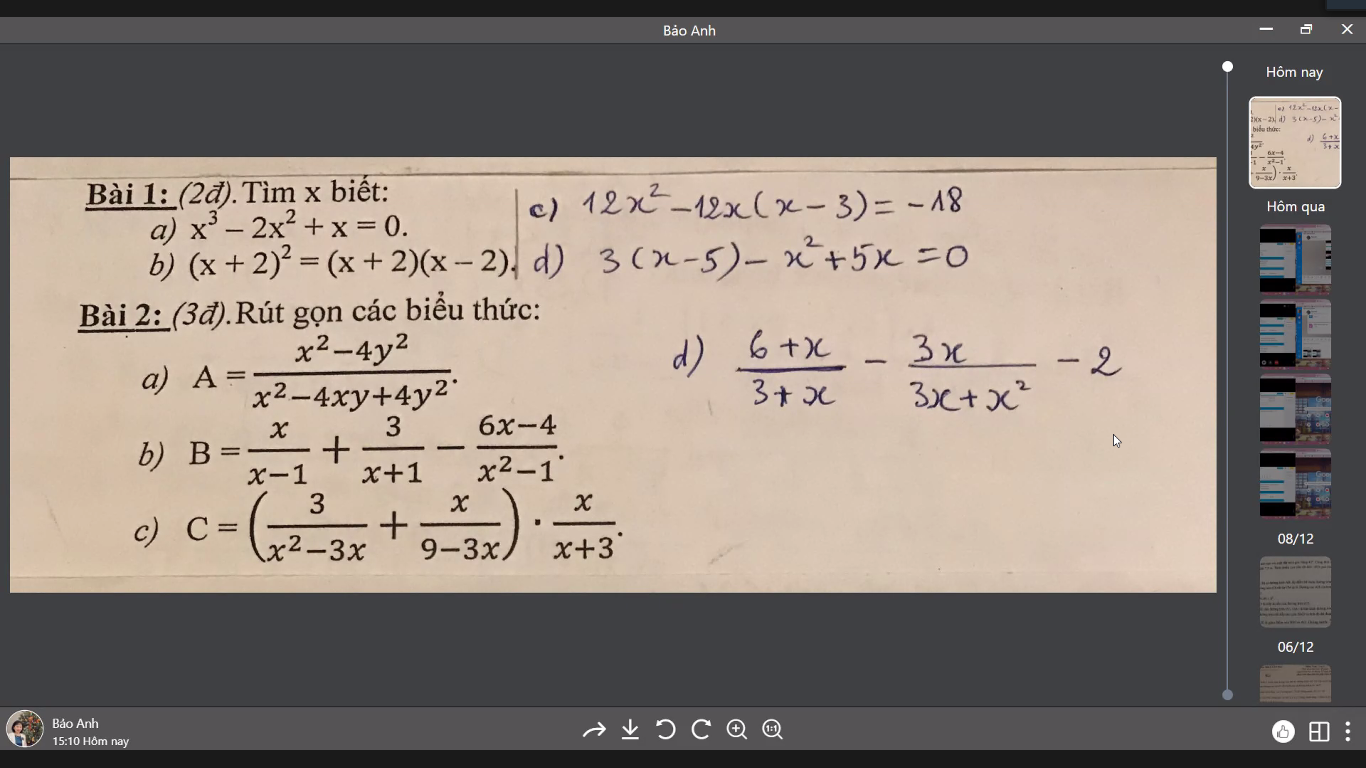
Bài 2:
\(a,\dfrac{x^2-4y^2}{x^2-4xy+4y^2}=\dfrac{\left(x-2y\right)\left(x+2y\right)}{\left(x-2y\right)^2}=\dfrac{x+2y}{x-2y}\)
\(b,\dfrac{x}{x-1}+\dfrac{3}{x+1}-\dfrac{6x-4}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)+3\left(x-1\right)-\left(6x-4\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+x+3x-3-6x+4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-2x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\)
\(c,\left(\dfrac{3}{x^2-3x}+\dfrac{x}{9-3x}\right).\dfrac{x}{x+3}=\left(\dfrac{3}{x\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{x}{3\left(x-3\right)}\right).\dfrac{x}{x+3}=\dfrac{9-x^2}{x\left(x-3\right)}.\dfrac{x}{x+3}=\dfrac{\left(3-x\right)\left(3+x\right)}{-x\left(3-x\right)}.\dfrac{x}{x+3}=-1\)
\(d,\dfrac{6+x}{3+x}-\dfrac{3x}{3x+x^2}-2=\dfrac{6+x}{3+x}-\dfrac{3}{3+x}-2=\dfrac{6+x-3}{3+x}-2=\dfrac{3+x}{3+x}-2=1-2=-1\)
Bài 1
\(x^3-2x^2+x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\) hoặc \(\left(x-1\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=1\)
\(\left(x+2\right)^2=\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)^2-\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x+2-x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4x+8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4x=-8\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{8}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
d. 3(x - 5) - x(x - 5)
⇔ (x - 5)(3 - x)
⇔ x - 5 = 0 hoặc 3 - x = 0
⇔ x =5 - x = - 3
⇔ x =5 x = 3