Tìm GTLN của biểu thức C=\(\dfrac{x+2}{\left|x\right|}\) với x là số nguyên

Những câu hỏi liên quan
1. Cho số nguyên dương x.a, Tìm GTNN của biểu thức Psqrt[3]{10^x-2}+sqrt{x^x+3}+sqrt{left(pi^2+1right)^{x-1}+3}.b, Tìm GTLN của biểu thức Qsqrt[5]{left(6x^2+5right)^{1-x}}+sqrt[3]{3-2x^2}.c, Chứng minh rằng: dfrac{left(x+1right)^6}{left(x^3+7right)left(x^3+3x^2+4right)}ge1.2. Cho tam giác OEF vuông tại O có OE a, OF b, EF c thỏa mãn điều kiện a, b, c là các số dương. Chứng minh rằng biểu thức Adfrac{a+b}{c}+dfrac{c}{a+b} không nhận bất kì giá trị nguyên dương nào.
Đọc tiếp
1. Cho số nguyên dương x.
a, Tìm GTNN của biểu thức \(P=\sqrt[3]{10^x-2}+\sqrt{x^x+3}+\sqrt{\left(\pi^2+1\right)^{x-1}+3}\).
b, Tìm GTLN của biểu thức \(Q=\sqrt[5]{\left(6x^2+5\right)^{1-x}}+\sqrt[3]{3-2x^2}\).
c, Chứng minh rằng: \(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^6}{\left(x^3+7\right)\left(x^3+3x^2+4\right)}\ge1\).
2. Cho tam giác OEF vuông tại O có OE = a, OF = b, EF = c thỏa mãn điều kiện a, b, c là các số dương. Chứng minh rằng biểu thức \(A=\dfrac{a+b}{c}+\dfrac{c}{a+b}\) không nhận bất kì giá trị nguyên dương nào.
Bài 1:
A=\(\left(\dfrac{x+2}{x\sqrt{x}-1}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}+\dfrac{1}{1-\sqrt{x}}\right):\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{2}\)
a) Tìm tập xác định của biểu thức A
b) Rút gọn biểu thức A
c) Chứng minh rằng A>0 với mọi x≠1
d) Tìm x để A đạt GTLN, tìm GTLN đó
a: ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\x\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Ta có: \(A=\left(\dfrac{x+2}{x\sqrt{x}-1}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}+\dfrac{1}{1-\sqrt{x}}\right):\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+2+x-\sqrt{x}-x-\sqrt{x}-1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(x+\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{2}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
c: Ta có: \(x+\sqrt{x}+1>0\forall x\) thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}>0\forall x\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
b. Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức B =\(\dfrac{x-1}{\left|x-2\right|}\)với x là số nguyên.
Biểu thức không có max. Bạn coi lại đề.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (2)
À ha sorry bạn. Mình quên mất điều kiện $x$ nguyên.
Xét 2 TH sau:
TH1: $x>2$:
$B=\frac{x-1}{x-2}=1+\frac{1}{x-2}$
Để $B$ max thì $\frac{1}{x-2}$ max $\Leftrightarrow x-2$ min
Vậy $x-2$ phải là số nguyên dương bé nhất, tức là $x-2=1$
$\Leftrightarrow x=3$
Khi đó: \(B_{\max}=\frac{3-1}{|3-2|}=2(*)\)
TH2: $x< 2$
$B=\frac{x-1}{2-x}=-(1+\frac{1}{x-2})$
Để B max thì $1+\frac{1}{x-2}$ min
$\Leftrightarrow x-2$ max. Mà $x<2$ nên $x-2$ phải là số nguyên âm lớn nhất
$\Leftrightarrow x-2=-1$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$
Khi đó: $B=0(**)$
Từ $(*); (**)\Rightarrow B_{\max}=2$ khi $x=3$
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
B1:Cho biểu thức Aleft(dfrac{1}{x+2}-dfrac{2}{x-2}-dfrac{x}{4-x}right):dfrac{6left(x+2right)}{left(2-xright)left(x+1right)}a. Rút gọn biểu thức Ab. Tìm x để A 0c. Tìm x biết x^2+3x+20 d. Tìm x để A đạt GTLN, tìm GTLN đó.Cho biểu thứcAleft(dfrac{2+x}{2-x}-dfrac{2-x}{2+x}-dfrac{4x^2}{x^2-4}right):dfrac{x^2-6x+9}{left(2-xright)left(x-3right)} a. Rút gọn Ab. Tính giá trị của A biết left|x-5right|2 c. Tìm giá trị nguyên dương của x để A 4 và A có giá trị là một số...
Đọc tiếp
B1:Cho biểu thức \(A=\left(\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{2}{x-2}-\dfrac{x}{4-x}\right):\dfrac{6\left(x+2\right)}{\left(2-x\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
a. Rút gọn biểu thức A
b. Tìm x để A > 0
c. Tìm x biết \(x^2+3x+2=0\)
d. Tìm x để A đạt GTLN, tìm GTLN đó.
Cho biểu thức\(A=\left(\dfrac{2+x}{2-x}-\dfrac{2-x}{2+x}-\dfrac{4x^2}{x^2-4}\right):\dfrac{x^2-6x+9}{\left(2-x\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
a. Rút gọn A
b. Tính giá trị của A biết \(\left|x-5\right|=2\)
c. Tìm giá trị nguyên dương của x để A < 4 và A có giá trị là một số nguyên.
B1: ĐXXĐ: \(x\ne\pm2;x\ne-1\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\right):\dfrac{-6\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-2-2x-2+x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\right):\dfrac{-6\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-4}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}:\dfrac{-6\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-4}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}.\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}{-6\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{3\left(x+2\right)^2}\)
b, \(A=\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{3\left(x+2\right)^2}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+2>0\) (vì \(3\left(x+2\right)^2\ge0\forall x\))
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-1\).
-Vậy \(x\in\left\{x\in Rlx>-1;x\ne2\right\}\) thì \(A>0\).
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Bài 4: Cho biểu thức A \(=\left(\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{2}{x-2}-\dfrac{x}{4-x^2}\right):\dfrac{6\left(x+2\right)}{\left(2-x\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
a) Rút gọn A
b)Tìm x để A > 0
c) Tìm x biết x2 + 3x + 2 \(=0\)
d) Tìm x để A đạt GTLN, tìm GTLN đó
a: \(A=\dfrac{x-2-2x-4+x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{-\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}{6\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-6}{\left(x+2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{-\left(x+1\right)}{6\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+2\right)^2}\)
b: A>0
=>x+1>0
=>x>-1
c: x^2+3x+2=0
=>(x+1)(x+2)=0
=>x=-2(loại) hoặc x=-1(loại)
Do đó: Khi x^2+3x+2=0 thì A ko có giá trị
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho biểu thức \(A=\left(\dfrac{9}{x^3-9x}+\dfrac{1}{x+3}\right):\left(\dfrac{x-3}{x^2+3x}-\dfrac{x}{3x+9}\right)\)
a, Tìm điều kiện của x để giá trị của phân thức xác định
b, Rút gọn biểu thức
c, Tính giá trị biểu thức khi x = 4
d, Tìm giá trị nguyên của x để A có giá trị là số nguyên.
a,ĐK: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne\pm3\end{cases}}\)
b, \(A=\left(\frac{9}{x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\frac{1}{x+3}\right):\left(\frac{x-3}{x\left(x+3\right)}-\frac{x}{3\left(x+3\right)}\right)\)
\(=\frac{9+x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\frac{3\left(x-3\right)-x^2}{3x\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^2-3x+9}{x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}.\frac{3x\left(x+3\right)}{-x^2+3x-9}=\frac{-3}{x-3}\)
c, Với x = 4 thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ thì
\(A=\frac{-3}{4-3}=-3\)
d, \(A\in Z\Rightarrow-3⋮\left(x-3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x-3\inƯ\left(-3\right)=\left\{-3;-1;1;3\right\}\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;2;4;6\right\}\)
Mà \(x\ne0\Rightarrow x\in\left\{2;4;6\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
cho biểu thức P=\(\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}-\dfrac{4}{x+2\sqrt{x}}\right):\left(1+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\right)\) với x>0
1.rút gọn biểu thức P
2.tìm các số nguyên x thảo mãn P>0
Cho biểu thức: \(A=\left(\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+3}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-3}\right):\left(\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}-3}-1\right)\)
a/ Tìm điều kiện xác định của biểu thức A
b/ Rút gọn A
c/ Tìm các giá trị nguyên của x để giá trị A là một số nguyên.
Tìm GTLN và GTNN nếu có của các biểu thức sau :
a. \((x+\dfrac{2}{3})^2+\dfrac{1}{2}với(x\in Q)\)
b.\(\left|x-2020\right|+2021\)
Cho biểu thức: K=(\(\dfrac{x^2}{x^2-5x+6}\)+\(\dfrac{x^2}{x^2-3x+2}\)).\(\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{x^4+x^2+1}\)
a, Tìm đkxđ rồi rút gọn K
b, Tìm GTLN của K
a: ĐKXĐ: x<>1; x<>2; x<>3
\(K=\left(\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{x^4+2x^2+1-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3-x^2+x^3-3x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x^2+1+x\right)\left(x^2+1-x\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^3-4x^2}{\left(x-2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{1}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x^4+x^2+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2}{x^4+x^2+1}\)
b:
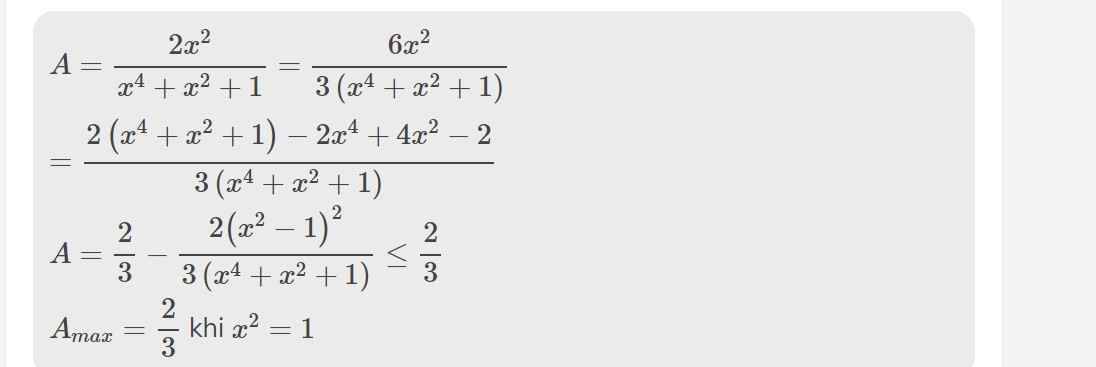
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)


















