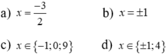giải phương trình sau : ( x2+5x+4 ) . ( 9x2+30x+16 ) = 4x2

Những câu hỏi liên quan
giải phương trình (x2+5x+4) . (9x2 +30x +16)= 4x2
\(pt\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x+4\right)\left(3x^2+15x+8\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình dưới đây1) x2 - 9 (x - 3)(5x +2)2) x3 - 1 (x - 1)(x2 - 2x +16)3) 4x2 (x - 1) - x + 1 04) x3 + 4x2 - 9x - 36 05) (3x + 5)2 (x - 1)26) 9 (2x + 1)2 4 (x - 5)27) x2 + 2x 158) x4 + 5x3 + 4x2 09) (x2 - 4) - (x - 2)(3 - 2x) 010) (3x + 2)(x2 - 1) (9x2 - 4) (x + 1)11) (3x - 1)(x2 + 2) (3x - 1)(7x - 10)12) (2x2 + 1) (4x - 3) (x - 12)(2x2 + 1)
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình dưới đây
1) x2 - 9 = (x - 3)(5x +2)
2) x3 - 1 = (x - 1)(x2 - 2x +16)
3) 4x2 (x - 1) - x + 1 = 0
4) x3 + 4x2 - 9x - 36 = 0
5) (3x + 5)2 = (x - 1)2
6) 9 (2x + 1)2 = 4 (x - 5)2
7) x2 + 2x = 15
8) x4 + 5x3 + 4x2 = 0
9) (x2 - 4) - (x - 2)(3 - 2x) = 0
10) (3x + 2)(x2 - 1) = (9x2 - 4) (x + 1)
11) (3x - 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x - 1)(7x - 10)
12) (2x2 + 1) (4x - 3) = (x - 12)(2x2 + 1)
1: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(5x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(-4x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{3;\dfrac{1}{4}\right\}\)
2: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1-x^2+2x-16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-15\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;5\right\}\)
3: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;\dfrac{1}{2};-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
4: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+4\right)-9\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-4;3;-3\right\}\)
5: \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+5=x-1\\3x+5=1-x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-6\\4x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
6: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3\right)^2-\left(2x-10\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3-2x+10\right)\left(6x+3+2x-10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+13\right)\left(8x-7\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{13}{4};\dfrac{7}{8}\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(5x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3=5x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=5\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
2.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+1=x^2-2x+16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=15\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
3.
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{1}{2};x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
7.
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
8.\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+x^3+4x^3+4x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x+1\right)+4x^2\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^3+4x^2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=0;x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
9.\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2=3-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải phương trình :
1) √x2+x+2 + 1/x= 13-7x/2
2) x2 + 3x = √1-x + 1/4
3) ( x+3)√48-x2-8x= 28-x/ x+3
4) √-x2-2x +48= 28-x/x+3
5) 3x2 + 2(x-1)√2x2-3x +1= 5x + 2
6) 4x2 +(8x - 4)√x -1 = 3x+2√2x2 +5x-3
7) x3/ √16-x2 + x2 -16 = 0
BÀI 1. Giải các phương trình sau bằng công thức nghiệm hoặc (công thức nghiện thu gọn). 1) x2 - 11x + 38 = 0 ; 2) 6x2 + 71x + 175 = 0 ; 3) 5x2 - 6x + 27 = 0 ; 4) - 30x2 + 30x - 7,5 = 0 ; 5) 4x2 - 16x + 17 = 0 ; 6) x2 + 4x - 12 = 0 ;
1, \(\Delta=\left(-11\right)^2-4.1.38=121-152=-31< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) pt vô nghiệm
2, \(\Delta=71^2-4.6.175=5041-4200=841\)
\(x_1=\dfrac{-71+\sqrt{841}}{2.6}=\dfrac{-71+29}{12}=\dfrac{-42}{12}=-\dfrac{7}{2}\)
\(x_2=\dfrac{-71-\sqrt{841}}{2.6}=\dfrac{-71-29}{12}=\dfrac{-10}{12}=-\dfrac{25}{3}\)
3, \(\Delta=\left(-3\right)^2-5.27=9-135=-126< 0\)
⇒ pt vô nghiệm
4, \(\Delta=15^2-\left(-30\right)\left(-7,5\right)=225-225=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x_1=x_2=\dfrac{-30}{2.\left(-30\right)}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
5, \(\Delta'=\left(-8\right)^2-4.17=64-68=-4\)
⇒ pt vô nghiệm
6, \(\Delta=4^2-4.1.\left(-12\right)=16+48=64\)
\(x_1=\dfrac{-4+\sqrt{64}}{2.1}=\dfrac{-4+8}{2}=\dfrac{4}{2}=2\)
\(x_2=\dfrac{-4-\sqrt{64}}{2.1}=\dfrac{-4-8}{2}=\dfrac{-12}{2}=-6\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
a) 4+4xy +x2 +y2
B) 25-30x +9x2
d) x2 + 1/2x +1/16
Em cần làm gì với các đa thức này vậy em
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Không giải phương trình, hãy tính tổng và tích các nghiệm (nếu có) của mỗi phương trình sau:
a
)
4
x
2
+
2
x
−
5
0
b
)
9
x
2...
Đọc tiếp
Không giải phương trình, hãy tính tổng và tích các nghiệm (nếu có) của mỗi phương trình sau:
a ) 4 x 2 + 2 x − 5 = 0 b ) 9 x 2 − 12 x + 4 = 0 c ) 5 x 2 + x + 2 = 0 d ) 159 x 2 − 2 x − 1 = 0
a) Phương trình 4 x 2 + 2 x − 5 = 0
Có a = 4; b = 2; c = -5, a.c < 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm x 1 ; x 2
Theo hệ thức Vi-et ta có: 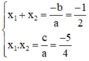
b) Phương trình . 9 x 2 − 12 x + 4 = 0
Có a = 9; b' = -6; c = 4 ⇒ Δ 2 = ( - 6 ) 2 - 4 . 9 = 0
⇒ Phương trình có nghiệm kép x 1 = x 2 .
Theo hệ thức Vi-et ta có: 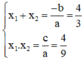
c) Phương trình 5 x 2 + x + 2 = 0
Có a = 5; b = 1; c = 2 ⇒ Δ = 1 2 − 4.2.5 = − 39 < 0
⇒ Phương trình vô nghiệm.
d) Phương trình 159 x 2 − 2 x − 1 = 0
Có a = 159; b = -2; c = -1; a.c < 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt x 1 ; x 2 .
Theo hệ thức Vi-et ta có: 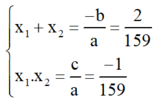
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:a)
x
+
2
3
+
x
+
1
3
0
;
b)
2
x
4
+
3
x
2
−
5
0
;
c)
x...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) x + 2 3 + x + 1 3 = 0 ;
b) 2 x 4 + 3 x 2 − 5 = 0 ;
c) x 4 − 8 x 3 − 9 x 2 = 0 ;
d) x 3 − 4 x 2 + 4 − x = 0 .
Bài 5: Giải các phương trình sau:a. (3x - 1)2 - (x + 3)2 0b. x3 dfrac{x}{49}c. x2 - 7x + 12 0d. 4x2 - 3x -1 0e. x3 - 2x - 4 0f. x3 + 8x2 + 17x +10 0g. x3 + 3x2 + 6x + 4 0h. x3 - 11x2 + 30x 0
Đọc tiếp
Bài 5: Giải các phương trình sau:
a. (3x - 1)2 - (x + 3)2 = 0
b. x3 = \(\dfrac{x}{49}\)
c. x2 - 7x + 12 = 0
d. 4x2 - 3x -1 = 0
e. x3 - 2x - 4 = 0
f. x3 + 8x2 + 17x +10 = 0
g. x3 + 3x2 + 6x + 4 = 0
h. x3 - 11x2 + 30x = 0
a. (3x - 1)2 - (x + 3)2 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1+x+3\right)\left(3x-1-x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+2\right)\left(2x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+2=0\) hoặc \(2x-4=0\)
1. \(4x+2=0\Leftrightarrow4x=-2\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
2. \(2x-4=0\Leftrightarrow2x=4\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
S=\(\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};2\right\}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
b. \(x^3=\dfrac{x}{49}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow49x^3=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow49x^3-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(49x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(7x+1\right)\left(7x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\) hoặc \(7x+1=0\) hoặc \(7x-1=0\)
1. x=0
2. \(7x+1=0\Leftrightarrow7x=-1\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{7}\)
3. \(7x-1=0\Leftrightarrow7x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{7}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
*Cách khác:
a) Ta có: \(\left(3x-1\right)^2-\left(x+3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)^2=\left(x+3\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=-x-3\\3x-1=x+3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=-2\\2x=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};2\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải các phương trình sau
a) 4x2-(5x+1)2=0
b) 25(x-1)2-(x+2)2=0
c) (x2+4x-1)2-(x2-3x+2)20
a: =>(2x-5x-1)(2x+5x+1)=0
=>(-3x-1)(7x+1)=0
=>x=-1/3 hoặc x=-1/7
b: =>(5x-5)^2-(x+2)^2=0
=>(5x-5-x-2)(5x-5+x+2)=0
=>(4x-7)(6x-3)=0
=>x=1/2 hoặc x=7/4
c: =>(x^2+4x-1-x^2+3x-2)(x^2+4x-1+x^2-3x+2)=0
=>(7x-3)(2x^2+x+1)=0
=>7x-3=0
=>x=3/7
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a/2x5y-6x3y2
b/14x2y-xy2+28x2y2
c/x2+4x+4
d/9x2+6x+1
e/2x-1-x2
j/-x3+9x2-27x+27
g/(x+y)2-9x2
h/x2+xy+x+y
i/x2-4+xy-2y
k/x3-4x2+4x
k/x2-3x+2
l/x2-3x+2
m/x2-5x+6
n/x2-3x-4
c: \(x^2+4x+4=\left(x+2\right)^2\)
d: \(9x^2+6x+1=\left(3x+1\right)^2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)