tìm x biết |x2+|6x-2||=x2+4

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Câu 1
Rút gọn các biểu thức sau:
a. 2x(3x + 2) - 3x(2x + 3)
b. (x + 2)3 + (x - 3)2 - x2(x + 5)
c. (3x3 - 4x2 + 6x) : 3x
Câu 2
Phân tích đa thức sau thành nhân tử: 2x3 - 12x2 + 18x
Câu 3
Tìm x, biết: 3x(x - 5) - x2 + 25 0
Câu 4 Cho hình bình hành ABCD (AB AD). Gọi E và K lần lượt là trung điểm của CD và AB. BD cắt AE, AC, CK lần lượt tại N, O và I. Chứng minh rằng:
a. Tứ giắc AECK là hình bình hành.
b. Ba điểm E, O, K thẳng hàng.
c. DN NI IB
d. AE...
Đọc tiếp
Câu 1
Rút gọn các biểu thức sau:
a. 2x(3x + 2) - 3x(2x + 3)
b. (x + 2)3 + (x - 3)2 - x2(x + 5)
c. (3x3 - 4x2 + 6x) : 3x
Câu 2
Phân tích đa thức sau thành nhân tử: 2x3 - 12x2 + 18x
Câu 3
Tìm x, biết: 3x(x - 5) - x2 + 25 = 0
Câu 4 Cho hình bình hành ABCD (AB > AD). Gọi E và K lần lượt là trung điểm của CD và AB. BD cắt AE, AC, CK lần lượt tại N, O và I. Chứng minh rằng:
a. Tứ giắc AECK là hình bình hành.
b. Ba điểm E, O, K thẳng hàng.
c. DN = NI = IB
d. AE = 3KI
Câu 5 Cho x, y là hai số thực tùy ý, tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức sau:
P = x2 + 5y2 + 4xy + 6x + 16y + 32
Câu 1:
a) 2x(3x+2) - 3x(2x+3) = 6x^2+4x - 6x^2-9x = -5x
b) \(\left(x+2\right)^3+\left(x-3\right)^2-x^2\left(x+5\right)\)
\(=x^3+6x^2+12x+8+x^2-6x+9-x^3-5x^2\)
\(=2x^2+6x+17\)
c) \(\left(3x^3-4x^2+6x\right)\div\left(3x\right)=x^2-\dfrac{4}{3}x+2\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Câu 2:
\(2x^3-12x^2+18x=2x\left(x^2-6x+9\right)=2x\left(x^2-2.x.3+3^2\right)=2x\left(x-3\right)^2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Tìm số nguyên x biết:
(x+3) (x2 +4) >0
Vì \(x^2\ge0\forall x\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+4>0\forall x\in Z\)
Suy ra để \(\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+4\right)>0\) thì \(x+3>0\Leftrightarrow x>-3\)
Vậy \(x>-3\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x, biết:
a) ( 6x3+x2) : 2x - 3x (x-1)+2=0
b) (5x4-3x2) : x2-x(5x+6)=0
Lời giải:
a.
PT $\Leftrightarrow 3x^2+\frac{x}{2}-3x^2+3x+2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{7}{2}x+2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{7}{2}x=-2$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-2: \frac{7}{2}=\frac{-4}{7}$
b.
PT $\Leftrightarrow 5x^2-3-5x^2-6x=0$
$\Leftrightarrow -3-6x=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 6x=-3$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-3}{6}=\frac{-1}{2}$
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm số nguyên x biết:
3.(x2-2)-(2x2-1)=4
Ai làm đầu tiên e tick ạ!!
SOS
3(x²-2)-(2x²-1)=4
=> 3x²-6-2x²+1=4
=> x²-5=4
=> x²=9
=> x=±3
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x, y biết
x
2
+
y
2
10
x
2
-
2
y
2
7
và x4.y4 81.
Đọc tiếp
Tìm x, y biết x 2 + y 2 10 = x 2 - 2 y 2 7 và x4.y4 = 81.
Đặt x2 = a (a ≥ 0), y2 = b (b ≥ 0)
Ta có: 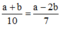 và a2b2 = 81.
và a2b2 = 81.
Theo tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
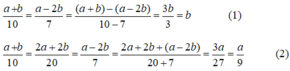
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra a/9 = b ⇒ a = 9b
Do a2b2 = 81 nên (9b)2.b2 = 81 ⇒ 81b4 = 81 ⇒ b4 = 1 ⇒ b = 1 (vì b ≥ 0)
Suy ra a = 9. 1 = 9
Ta có x2 = 9 và y2 = 1. Suy ra x = 3 hoặc x = -3, y = 1 hoặc y = -1.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Tính:
a) x2(x-2x3); b) (x2+1)(5-x); c) (x-2)(x2+3x-4); d) (x-2)(x-x2+4); e) (x2-1)(x2+2x); f) (2x-1)(3x+2)(3-x)
Bài 2: Tính:
a) (x-2y)2; b) (2x2+3)3; c) (x-2)(x2+2x+4); d) (2x-1)3
Bài 3: Rút gọn biểu thức:
a) (6x+1)2+(6x-1)2-2(1+6x)(6x-1); b) 3(22+1)(24+1)(28+1)(216+1); c) x(2x2-3)-x2(5x+1)+x2; d) 3x(x-2)-5x(1-x)-8(x2-3)
Bài 4: Tính nhanh:
a) 1012; b) 97.103; c) 772+232+77.46; d) 1052-52; e) A (x-y)(x2+xy+y2)+2y3 tại x dfrac{2}{3} và y dfrac{1}{3}
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Tính:
a) x2(x-2x3); b) (x2+1)(5-x); c) (x-2)(x2+3x-4); d) (x-2)(x-x2+4); e) (x2-1)(x2+2x); f) (2x-1)(3x+2)(3-x)
Bài 2: Tính:
a) (x-2y)2; b) (2x2+3)3; c) (x-2)(x2+2x+4); d) (2x-1)3
Bài 3: Rút gọn biểu thức:
a) (6x+1)2+(6x-1)2-2(1+6x)(6x-1); b) 3(22+1)(24+1)(28+1)(216+1); c) x(2x2-3)-x2(5x+1)+x2; d) 3x(x-2)-5x(1-x)-8(x2-3)
Bài 4: Tính nhanh:
a) 1012; b) 97.103; c) 772+232+77.46; d) 1052-52; e) A= (x-y)(x2+xy+y2)+2y3 tại x= \(\dfrac{2}{3}\) và y= \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Bạn chú ý đăng lẻ câu hỏi! 1/
a/ \(=x^3-2x^5\)
b/\(=5x^2+5-x^3-x\)
c/ \(=x^3+3x^2-4x-2x^2-6x+8=x^3=x^2-10x+8\)
d/ \(=x^2-x^3+4x-2x+2x^2-8=3x^2-x^3+2x-8\)
e/ \(=x^4-x^2+2x^3-2x\)
f/ \(=\left(6x^2+x-2\right)\left(3-x\right)=17x^2+5x-6-6x^3\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
thu gọn biểu thức
a) (6x-2)2+4(3x-1)(2+y)+(y+2)2-(6x+y)2
b)5(2x-1)2+2(x-1)(x+3)-2(5-2x)2-2x(7x+12)
c)2(5x-1)(x2-5x+1)+(x2-5x+1)2+(5x-1)2-(x2-1)(x2+1)
d)(x2+4)2-(x2+4)(x2-4)(x2+16)-8(x-4)(x+4)
`#3107`
`a)`
`(6x - 2)^2 + 4(3x - 1)(2 + y) + (y + 2)^2 - (6x + y)^2`
`= [(6x - 2)^2 - (6x + y)^2] + 4(3x - 1)(2 + y) + (2 + y)^2`
`= (6x - 2 - 6x - y)(6x -2 + 6x + y) + (2 + y)*[ 4(3x - 1) + 2 + y]`
`= (2 - y)(12x + y - 2) + (2 + y)*(12x - 4 + 2 + y)`
`= (2 - y)(12x + y - 2) + (2 + y)*(12x + y - 2)`
`= (12x + y - 2)(2 - y + 2 + y)`
`= (12x + y - 2)*4`
`= 48x + 4y - 8`
`b)`
\(5(2x-1)^2+2(x-1)(x+3)-2(5-2x)^2-2x(7x+12)\)
`= 5(4x^2 - 4x + 1) + 2(x^2 + 2x - 3) - 2(25 - 20x + 4x^2) - 14x^2 - 24x`
`= 20x^2 - 20x + 5 + 2x^2 + 4x - 6 - 50 + 40x - 8x^2 - 14x^2 - 24x`
`= - 51`
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)
`c)`
\(2(5x-1)(x^2-5x+1)+(x^2-5x+1)^2+(5x-1)^2-(x^2-1)(x^2+1)\)
`= [ 2(5x - 1) + x^2 - 5x + 1] * (x^2 - 5x + 1) + (5x - 1)^2 - [ (x^2)^2 - 1]`
`= (10x - 2 + x^2 - 5x + 1) * (x^2 - 5x + 1) + (5x - 1)^2 - x^4 + 1`
`= (x^2 + 5x - 1)(x^2 - 5x + 1) + (5x - 1)^2 - x^4 + 1`
`= x^4 - (5x - 1)^2 + (5x - 1)^2 - x^4 + 1`
`= 1`
`d)`
\((x^2+4)^2-(x^2+4)(x^2-4)(x^2+16)-8(x-4)(x+4)\)
`= (x^2 + 4)*[x^2 + 4 - (x^2 - 4)(x^2 + 16)] - 8(x^2 - 16)`
`= (x^2 + 4)(x^4 + 12x^2 - 64) - 8x^2 + 128`
`= x^6 + 16x^4 - 16x^2 - 256 - 8x^2 + 128`
`= x^6 + 16x^4 - 24x^2 - 128`
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1 : Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của các biểu thức sau : a, A x2 + 3x + 4 d, D 4x2+ 4x - 24b, B 2x2 - x + 1 e, E x2 + 6x - 11 c, C 5x2 + 2x - 3 g, G dfrac{1}{4}x^2+x-dfrac{1}{3} MONG MỌI NGƯỜI GIÚP VỚI Ạ !!! EM CẦN GẤP !
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1 : Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của các biểu thức sau :
a, A = x2 + 3x + 4 | d, D = 4x2+ 4x - 24 |
b, B = 2x2 - x + 1 | e, E = x2 + 6x - 11 |
| c, C = 5x2 + 2x - 3 | g, G = \(\dfrac{1}{4}x^2+x-\dfrac{1}{3}\) |
MONG MỌI NGƯỜI GIÚP VỚI Ạ !!! EM CẦN GẤP !
a) \(A=x^2+3x+4=\left(x+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{4}\ge\dfrac{7}{4}\)
\(minA=\dfrac{7}{4}\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b) \(B=2x^2-x+1=2\left(x-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{8}\ge\dfrac{7}{8}\)
\(minB=\dfrac{7}{8}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
c) \(C=5x^2+2x-3=5\left(x+\dfrac{1}{5}\right)^2-\dfrac{16}{5}\ge-\dfrac{16}{5}\)
\(minC=-\dfrac{16}{5}\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{5}\)
d) \(D=4x^2+4x-24=\left(2x+1\right)^2-25\ge-25\)
\(minD=-25\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
e) \(E=x^2+6x-11=\left(x+3\right)^2-20\ge-20\)
\(minE=-20\Leftrightarrow x=-3\)
f) \(G=\dfrac{1}{4}x^2+x-\dfrac{1}{3}=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x+1\right)^2-\dfrac{4}{3}\ge-\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(minG=-\dfrac{4}{3}\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (11)
a: Ta có: \(A=x^2+3x+4\)
\(=x^2+2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}+\dfrac{9}{4}+\dfrac{7}{4}\)
\(=\left(x+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{4}\ge\dfrac{7}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
d: Ta có: \(D=4x^2+4x-24\)
\(=4x^2+4x+1-25\)
\(=\left(2x+1\right)^2-25\ge-25\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
e: ta có: \(E=x^2+6x-11\)
\(=x^2+6x+9-20\)
\(=\left(x+3\right)^2-20\ge-20\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=-3
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm số nguyên x biết:
a) (x-2).35=37
b) x2-2x=0
c) (2x-1)2=49
Làm 1 câu bất kì cũng dc ạ!
a) (x - 2).3⁵ = 3⁷
x - 2 = 3⁷ : 3⁵
x - 2 = 3²
x - 2 = 9
x = 9 + 2
x = 11
b) x² - 2x = 0
x(x - 2) = 0
⇒ x = 0 hoặc x - 2 = 0
*) x - 2 = 0
x = 2
Vậy x = 0; x = 2
c) (2x - 1)² = 49
⇒ 2x - 1 = 7 hoặc 2x - 1 = -7
*) 2x - 1 = 7
2x = 7 + 1
2x = 8
x = 8 : 2
x = 4
*) 2x - 1 = -7
2x = -7 + 1
2x = -6
x = -6 : 2
x = -3
Vậy x = -3; x = 4
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)


























