tìm x để
x4+4x3-2x2-12x+3
Tìm nghiệm của đa thức:
H(x)=2x2+x
I(x)=4x3-x
M(x)=x3+2x2
cho H(x)=0
\(=>2x^2+x=0\)
\(=>x\left(2x+1\right)=0=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
I(x)=0
\(=>4x^3-x=0=>4.x.x.x-x=0\)
\(=>x\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\4x^2-1=0\end{matrix}\right.=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^2=\dfrac{1}{4}\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
cho M(x)=0
\(=>x^3+2x^2=0\)
\(=>x^2\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2=0\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
1) Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
a) 2x4-4x3+2x2
b) 2x2-2xy+5x-5y
2) Tìm x, biết:
a) 4x(x-3)-x+3=0
b)(2x-3)2-(x+1)2=0
1.
a) \(2x^4-4x^3+2x^2\)
\(=2x^2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(=2x^2\left(x-1\right)^2\)
b) \(2x^2-2xy+5x-5y\)
\(=\left(2x^2-2xy\right)+\left(5x-5y\right)\)
\(=2x\left(x-y\right)+5\left(x-y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\cdot\left(2x+5\right)\)
2 .
a,
\(4x\left(x-3\right)-x+3=0\)
⇒\(4x\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-3\right)=0\)
⇒\(\left(x-3\right)\left(4x-1\right)=0\)
⇒\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\4x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\4x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy \(x\in\left\{3;\dfrac{1}{4}\right\}\)
b,
\(\)\(\left(2x-3\right)^2-\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
⇒\(\left(2x-3-x-1\right)\left(2x-3+x+1\right)\) = 0
⇒\(\left(x-4\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4=0\\3x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\3x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy \(x\in\left\{4;\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)
Bài 3 : Cho x là số nguyên.Cmr :
B= x4 - 4x3 - 2x2 + 12x + 9 là bình phương số nguyên
Bài 4 : Cho x,y,z là số nguyên.Cmr :
C= 4x.(x + y).(x + y + z).(x + z) + y2z2 là một số chính phương
Giúp mình nha.Mai là hạn cuối rồi!
Bài 3:
\(B=x^4-4x^3-2x^2+12x+9\)
\(=x^4-3x^3-x^3+3x^2-5x^2+15x-3x+9\)
\(=\left(x-3\right)\left(x^3-x^2-5x-3\right)\)
\(=\left(x-3\right)\left(x^3-3x^2+2x^2-6x+x-3\right)\)
\(=\left(x-3\right)^2\cdot\left(x+1\right)^2\)
\(=\left(x^2-2x-3\right)^2\)
Bài 3:
\(B=x^4-4x^3-2x^2+12x+9=\left(x^4+x^3\right)-\left(5x^3+5x^2\right)+\left(3x^2+3x\right)+\left(9x+9\right)=\left(x^3-5x^2+3x+9\right)\left(x+1\right)=\left[\left(x^3+x^2\right)-\left(6x^2+6x\right)+\left(9x+9\right)\right]\left(x+1\right)=\left(x^2-6x+9\right)\left(x+1\right)^2=\left(x-3\right)^2\left(x+1\right)^2=\left[\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)\right]^2\)
cho đa thức Q(x)=-3x4+4x3+2x2+2/3-3x-2x4-4x3+8x4+1+3x
Cho biểu thức P= 1+ 3/x2+5x+6 : ( 8x2/ 4x3-8x2 - 3x/ 3x2-12 -1/x+2)
A) Rút gọn P
B) Tìm các giá trị của x để P= 0; P= 1
C) Tìm cã giá trị của x để P> 0
Cho biểu thức
Q= (2x-x2/ 2x2 +8 - 2x2/ 3x3-2x2+4x-8) (2/x2 + 1-x/x)
A) Rút gọn Q
B) Tìm giá trị nguyên của x để Q có giá trị nguyên
Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(P=1+\dfrac{3}{x^2+5x+6}:\left(\dfrac{8x^2}{4x^3-8x^2}-\dfrac{3x}{3x^2-12}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\left(\dfrac{8x^2}{4x^2\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{3x}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\left(\dfrac{4}{x-2}-\dfrac{x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\dfrac{4\left(x+2\right)-x-\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{4x+8-x-x+2}\)
\(=1+3\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)+3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+10x+6x+30+3x-6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+19x-6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
Cho hai đa thức
P ( x ) = 2 x 3 − 3 x + x 5 − 4 x 3 + 4 x − x 5 + x 2 − 2 ; Q ( x ) = x 3 − 2 x 2 + 3 x + 1 + 2 x 2
Tìm bậc của đa thức M(x) = P(x) + Q(x)
A. 4
B. 2
C. 3
D. 1
Ta có
P ( x ) = 2 x 3 − 3 x + x 5 − 4 x 3 + 4 x − x 5 + x 2 − 2 = x 5 − x 5 + 2 x 3 − 4 x 3 + x 2 + ( 4 x − 3 x ) − 2 = − 2 x 3 + x 2 + x − 2 Và Q ( x ) = x 3 − 2 x 2 + 3 x + 1 + 2 x 2 = x 3 + − 2 x 2 + 2 x 2 + 3 x + 1 = x 3 + 3 x + 1
Khi đó
M ( x ) = P ( x ) + Q ( x ) = − 2 x 3 + x 2 + x − 2 + x 3 + 3 x + 1 = − 2 x 3 + x 2 + x − 2 + x 3 + 3 x + 1 = − 2 x 3 + x 3 + x 2 + ( x + 3 x ) − 2 + 1 = − x 3 + x 2 + 4 x − 1
Bậc của M ( x ) = - x 3 + x 2 + 4 x - 1 l à 3
Chọn đáp án C
a) tìm a để đa thức 4x3 - 2x2+ a chia hết cho đa thức 2x - 3
b) Tìm giá trị a để đa thức 3x3 + 2x2 + x + a chia cho đa thức x + 1 có số dư bằng 2
\(a,\Leftrightarrow4x^3-2x^2+a=\left(2x-3\right).a\left(x\right)\)
Thay \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\Leftrightarrow4.\dfrac{27}{8}-2.\dfrac{9}{4}+a=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{27}{2}-\dfrac{9}{2}+a=0\\ \Leftrightarrow a=-9\)
\(b,\Leftrightarrow3x^3+2x^2+x+a=\left(x+1\right).b\left(x\right)+2\)
Thay \(x=-1\Leftrightarrow-3+2-1+a=2\Leftrightarrow a=4\)
a) \(x^3-x^2+3x-3>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)+3\left(x-1\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+3\right)\left(x-1\right)>0\)
Mà: \(x^2+3>0\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
b) \(x^3+x^2+9x+9< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)+9\left(x+1\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+9\right)\left(x+1\right)< 0\)
Mà: \(x^2+9>0\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -1\)
d) \(4x^3-14x^2+6x-21< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2\left(2x-7\right)+3\left(2x-7\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2+3\right)\left(2x-7\right)< 0\)
Mà: \(2x^2+3>0\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-7< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x< 7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< \dfrac{7}{2}\)
d) \(x^2\left(2x^2+3\right)+2x^2>-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^4+3x^2+2x^2+3>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^4+5x^2+3>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1\right)\left(2x^2+3\right)>0\)
Mà:
\(x^2+1>0\forall x\)
\(2x^2+3>0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in R\)
a: =>x^2(x-1)+3(x-1)>0
=>(x-1)(x^2+3)>0
=>x-1>0
=>x>1
b: =>x^2(x+1)+9(x+1)<0
=>(x+1)(x^2+9)<0
=>x+1<0
=>x<-1
c: 4x^3-14x^2+6x-21<0
=>2x^2(2x-7)+3(2x-7)<0
=>2x-7<0
=>x<7/2
d: =>x^2(2x^2+3)+2x^2+3>0
=>(2x^2+3)(x^2+1)>0(luôn đúng)
Đố em tìm được giá trị của x để giá trị của phân thức 4 x 2 - 4 x 3 + x 4 x 3 - 2 x 2 bằng: 0
Điều kiện: x 3 - 2 x 2 = x 2 x - 2 ≠ 0 ⇒ x ≠ 0 và x ≠ 2
Ta có: 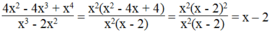
Nếu phân thức có giá trị bằng 0 thì biểu thức x - 2 cũng có giá trị bằng 0. Suy ra: x - 2 = 0 ⇒ x = 2 mà x = 2 không thỏa mãn điều kiện.
Vậy không có giá trị nào của x để phân thức có giá trị bằng 0.
Tìm m để
x4 - x3 - (m + 1)x2 + (m2 + m + 1)x - m2 ≥ 0 ∀x ∈ R