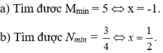tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức A= x2-4x+\(\frac{1}{x^2-4x+4}\)+5

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức A,B,C và giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức D,E:
A= x2-4x+1 D= 5-8x-x2
B= 4x2+4x+11 E= 4x-x2+1
C= (x-1).(x+3).(x+2).(x+6)
`A=x^2-4x+1`
`=x^2-4x+4-3`
`=(x-2)^2-3>=-3`
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x=2
`B=4x^2+4x+11`
`=4x^2+4x+1+10`
`=(2x+1)^2+10>=10`
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi `x=-1/2`
`C=(x-1)(x+3)(x+2)(x+6)`
`=[(x-1)(x+6)][(x+3)(x+2)]`
`=(x^2+5x-6)(x^2+5x+6)`
`=(x^2+5x)^2-36>=-36`
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi `x=0\or\x=-5`
`D=5-8x-x^2`
`=21-16-8x-x^2`
`=21-(x^2+8x+16)`
`=21-(x+4)^2<=21`
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi `x=-4`
`E=4x-x^2+1`
`=5-4+4-x^2`
`=5-(x^2-4x+4)`
`=5-(x-2)^2<=5`
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi `x=5`
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
A= x2 - 4x +1
= x2 - 4x + 4 - 3
= (x-2)2 -3
Ta có (x-2)2 ≥ 0 ∀ x
⇒ (x-2)2 -3 ≥ -3 ∀ x
Vậy AMin= -3 tại x=2
B= 4x2+4x+11
= 4x2+4x+1+10
= (2x+1)2+10
Ta có (2x+1)2 ≥ 0 ∀ x
⇒ (2x+1)2+10 ≥ 10 ∀ x
Vậy BMin=10 tại x= \(\dfrac{-1}{2}\)
C=(x-1)(x+3)(x+2)(x+6)
= (x-1)(x+6)(x+3)(x+2)
= (x2+5x-6) (x2+5x+6)
= (x2+5x)2 -36
Ta có (x2+5x)2 ≥ 0 ∀ x
⇒ (x2+5x)2 -36 ≥ -36 ∀ x
Vậy CMin=-36 tại x=0 hoặc x= -5
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức A, B, C và giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức D, E:
A = x2 – 4x + 1
B = 4x2 + 4x + 11
C = (x – 1)(x + 3)(x + 2)(x + 6)
D = 5 – 8x – x2
E = 4x – x2 +1
Tính giá trị nhỏ nhất:
\(A=x^2-4x+1=(x^2-4x+4)-3=(x-2)^2-3\)
Vì $(x-2)^2\geq 0, \forall x\in\mathbb{R}$ nên $A=(x-2)^2-3\geq 0-3=-3$
Vậy $A_{\min}=-3$
Giá trị này đạt tại $(x-2)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2$
$B=4x^2+4x+11=(4x^2+4x+1)+10=(2x+1)^2+10\geq 0+10=10$
Vậy $B_{\min}=10$
Giá trị này đạt tại $(2x+1)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{1}{2}$
$C=(x-1)(x+3)(x+2)(x+6)$
$=(x-1)(x+6)(x+3)(x+2)$
$=(x^2+5x-6)(x^2+5x+6)$
$=(x^2+5x)^2-36\geq 0-36=-36$
Vậy $C_{\min}=-36$. Giá trị này đạt $x^2+5x=0\Leftrightarrow x=0$ hoặc $x=-5$
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
Tìm giá trị lớn nhất:
$D=5-8x-x^2=21-(x^2+8x+16)=21-(x+4)^2$
Vì $(x+4)^2\geq 0, \forall x\in\mathbb{R}$ nên $D=21-(x+4)^2\leq 21$
Vậy $D_{\max}=21$. Giá trị này đạt tại $(x+4)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=-4$
$E=4x-x^2+1=5-(x^2-4x+4)=5-(x-2)^2\leq 5$
Vậy $E_{\max}=5$. Giá trị này đạt tại $(x-2)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2$
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
chứng tỏ các bất phương trình sau luôn nghiệm đungs với mọi x
x2 - 4x+5>0
chứng minh rằng -x2+4x-10/x2+1<0 với mọi x
tìm x để biểu thức x2-4x+5 đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất
tìm x để biểu thức -x2+4x+4 đạt giá trị lớn nhất
Ta có :
\(x^2-4x+5=\left(x^2-2.2x+2^2\right)+1=\left(x-2\right)^2+1\ge1>0\)
Vậy đa thức \(x^2-4x+5\) vô nghiệm với mọi giá trị của x
Chúc bạn học tốt ~
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức\(A=x^2-4x+\dfrac{1}{x^2-4x+4}+5\)
`A=x^2-4x+1/(x^2-4x+4)+5`
`=x^2-4x+4+1/(x^2-4x+4)+1`
Áp dụng BĐT cosi với 2 số dương ta có:
`x^2-4x+4+1/(x^2-4x+4)=(x-2)^2+1/(x-2)^2>=2`
`=>x^2-4x+4+1/(x^2-4x+4)+1>=3`
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi `(x-2)^2=1/(x-2)^2`
`<=>(x-2)^4=1`
`<=>` $\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=3\\x=1\end{array} \right.$
Vậy `min_A=3<=>` $\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=3\\x=1\end{array} \right.$
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức:
a) M = 2 x 2 +4x + 7; b)N = x 2 -x +1.
a, Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức: A=4x-x^2+3
b. Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức:B=4x^2-12x+15
c,Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức:C=4x^2+2y^2-4xy-4y+1
a)
\(A=4x-x^2+3=-\left(x^2-4x-3\right)=-\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+7=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\)
Daaus = xayr ra khi: x = 2
b) \(B=4x^2-12x+15=4\left(x^2-3x+9\right)-21=4\left(x-3\right)^2-21\ge-21\)
Dấu = xảy ra khi x = 3
c) \(C=4x^2+2y^2-4xy-4y+1=\left(4x^2-4xy+y^2\right)+\left(y^2-4y+4\right)-3=\left(2x-y\right)^2+\left(y-2\right)^2-3\ge-3\)
Dấu = xảy ra khi
2x = y và y = 2
=> x = 1 và y = 2
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a) A = \(-x^2+4x+3=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\)
Dấu "=" <=> x = 2
b) \(4x^2-12x+15=\left(2x-3\right)^2+6\ge6\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra <=> \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
c) \(4x^2+2y^2-4xy-4y+1\)
= \(\left(4x^2-4xy+y^2\right)+\left(y^2-4y+4\right)-3\)
= \(\left(2x-y\right)^2+\left(y-2\right)^2-3\ge-3\)
Dấu "=" <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức
a, M= x2-10x+3
b, N= x2-x+2
c, P=3x2-12x
Bài 2: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức
a, M= 2x2-4x+3
b, N= x2-4x+5+y2+2y2
MONG MN GIÚP ĐỠ :3
Bài 1:
a: \(M=x^2-10x+3\)
\(=x^2-10x+25-22\)
\(=\left(x^2-10x+25\right)-22\)
\(=\left(x-5\right)^2-22>=-22\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-5=0
=>x=5
b: \(N=x^2-x+2\)
\(=x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{7}{4}\)
\(=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{4}>=\dfrac{7}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-1/2=0
=>x=1/2
c: \(P=3x^2-12x\)
\(=3\left(x^2-4x\right)\)
\(=3\left(x^2-4x+4-4\right)\)
\(=3\left(x-2\right)^2-12>=-12\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-2=0
=>x=2
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a) tìm giá trị lớn nhất của các biểu thức :
A= 2x-3x^2-4 B=-x^2-4x
b) Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của các biểu thức :
A= x^2-2x-1 B= 4x^2+4x+5
a) Giá trị lớn nhất:
\(A=2x-3x^2-4=-3\left(x^2-\frac{2}{3}x+\frac{4}{3}\right)=-3\left[x^2-2.x.\frac{1}{3}+\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)^2+\frac{35}{9}\right]=-3\left(x-\frac{1}{3}^2\right)-\frac{35}{3}\)
Vì \(\left(x-\frac{1}{3}\right)^2\ge0\left(x\in R\right)\)
Nên \(-3\left(x-\frac{1}{3}\right)^2\le0\left(x\in R\right)\)
do đó \(-3\left(x-\frac{1}{3}\right)^2-\frac{35}{3}\le-\frac{35}{3}\left(x\in R\right)\)
Vậy \(Max_A=-\frac{35}{3}\)khi \(x-\frac{1}{3}=0\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{3}\)
\(B=-x^2-4x=-\left(x^2+4x\right)=-\left(x^2+2.x.2+2^2-2^2\right)=-\left(x+2\right)^2+4\)
Vì \(\left(x+2\right)^2\ge0\left(x\in R\right)\)
nên \(-\left(x+2\right)^2\le0\left(x\in R\right)\)
do đó \(-\left(x+2\right)^2+4\le4\left(x\in R\right)\)
Vậy \(Max_B=4\)khi \(x+2=0\Rightarrow x=-2\)
b) Giá trị nhỏ nhất
\(A=x^2-2x-1=x^2-2.x.+1-2=\left(x-1\right)^2-2\)
Vì \(\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\left(x\in R\right)\)
nên \(\left(x-1\right)^2-2\ge-2\left(x\in R\right)\)
Vậy \(Min_A=-2\)khi \(x-1=0\Rightarrow x=1\)
\(B=4^2+4x+5=\left(2x\right)^2+2.2x.1+1+4=\left(2x+1\right)^2+4\)
vì \(\left(2x+1\right)^2\ge0\left(x\in R\right)\)
nên \(\left(2x+1\right)^2+4\ge4\left(x\in R\right)\)
Vậy \(Min_B=4\)khi \(2x+1=0\Rightarrow x=-\frac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của các biểu thức sau
a. A = x2 - 4x + 6
b. B = y2 - y + 1
c . C = x2 - 4x + y2 - y + 5
a.
\(A=x^2-4x+4+2=\left(x-2\right)^2+2\ge2\)
GTNN của A đạt 2 khi và chỉ khi \(x=2\)
b.
\(B=y^2-2.\dfrac{1}{2}y+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}=\left(y-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\)
GTNN của B đạt \(\dfrac{3}{4}\) khi và chỉ khi \(y=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c.
\(C=x^2-4x+4+y^2-2.\dfrac{1}{2}y+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\\ =\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(y-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\)
GTNN của C đạt \(\dfrac{3}{4}\) khi và chỉ khi \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 4
Bình luận (1)
a) \(A=x^2-4x+6\)
\(A=x^2-4x+4+2\)
\(A=\left(x-2\right)^2+2\)
Mà: \(\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\forall x\) nên \(A=\left(x-2\right)^2+2\ge2\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra:
\(\left(x-2\right)^2+2=2\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy: \(A_{min}=2\) khi \(x=2\)
b) \(B=y^2-y+1\)
\(B=y^2-2\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot y+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(B=\left(y-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Mà: \(\left(y-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge\forall x\) nên \(B=\left(y-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra:
\(\left(y-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{3}{4}\Leftrightarrow y-\dfrac{1}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy \(B_{min}=\dfrac{3}{4}\) khi \(y=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c) \(C=x^2-4x+y^2-y+5\)
\(C=x^2-4x+4+y^2-y+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(C=\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(y-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Mà: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\forall x\\\left(y-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\end{matrix}\right.\) nên
\(C=\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(y-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\y-\dfrac{1}{2}=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(C_{min}=\dfrac{3}{4}\) khi \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)