Phân tích \(x^2-2x-5=0\) thành nhân tử

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Phân tích thành nhân tử
(x-3)^2-5(x-2)+5=0
(2x-1)^2-3(x-2)(x+2)-25=0
\(\left(x-3\right)^2-5\left(x-2\right)+5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9-5x+10+5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-11x+24=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-8\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(2x-1\right)^2-3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-25=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-3\left(x^2-4\right)-25=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x-24-3x^2+12=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-4x-12=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a: Ta có: \(\left(x-3\right)^2-5\left(x-2\right)+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9-5x+10+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-11x+24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-8\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(2x-1\right)^2-3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-3x^2+12-25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Phân tích vế trái thành nhân tử, giải phương trình sau: (2x – 5)2 – (x + 2)2 = 0
(2x – 5)2 – (x + 2)2 = 0
⇔ [(2x – 5) + (x + 2)].[(2x – 5) – (x + 2)]= 0
⇔ (2x – 5 + x + 2).(2x – 5 – x - 2) = 0
⇔ (3x – 3)(x – 7) = 0
⇔ 3x – 3 = 0 hoặc x – 7 = 0
+ 3x – 3 = 0 ⇔3x = 3 ⇔ x = 1.
+ x – 7 = 0 ⇔ x = 7.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {1; 7}.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
phân tích vế trái thành nhân tử, giải phương trình sau: 2x(x – 3) + 5(x – 3) = 0
2x(x – 3) + 5(x – 3) = 0
⇔ (2x + 5)(x – 3) = 0
⇔ 2x + 5 = 0 hoặc x – 3 = 0
+ 2x + 5 = 0 ⇔2x = -5 ⇔ x = -5/2
+ x – 3 = 0 ⇔x = 3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 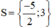
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Phân tích thành nhân tử: x * sqrt(x) + 2x + sqrt(x) +2(với x>0)
\(x\sqrt{x}+2x+\sqrt{x}+2\left(x>0\right)\)
\(=\left(x\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}\right)+\left(2x+2\right)\)
\(=\sqrt{x}\left(x+1\right)+2\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
\(x^2-2x-4y^2-4y=0\)
\(x^2-4y^2-2x-4y\)
\(=\left(x-2y\right)\left(x+2y\right)-2\left(x+2y\right)\)
\(=\left(x+2y\right)\left(x-2y-2\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử : 2x^4-x^3+2x^2+3x-2=0
Ta có
2x^4-x^3+2x^2+3x-2
=x^3(2x-1)+(2x^2-x)+(4x-2)
=x^3(2x-1)+x(2x-1)+2(2x-1)
=(x^3+x+2)(2x-1)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bằng cách phân tích vế trái thành nhân tử, giải các PT sau:
d) \(x\left(2x-7\right)-4x+14=0\)
e) \(\left(2x-5\right)^2-\left(x+2\right)^2=0\)
f) \(x^2-x-\left(3x-3\right)=0\)
d) \(PT\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x-7\right)-4\left(x-7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-7\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-7=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{7}{2};4\right\}\)
e) \(PT\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-5-x-2\right)\left(2x-5+x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-7\right)\left(3x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-7=0\\3x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=7\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{7;1\right\}\)
f) \(PT\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)-3\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{1;3\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
\(d,x\left(2x-7\right)-4x+14=0\)
\(x\left(2x-7\right)-2\left(2x-7\right)=0\)
\(\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
d: =>(2x-7)(x-2)=0
=>x=7/2 hoặc x=2
e: =>(2x-5-x-2)(2x-5+x+2)=0
=>(x-7)(3x-3)=0
=>x=7 hoặc x=1
f: =>x(x-1)-3(x-1)=0
=>(x-1)(x-3)=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=3
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Bài1: Thực hiện phép tính a) 2x(3x2 – 5x + 3) b) - 2x ( x2 + 5x+3) Bài 4: Tìm x, biết.a/ 3x + 2(5 – x) 0 b/ x(2x – 1)(x + 5) – (2x2 + 1)(x + 4,5) 3,5c/ 3x2 – 3x(x – 2) 36.II. PHÂN TÍCH ĐA THỨC THÀNH NHÂN TỬ Bài1: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử.a/ 14x2y – 21xy2 + 28x2y2 b/ x(x + y) – 5x – 5y.c/ 10x(x – y) – 8(y – x). d/ (3x + 1)2 – (x + 1)2e/ 5x2 – 10xy + 5y2 – 20z2. f/ x2 + 7x – 8g/ x3 – x + 3x2y + 3xy2 + y3 – y h/ x2 + 4x + 3.
Đọc tiếp
Bài1: Thực hiện phép tính
a) 2x(3x2 – 5x + 3) b) - 2x ( x2 + 5x+3)
Bài 4: Tìm x, biết.
a/ 3x + 2(5 – x) = 0 b/ x(2x – 1)(x + 5) – (2x2 + 1)(x + 4,5) = 3,5
c/ 3x2 – 3x(x – 2) = 36.
II. PHÂN TÍCH ĐA THỨC THÀNH NHÂN TỬ
Bài1: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử.
a/ 14x2y – 21xy2 + 28x2y2 b/ x(x + y) – 5x – 5y.
c/ 10x(x – y) – 8(y – x). d/ (3x + 1)2 – (x + 1)2
e/ 5x2 – 10xy + 5y2 – 20z2. f/ x2 + 7x – 8
g/ x3 – x + 3x2y + 3xy2 + y3 – y h/ x2 + 4x + 3.
Bài 1:
a: \(=6x^3-10x^2+6x\)
b: \(=-2x^3-10x^2-6x\)
Bài 4:
a: =>3x+10-2x=0
=>x=-10
c: =>3x2-3x2+6x=36
=>6x=36
hay x=6
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1:
\(a,=6x^3-10x^2+6x\\ b,=-2x^3-10x^2-6x\)
Bài 4:
\(a,\Leftrightarrow3x+10-2x=0\Leftrightarrow x=-10\\ b,\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x^2+9x-5\right)-\left(2x^3+9x^2+x+4,5\right)=3,5\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^3+9x^2-5x-2x^3-9x^2-x-4,5=3,5\\ \Leftrightarrow-6x=8\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\ c,\Leftrightarrow3x^2-3x^2+6x=36\Leftrightarrow x=6\)
Bài 1:
\(a,=7xy\left(2x-3y+4xy\right)\\ b,=x\left(x+y\right)-5\left(x+y\right)=\left(x-5\right)\left(x+y\right)\\ c,=\left(x-y\right)\left(10x+8\right)=2\left(5x+4\right)\left(x-y\right)\\ d,=\left(3x+1-x-1\right)\left(3x+1+x+1\right)\\ =2x\left(4x+2\right)=4x\left(2x+1\right)\\ e,=5\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-4z^2\right]=5\left(x-y-2z\right)\left(x-y+2z\right)\\ f,=x^2+8x-x-8=\left(x+8\right)\left(x-1\right)\\ g,\left(x+y\right)^3-\left(x+y\right)=\left(x+y\right)\left[\left(x+y\right)^2-1\right]\\ =\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y-1\right)\left(x+y+1\right)\\ h,=x^2+3x+x+3=\left(x+3\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Phân tích thành nhân tử: 3 + 2x (x < 0)
\(2x+3=2\left(x+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Phân tích thành nhân tử: 3 + 2x (x < 0)
Này nhóm kiểu gì nữa em
Em xem lại đề nhe!
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(3+2x=2\left(x+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)

























