12x-3x 1=937
x =...
giải giúp mình bài này
rút gọn
a/ 3x(12x-4)-9x(4x-3)_
b/ x(5-2x)+2x(x-1)
c/ 5x(12x+7)-3x(20x-5)
d/ 3x(2x-7)+2x(5-3x)
e/ (12x-5)(4x-1)(3x-7)(1-16x)
mình đang cần gấp
thanks trước nha!!!!
a/ 3x(12x-4)-9x(4x-3)
=36x2-12x-36x2+27x
=(36x2-36x2)-12x+27x
=15x
b/ x(5-2x)+2x(x-1)
=5x-2x2+2x2-2x
=(5x-2x)-(-2x2+2x2)
=3x
c/ 5x(12x+7)-3x(20x-5)
=60x2+35x-60x2+15x
=(60x2-60x2)+(35x+15x)\
=50x
d/ 3x(2x-7)+2x(5-3x)
=6x2-21x+10x-6x2
=(6x2-6x2)+(10x-21x)
=-11x
e/ đề sai hay sao ý ra số to lắm @@
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 1 x + 2 − 1 x − 2 = 3 x − 12 x 2 − 4 ;
b) − x 2 + 12 x + 4 x 2 + 3 x − 4 = 12 x + 4 + 12 3 x − 3 ;
c) 1 x − 1 + 2 x 2 − 5 x 3 − 1 = 4 x 2 + x + 1
Giải pt : \(12x\sqrt{3x+1}+12x+\sqrt{3x+1}+1\)
mik giải đc \(x=\frac{1-\sqrt{17}}{24}\)
mình nhầm \(12x\sqrt{3x+1}+12x+\sqrt{3x+1}+2=0\)
nhé!
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge-\frac{1}{3}\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{3x+1}=a\ge0\Rightarrow3x=a^2-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(a^2-1\right)a+4\left(a^2-1\right)+a+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4a^3+4a^2-3a-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4a^3+2a^2-4a+2a^2+a-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a\left(2a^2+a-2\right)+\left(2a^2+a-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2a+1\right)\left(2a^2+a-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a^2+a-2=0\) (do \(a\ge0\Rightarrow2a+1>0\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=\frac{-1+\sqrt{17}}{4}\\a=\frac{-1-\sqrt{17}}{4}< 0\left(l\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\sqrt{3x+1}=\frac{-1+\sqrt{17}}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow3x+1=\frac{9-\sqrt{17}}{8}\Rightarrow x=\frac{1-\sqrt{17}}{24}\)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a \(x^4=5x^2+2x-3\)
b \(x^4=6x^2+12x+10\)
c \(3x^3+3x^2+3x=-1\)
d \(8x^3-12x^2+6x-5=0\)
x ^{ 4 } +3x ^{ 3 } -12x ^{ 2 } -3x+1 = 0
4(3/4x-1)+(12x^2-3x):(-3x)-(2x+1)
1) (x+5)(x+2)-3(4x-3)=(5-x)2
2) (x+2)3-(x-2)3=12x(x-1)-8
3) 3x(12x-4)-9x(4x-3)=30
4) (12x-5)(4x-1)+(3x-7)(1-16x)=81
1) Ta có: \(\left(x+5\right)\left(x+2\right)-3\left(4x-3\right)=\left(5-x\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+5x+10-12x+9=25-10x+x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+19-25+10x-x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{6}{5}\)
Vậy: \(x=\frac{6}{5}\)
2) Ta có: \(\left(x+2\right)^3-\left(x-2\right)^3=12x\left(x-1\right)-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+6x^2+12x+8-\left(x^3-6x^2+12x-8\right)=12x^2-12x-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+6x^2+12x+8-x^3+6x^2-12x+8-12x^2+12x+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x=-24\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
Vậy: x=-2
3) Ta có: \(3x\left(12x-4\right)-9x\left(4x-3\right)=30\)
\(\Leftrightarrow36x^2-12x-36x^2+27x-30=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow15x-30=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow15x=30\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy: x=2
4) Ta có: \(\left(12x-5\right)\left(4x-1\right)+\left(3x-7\right)\left(1-16x\right)=81\)
\(\Leftrightarrow48x^2-12x-20x+5+3x-48x^2-7+112x-81=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow83x-83=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow83x=83\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Vậy: x=1
Không cần vẽ hình, hãy cho biết số nghiệm của mỗi hệ phương trình sau đây và giải thích vì sao:
a ) y = 3 − 2 x y = 3 x − 1 b ) y = − 1 2 x + 3 y = − 1 2 x + 1 c ) 2 y = − 3 x 3 y = 2 x d ) 3 x − y = 3 x − 1 3 y = 1
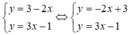
a) Xét (d): y = -2x + 3 có a = -2; b = 3
(d’) : y = 3x – 1 có a’ = 3 ; b’ = -1.
Có a ≠ a’ ⇒ (d) cắt (d’)
⇒ Hệ 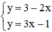 có nghiệm duy nhất.
có nghiệm duy nhất.
b) 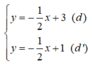
Xét (d): 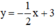 có a =
có a = 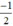 ; b = 3
; b = 3
(d’): 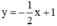 có a’ =
có a’ = 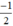 ; b’ = 1.
; b’ = 1.
Có a = a’; b ≠ b’ ⇒ (d) // (d’)
⇒ Hệ phương trình 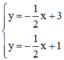 vô nghiệm.
vô nghiệm.
c) Ta có: 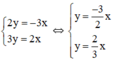
Xét (d): y = 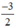 x có a =
x có a = 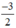 ; b = 0
; b = 0
(d’) : y = 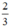 x có a’ =
x có a’ = 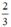 ; b’ = 0
; b’ = 0
Ta có: a ≠ a’ ⇒ (d) cắt (d’)
⇒ Hệ 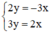 có nghiệm duy nhất.
có nghiệm duy nhất.
d) Ta có:
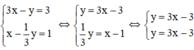
Ta có: a = a’=3; b = b’ = -3
Nhận thấy hai đường thẳng trên trùng nhau
⇒ Hệ phương trình có vô số nghiệm.
Kiến thức áp dụng
+ Xét hệ (I): 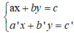
Gọi (d): ax + by = c và (d’): a’x + b’y = c’.
Số nghiệm của hệ (I) phụ thuộc vào vị trí tương đối của (d) và (d’).
(d) cắt (d’) ⇒ hệ (I) có nghiệm duy nhất.
(d) // (d’) ⇒ hệ (I) vô nghiệm
(d) ≡ (d’) ⇒ hệ (I) có vô số nghiệm.
+ Cho đường thẳng (d): y = ax + b và (d’): y = a’x + b’.
(d) cắt (d’) ⇔ a ≠ a’
(d) // (d’) ⇔ a = a’ và b ≠ b’
(d) trùng (d’) ⇔ a = a’ và b = b’.
\(12x^2-3x-1=\sqrt{3x+1}\)
(3x+1)^2-12x-(3x+5)^2+2(6x+3)