giải các pt sau
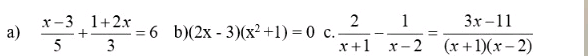
Giải các PT sau
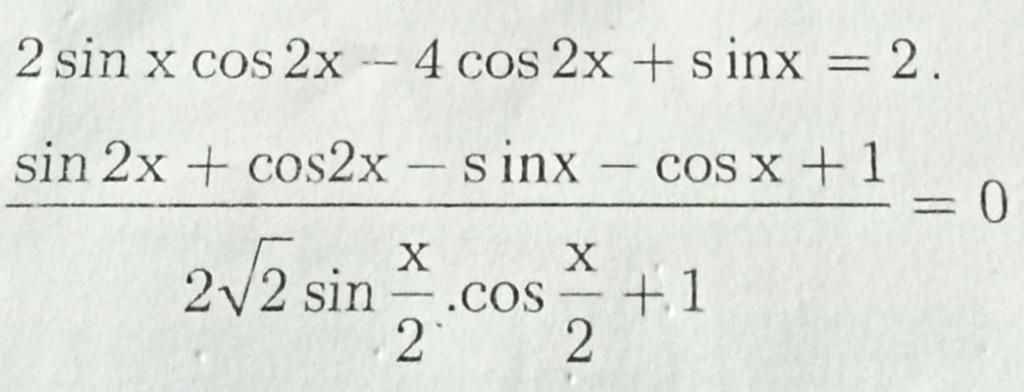
a: \(\Leftrightarrow2\cdot cos2x\left(sinx-2\right)+sinx-2=0\)
=>(sin x-2)(2*cos2x+1)=0
=>2*cos2x+1=0
=>cos2x=-1/2
=>2x=2/3pi+k2pi hoặc 2x=-2/3pi+k2pi
=>x=1/3pi+kpi hoặc x=-1/3pi+kpi
b:
ĐKXĐ: \(2\sqrt{2}\cdot sin\left(\dfrac{x}{2}\right)\cdot cos\left(\dfrac{x}{2}\right)+1< >0\)
=>\(\sqrt{2}\cdot sinx+1< >0\)
=>\(sinx< >-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< >-\dfrac{pi}{4}+k2pi\\x< >\dfrac{5}{4}pi+k2pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
PT\(\Rightarrow sin2x+cos2x-sinx-cosx+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(sin2x-sinx\right)+\left(cos2x-cosx+1\right)=0\)
=>\(sinx\left(2\cdot cosx-1\right)+\left(2cos^2x-1-cosx+1\right)=0\)
=>\(sinx\left(2\cdot cosx-1\right)+cosx\left(2cosx-1\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(2cosx-1\right)\left(sinx+cosx\right)=0\)
=>\(\sqrt{2}sin\left(x+\dfrac{pi}{4}\right)\cdot\left(2cosx-1\right)=0\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}sin\left(x+\dfrac{pi}{4}\right)=0\\2cosx-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{pi}{4}=kpi\\cosx=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{pi}{4}+kpi\\x=\pm\dfrac{pi}{3}+k2pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được:
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\pm\dfrac{pi}{3}+k2pi\\x=\dfrac{3}{4}pi+k2pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải các pt, bpt sau:
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x+2}-\dfrac{5}{x-2}=\dfrac{20}{4-x^2}\) (\(ĐK:x\)≠\(2;-2\))
⇔ \(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)-5\left(x+2\right)}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{20}{4-x^2}\)
⇔ \(-\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)+5\left(x+2\right)=20\)
⇔ \(-\left(x^2-2x+x-2\right)+5x+10=20\)
⇔ \(-x^2+x+2+5x+10-20=0\)
⇔ \(-x^2+6x-8=0\)
⇔ \(-\left(x^2-6x+9\right)=-1\)
⇔ \(\left(x-3\right)^2=1\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=1\\x-3=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
b: \(\Leftrightarrow20-5\left(3x+2\right)>4\left(x+7\right)\)
=>20-15x-10>4x+28
=>-15x+10-4x-28>0
=>-19x-18>0
=>-19x>18
hay x<-18/19
giải các PT trùng phương sau
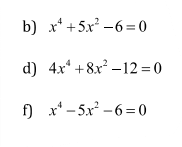
b) Đặt \(t=x^2\left(t\ge0\right)\). PT trở thành: \(t^2+5t-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t-1\right)\left(t+6\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=1\left(TM\right)\\t=-6\left(L\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2=1\Leftrightarrow x=\pm1\).
Vậy tập nghiệm của PT là \(S=\left\{\pm1\right\}\).
Các câu d, f em làm tương tự nhé!
Giải các pt sau ( Pt bậc hai một ẩn )3.(2x+3)=-x(x-2)-1
3.(2X+3)=-X.(X-2)-1 <=>6X+9=-\(x^2\)+2X-1 <=> \(x^2\) +4x+10=0 (\(\Delta\)' =4-10=-6 nhỏ hơn 0)
pt vô nghiệm
Giải giúp mình với ạ
Đề: giải các pt bậc hai 1 ẩn sau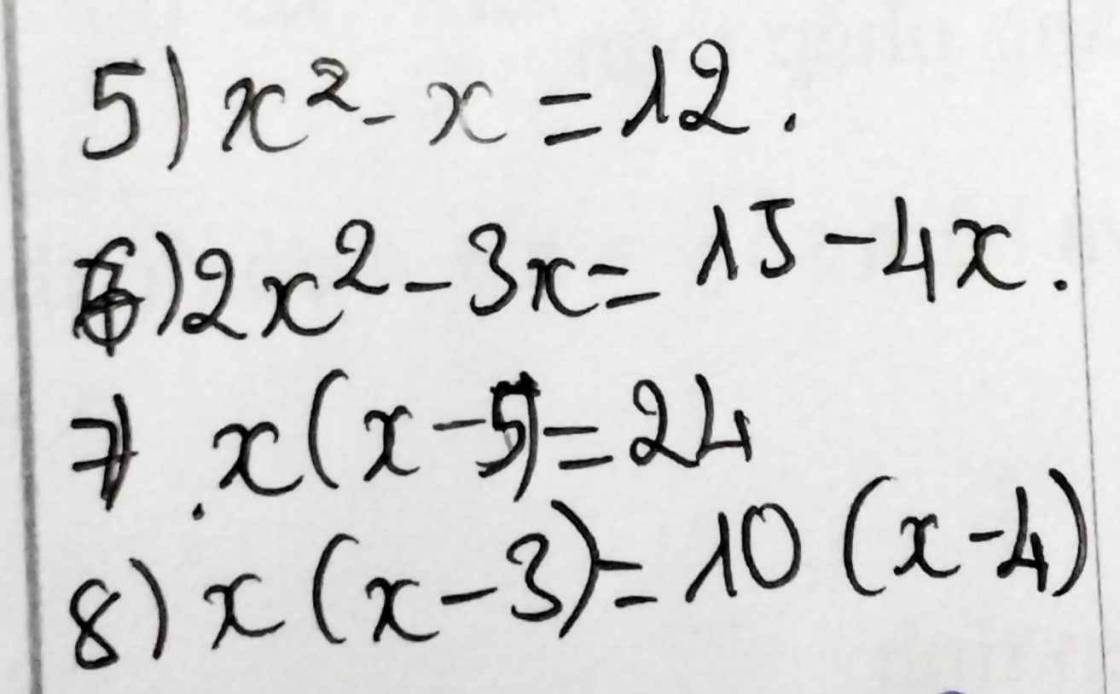
`x^2 -x=12`
`<=>x^2 -x-12=0`
`<=> x^2+3x-4x-12=0`
`<=> x(x+3)-4(x+3)=0`
`<=>(x+3)(x-4)=0`
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
`---`
`2x^2-3x=15-4x`
`<=> 2x^2-3x+4x=15`
`<=>2x^2 +x-15=0`
`<=>2x^2+6x-5x-15=0`
`<=> 2x(x+3)-5(x+3)=0`
`<=>(x+3)(2x-5)=0`
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\2x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
`---`
`x(x-5)=24`
`<=> x^2 -5x-24=0`
`<=>x^2+3x-8x-24=0`
`<=>x(x+3) -8(x+3)=0`
`<=>(x+3)(x-8)=0`
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x-8=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
`----`
`x(x-3)=10(x-4)`
`<=> x^2 -3x =10x -40`
`<=>x^2 -3x-10x +40=0`
`<=> x^2 -13x+40=0`
`<=>x^2-5x-8x+40=0`
`<=> x (x-5) - 8(x-5)=0`
`<=>(x-5)(x-8)=0`
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\x-8=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
5. \(x^2-x=12\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-12=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
6. \(2x^2-3x=15-4x\Leftrightarrow2x^2+x-15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
7. \(x\left(x-5\right)=24\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x-24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
8. \(x\left(x-3\right)=10\left(x-4\right)\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x=10x-40\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-13x+40=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
giải các pt sau bằng cách đặt ẩn phụ
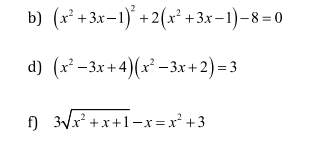
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+3x-1\right)^2+4\left(x^2+3x-1\right)-2\left(x^2+3x-1\right)-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+3x-1\right)\left(x^2+3x-1+4\right)-2\left(x^2+3x-1+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+3x-3=0\)
\(\Delta=3^2-4\cdot1\cdot\left(-3\right)=9+12=21>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-3-\sqrt{21}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{-3+\sqrt{21}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+6\left(x^2-3x\right)+8=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+5\left(x^2-3x\right)+\left(x^2-3x\right)+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+1=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-3\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot1=5>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Cho các PT sau: 3x2-4x+1=0; -x2+6x-5=0 a, Giải các PT trên bằng công thức nghiệm hoặc công thức nghiệm thu gọn.
a: 3x^2-4x+1=0
a=3; b=-4; c=1
Vì a+b+c=0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm là:
x1=1 và x2=c/a=1/3
b: -x^2+6x-5=0
=>x^2-6x+5=0
a=1; b=-6; c=5
Vì a+b+c=0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm là;
x1=1; x2=5/1=5
Giải các pt sau bằng công thức nghiệm
5x2 - 6x + 1 = 0
TRẢ LỜI:
Phương trình bậc hai 5x2 – 6x + 1 = 0
Có: a = 5; b’ = -3; c = 1.; Δ’ = (b’)2 – ac = (-3)2 – 5.1 = 4 > 0
Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt:
Ta có: \(5x^2-6x+1=0\)
a=5; b=-6; c=1
Vì a+b+c=0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(x_1=1;x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
Bài 1 : Giải các pt sau :
c) |2x - 1| = x + 2
Bài 2 : giải các BPT sau :
a) 2( 3x - 1 ) < x + 4
b) 5 -2x/3 + x ≥ x/2 + 1
Bài 1:
c) |2x - 1| = x + 2
<=> 2x - 1 = +(x + 2) hoặc -(x + 2)
* 2x - 1 = x + 2
<=> 2x - x = 2 + 1
<=> x = 3
* 2x - 1 = -(x + 2)
<=> 2x - 1 = x - 2
<=> 2x - x = -2 + 1
<=> x = -1
Vậy.....