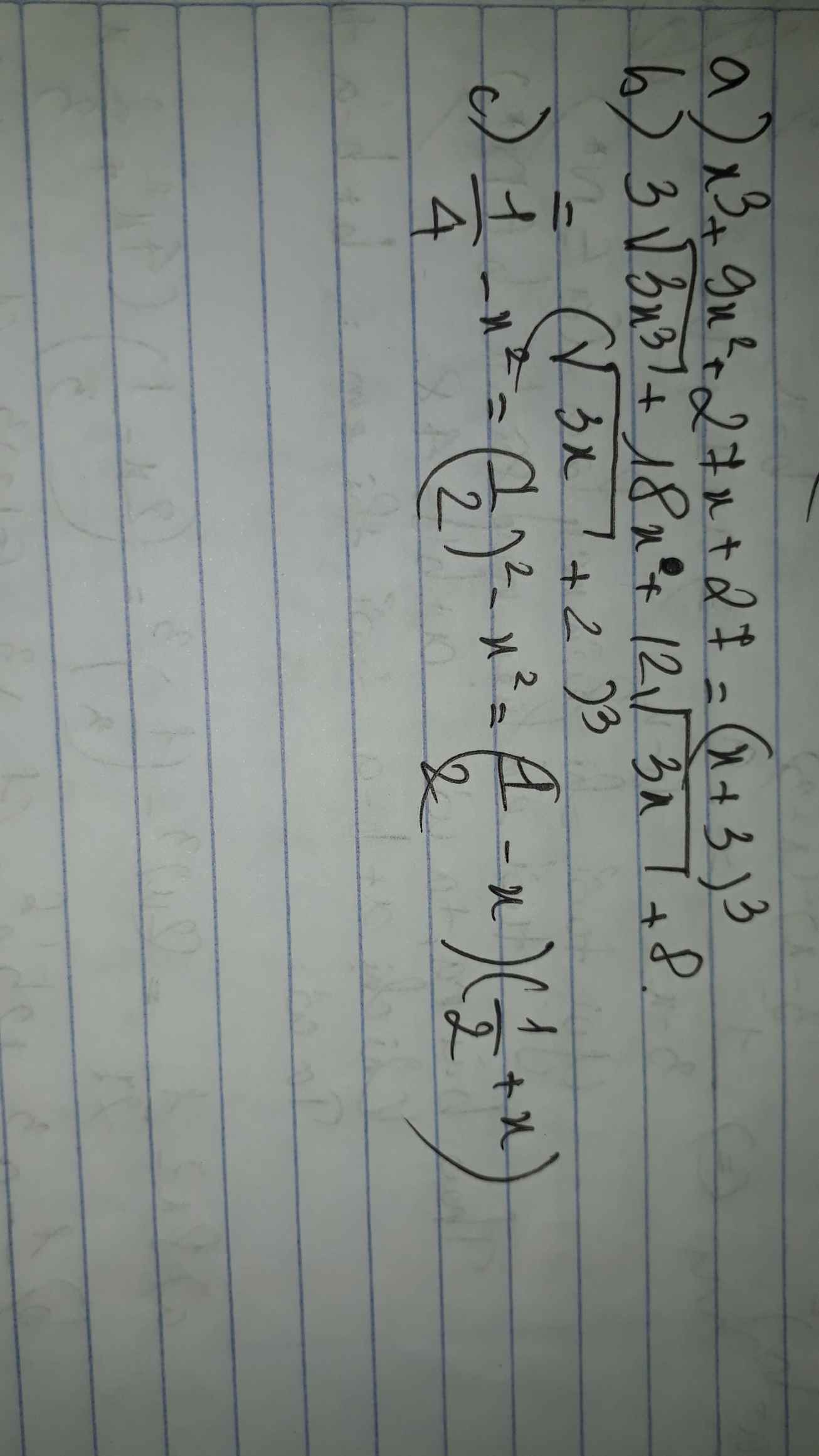phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử (x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4)-12

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Bài 1: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử a)4(2-x)^2+xy-2y b)3a^2x-3a^2y+abx-abyBài 2: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử a)x(x-y)^3-y(y-x)^2-y^2(x-y) b)2ax^3+6ax^2+6ax+18aBài 3: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử a)x^2y-xy^2-3x+3y b)3ax^2+3bx^2+bx+5a+5bBài 4: Tính giá trị biểu thức Aa(b+3)-b(3+b) tại a2003 và b1997Bài 5: Tìm x, biếta)8x(x-2017)-2x+40340 b)x^2(x-1)+16(1-x)0
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
a)4(2-x)\(^2\)+xy-2y b)3a\(^2\)x-3a\(^2\)y+abx-aby
Bài 2: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
a)x(x-y)\(^3\)-y(y-x)\(^2\)-y\(^2\)(x-y) b)2ax\(^3\)+6ax\(^2\)+6ax+18a
Bài 3: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
a)x\(^2\)y-xy\(^2\)-3x+3y b)3ax\(^2\)+3bx\(^2\)+bx+5a+5b
Bài 4: Tính giá trị biểu thức
A=a(b+3)-b(3+b) tại a=2003 và b=1997
Bài 5: Tìm x, biết
a)8x(x-2017)-2x+4034=0 b)x\(^2\)(x-1)+16(1-x)=0
\(1,\\ a,=4\left(x-2\right)^2+y\left(x-2\right)=\left(4x-8+y\right)\left(x-2\right)\\ b,=3a^2\left(x-y\right)+ab\left(x-y\right)=a\left(3a+b\right)\left(x-y\right)\\ 2,\\ a,=\left(x-y\right)\left[x\left(x-y\right)^2-y-y^2\right]\\ =\left(x-y\right)\left(x^3-2x^2y+xy^2-y-y^2\right)\\ b,=2ax^2\left(x+3\right)+6a\left(x+3\right)\\ =2a\left(x^2+3\right)\left(x+3\right)\\ 3,\\ a,=xy\left(x-y\right)-3\left(x-y\right)=\left(xy-3\right)\left(x-y\right)\\ b,Sửa:3ax^2+3bx^2+ax+bx+5a+5b\\ =3x^2\left(a+b\right)+x\left(a+b\right)+5\left(a+b\right)\\ =\left(3x^2+x+5\right)\left(a+b\right)\\ 4,\\ A=\left(b+3\right)\left(a-b\right)\\ A=\left(1997+3\right)\left(2003-1997\right)=2000\cdot6=12000\\ 5,\\ a,\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2017\right)\left(8x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2017\\x=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-16\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=4\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử (thêm bớt cùng một hạng tử):
x^3 - 2x - 4
phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử (đặt biến phụ):
x^4 + 2x^3 + 5x^2 + 4x - 12
#)Giải :
\(x^3-2x-4\)
\(=x^3+2x^2-2x^2+2x-4x-4\)
\(=x^3+2x^2+2x-2x^2-4x-4\)
\(=x\left(x^2+2x+2\right)-2\left(x^2+2x+2\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+2\right)\)
\(x^4+2x^3+5x^2+4x-12\)
\(=x^4+x^3+6x^2+x^3+x^2+6x-2x^2-2x-12\)
\(=x^2\left(x^2+x+6\right)+x\left(x^2+x+6\right)-2\left(x^2+x+6\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+x+6\right)\left(x^2+x-2\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+x+6\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Câu 1.
Đoán được nghiệm là 2.Ta giải như sau:
\(x^3-2x-4\)
\(=x^3-2x^2+2x^2-4x+2x-4\)
\(=x^2\left(x-2\right)+2x\left(x-2\right)+2\left(x-2\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+2\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử:
a,(x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4)-15
b,(x+2)(x+3)^2(x+4)-12
a) ( x + 1 )( x + 2 )( x + 3 )( x + 4 ) - 15
= [ ( x + 1 )( x + 4 ) ][ ( x + 2 )( x + 3 ) ] - 15
= ( x2 + 5x + 4 )( x2 + 5x + 6 ) - 15 (*)
Đặt t = x2 + 5x + 4
(*) trở thành
t( t + 2 ) - 15
= t2 + 2t - 15
= t2 - 3t + 5t - 15
= t( t - 3 ) + 5( t - 3 )
= ( t - 3 )( t + 5 )
= ( x2 + 5x + 4 - 3 )( x2 + 5x + 4 + 5 )
= ( x2 + 5x + 1 )( x2 + 5x + 9 )
b) ( x + 2 )( x + 3 )2( x + 4 ) - 12
= [ ( x + 2 )( x + 4 ) ]( x + 3 )2 - 12
= ( x2 + 6x + 8 )( x2 + 6x + 9 ) - 12 (*)
Đặt t = x2 + 6x + 8
(*) trở thành
t( t + 1 ) - 12
= t2 + t - 12
= t2 - 3t + 4t - 12
= t( t - 3 ) + 4( t - 3 )
= ( t - 3 )( t + 4 )
= ( x2 + 6x + 8 - 3 )( x2 + 6x + 8 + 4 )
= ( x2 + 6x + 5 )( x2 + 6x + 12 )
= ( x2 + x + 5x + 5 )( x2 + 6x + 12 )
= [ x( x + 1 ) + 5( x + 1 ) ]( x2 + 6x + 12 )
= ( x + 1 )( x + 5 )( x2 + 6x + 12 )
a, Gọi\(A=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)-15\)
\(=\left(x^2+5x+4\right)\left(x^2+5x+6\right)-15\)
Đặt\(y=x^2+5x+4\)
\(\Rightarrow A=y\left(y+2\right)-15\)
\(=y^2+2y-15\)
\(=\left(x-3\right)\left(x+5\right)\)
Hay\(A=\left(x^2+5x+1\right)\left(x^2+5x+9\right)\)
Vậy...
b,Gọi\(B=\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)^2\left(x+4\right)-12\)
\(=\left(x^2+6x+8\right)\left(x^2+6x+9\right)-12\)
Đặt\(z=x^2+6x+8\)
\(\Rightarrow B=z\left(z+1\right)-12\)
\(=z^2+z-12\)
\(=\left(z-3\right)\left(z+4\right)\)
Hay\(B=\left(x^2+6x+5\right)\left(x^2+6x+12\right)\)
Vậy...
Linz
\(a,\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)-15\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)-15\)
\(=\left(x^2+5x+4\right)\left(x^2+5x+6\right)-15\)(*)
Đặt \(t=x^2+5x+4\)
(*)\(=t\left(t+2\right)-15\)
\(=t^2+2t-15\)
\(=t^2-3t+5t-15\)
\(=t\left(t-3\right)+5\left(t-3\right)\)
\(=\left(t-3\right)\left(t+5\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+5x+4-3\right)\left(x^2+5x+4+3\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+5x+1\right)\left(x^2+5x+9\right)\)
\(b,\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)^2\left(x+4\right)-12\)
\(=\left(x+2\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(x+3\right)^2-12\)
\(=\left(x^2+6x+8\right)\left(x^2+6x+9\right)-12\)(*)
Đặt \(t=x^2+6x+8\)
(*)\(=t\left(t+1\right)-12\)
\(=t^2+t-12\)
\(=t^2-3t+4t-12\)
\(=t\left(t-3\right)+4\left(t-3\right)\)
\(=\left(t+4\right)\left(t-3\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+6x+12\right)\left(x^2+6x+5\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+6x+12\right)\left(x^2+x+5x+5\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+6x+12\right)\left[x\left(x+1\right)+5\left(x+1\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(x^2+6x+12\right)\left(x+5\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
1) Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử ( = cách nhẩm nghiệm và hệ số bất định)
a) x^4+6x^3+11x^2+6x+1
b)x^4+7x^3+14x^2+14x+4
c)x^4-1ox^3-15x^2+20x+4
2)phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử( = cách hệ số bất định)
a) x^4-8x^3+11x^2+8x+12
b) x^4+x^2+1
c)x^4+4
Đa thức x^3 - 2x^2 + x - xy^2 được phân tích thành nhân tử
Đa thức x^3 + 3x^2y +3xy^2 + y^3 được phân tích thành nhân tử là
Đa thức 4x(2y-z)+7y(2y-z) được phân tích thành nhân tử là:
Đa thức x^2+4x+4 được phân tích thành nhân tử là
Tìm x biết x(x-2)-x+2
\(1,=x\left(x^2-2x+1-y^2\right)=x\left[\left(x-1\right)^2-y^2\right]=x\left(x-y-1\right)\left(x+y-1\right)\\ 2,=\left(x+y\right)^3\\ 3,=\left(2y-z\right)\left(4x+7y\right)\\ 4,=\left(x+2\right)^2\\ 5,Sửa:x\left(x-2\right)-x+2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1 : Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử :1) 15x + 15y 2) 8x - 12y3) xy - x 4) 4x^2- 6xBài 2 : Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử :1) 2(x + y) - 5a(x + y) 2) a^2(x - 5) - 3(x - 5)3) 4x(a - b) + 6xy(a - b) 4) 3x(x - 1) + 5(x -1)Bài 3 : Tính giá trị của biểu thức :1) A 13.87 + 13.12 + 132) B (x - 3).2x + (x - 3).y tại x 13 và y 4Bài 4 : Tìm x :1) x(x - 5) - 2(x - 5) 0 2) 3x(x - 4) - x + 4 03) x(x - 7) -...
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1 : Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử :
1) 15x + 15y 2) 8x - 12y
3) xy - x 4) 4x^2- 6x
Bài 2 : Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử :
1) 2(x + y) - 5a(x + y) 2) a^2(x - 5) - 3(x - 5)
3) 4x(a - b) + 6xy(a - b) 4) 3x(x - 1) + 5(x -1)
Bài 3 : Tính giá trị của biểu thức :
1) A = 13.87 + 13.12 + 13
2) B = (x - 3).2x + (x - 3).y tại x = 13 và y = 4
Bài 4 : Tìm x :
1) x(x - 5) - 2(x - 5) = 0 2) 3x(x - 4) - x + 4 = 0
3) x(x - 7) - 2(7 - x) = 0 4) 2x(2x + 3) - 2x - 3 = 0
\(1,\\ 1,=15\left(x+y\right)\\ 2,=4\left(2x-3y\right)\\ 3,=x\left(y-1\right)\\ 4,=2x\left(2x-3\right)\\ 2,\\ 1,=\left(x+y\right)\left(2-5a\right)\\ 2,=\left(x-5\right)\left(a^2-3\right)\\ 3,=\left(a-b\right)\left(4x+6xy\right)=2x\left(2+3y\right)\left(a-b\right)\\ 4,=\left(x-1\right)\left(3x+5\right)\\ 3,\\ A=13\left(87+12+1\right)=13\cdot100=1300\\ B=\left(x-3\right)\left(2x+y\right)=\left(13-3\right)\left(26+4\right)=10\cdot30=300\\ 4,\\ 1,\Rightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ 2,\Rightarrow\left(x-7\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=7\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\\ 3,\Rightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\\ 4,\Rightarrow\left(2x+3\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 4
Bình luận (0)
Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử:
(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)(x-4)-80
(x2+x+1)(x2+x+2)-12
\(\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)-80=\left(x^2-5x+4\right)\left(x^2-5x+6\right)-80\)
Đặt \(x^2-5x+4=t\), ta có:
\(t\left(t+2\right)-80=t^2-2t+1-81=\left(t-1\right)^2-9^2=\left(t-1-9\right)\left(t-1+9\right)=\left(t-10\right)\left(t+8\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-5x+4-10\right)\left(x^2-5x+4+8\right)=\left(x^2-5x-6\right)\left(x^2-5x+12\right)\)
\(\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+2\right)-12\)
Đặt x2 + x + 1 = t, ta có:
t(t + 1) - 12
= t2 + t + 1/4 - 49/4
= (t + 1/2)2 - (7/2)2
= (t + 1/2 + 7/2)(t + 1/2 - 7/2)
= (t + 4)(t - 3)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
nhân váo như bình thường sau đó bấm máy tính shift solve =? rồi chia hoocne
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
x^3+9x^2+27x+27
3\(\sqrt{3x^3}\)+18x^2+12\(\sqrt{3x}\)+8
\(\dfrac{1}{4}\)-x^2
a) \(x^3+9x^2+27x+27=\left(x+3\right)^3\)
b) \(3\sqrt{3x^3}+18x^2+12\sqrt{3x}+8=\left(\sqrt{3x}+2\right)^3\)
c) \(\dfrac{1}{4}-x^2=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-x\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{2}+x\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử (x^2 + x + 1)(x^2 + x + 2) - 12
Ta có: \(\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+2\right)-12\)
\(=\left(x^2+x\right)^2+3\left(x^2+x\right)+2-12\)
\(=\left(x^2+x\right)^2+3\left(x^2+x\right)-10\)
\(=\left(x^2+x+5\right)\left(x^2+x-2\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+x+5\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)