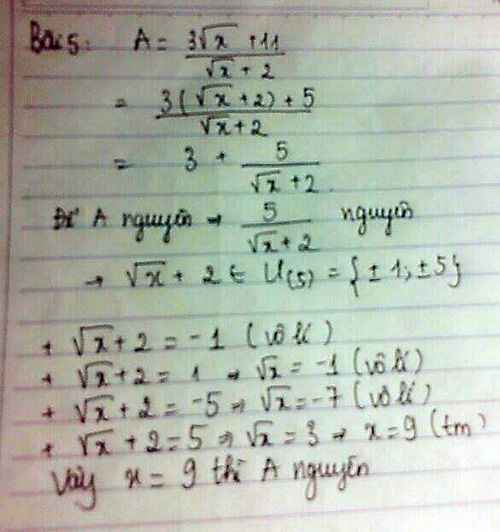TÌM SỐ HỮU TỈ X, BIẾT :\(X-2\sqrt{X}\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tìm các số hữu tỉ b,c biết \(x^2+bx+c=0;x=\sqrt{31-8\sqrt{15}}\)
\(x=\sqrt{31-8\sqrt{15}}=\sqrt{\left(4-\sqrt{15}\right)^2}=4-\sqrt{15}\)
Biểu thức nghịch đảo của x là \(\dfrac{1}{4-\sqrt{15}}=4+\sqrt{15}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=4\pm\sqrt{15}\) là nghiệm PT \(x^2+bx+c\left(1\right)\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}S=x_1+x_2\\P=x_1x_2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}S=8\\P=1\end{matrix}\right.\) (x1 và x2 là nghiệm của (1))
Áp dụng Viet đảo thì x là nghiệm của PT \(x^2-8x+1\)
Vậy \(b=-8;c=1\)
Đúng 4
Bình luận (3)
Bạn có thể làm thế này:
\(x=4-\sqrt{15}\)
Giả sử \(x=4-\sqrt{15}\) là nghiệm của PT \(x^2+bx+c=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4-\sqrt{15}\right)^2+b\left(4-\sqrt{15}\right)+c=0\\ \Leftrightarrow31-8\sqrt{15}+4b-b\sqrt{15}+c=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{15}\left(b+8\right)=-\left(4b+c+31\right)\)
Vì b,c hữu tỉ nên \(\sqrt{15}\left(b+8\right)\) hữu tỉ
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b+8=0\\4b+c+31=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b=-8\\c=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (2)
Tìm số hữu tỉ x, biết : x-\(2\sqrt{x}\)=0
\(x-2\sqrt{x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}\right)^2-2\sqrt{x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}=0\) và \(\sqrt{x}-2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=0\) và \(\sqrt{x}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow x=0\) và \(x=4\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(x-2\sqrt{x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}\right)^2-2\sqrt{x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}=0\)và \(\sqrt{x}-2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=0\)và \(\sqrt{x}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow x=0\)và \(x=4\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Tìm số hữu tỉ x biết \(x-2\sqrt{x}=0\)
ĐK : \(x\ge0\)
\(x-2\sqrt{x}=0\Rightarrow x=2\sqrt{x}\)
Bình phương hai vế ta có :
\(x^2=4x\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x(x-4)=0\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=4\end{cases}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm số hữu tỉ x biết
\(x-2\sqrt{x}=0\)
Đk:\(x\ge0\)
\(x-2\sqrt{x}=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\sqrt{x}\)
Bình phương 2 vế ta có:
\(x^2=4x\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-4\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=4\end{cases}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
tìm số hữu tỉ x biết: \(x-2\sqrt{x}=0\left(x\ge0\right)\))
x - 2\(\sqrt{x}\) = 0
<=> \(\sqrt{x}\)(\(\sqrt{x}\)- 2) = 0
<=> x = 0 hoặc x = 4
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(x-2\sqrt{x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}^2-2\sqrt{x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\sqrt{x}=0\\\sqrt{x}-2=0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\\sqrt{x}=2\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=4\end{cases}}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm số hữu tỉ x, biết:
\(x-2\sqrt{x}=0\left(x\ge0\right)\)
\(x-2\sqrt{x}=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\sqrt{x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=\left(2\sqrt{x}\right)^2\)\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-4\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x-4=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=4\end{cases}}\)( thoả mãn điều kiện )
Vậy \(x=0\)hoặc \(x=4\)
Tìm các số hữu tỉ x để \(\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}+11}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)là số nguyên
ĐK: \(x\ge0\)
\(A=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}+11}{\sqrt{x}+2}\Leftrightarrow A\sqrt{x}+2A=3\sqrt{x}+11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(A-3\right)\sqrt{x}=11-2A\left(1\right)\)
TH1: \(A=3\Rightarrow\) Không tồn tại x thỏa mãn.
TH2: \(A\ne3\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=\dfrac{11-2A}{A-3}\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow3< A\le\dfrac{11}{2}\)
Vậy \(3< A\le\dfrac{11}{2}\) thì \(A\in Z\).
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Tìm số hữu tỉ x biết
\(x-2.\sqrt{x}=0\) ( x > hoặc = 0 )
\(x-2\sqrt{x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\sqrt{x}=0\\\sqrt{x}-2=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=4\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x = 0 hoặc x = 4
\(x-2\sqrt{x}=0\)
<=> \(\sqrt{x}.\sqrt{x}-2\sqrt{x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\sqrt{x}=0\\\sqrt{x}-2=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=4\end{cases}}\)
a, tính Max A=\(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{9-x}\)
b,Tìm tất cả các số hữu tỉ x để A=\(\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}+11}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)là số nguyên
Lời giải:
a.
Áp dụng BĐT Bunhiacopxky:
$A^2=(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{9-x})^2\leq (x-1+9-x)(1+1)=16$
$\Rightarrow A\leq 4$
Vậy $A_{\max}=4$. Giá trị này đạt tại $x=5$
b.
$A=\frac{3(\sqrt{x}+2)+5}{\sqrt{x}+2}=3+\frac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}$
Để $A$ nguyên thì $\frac{5}{\sqrt{x}+2}=m$ với $m$ nguyên dương
$\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{x}+2=\frac{5}{m}$
$\sqrt{x}=\frac{5-2m}{m}$
Vì $\sqrt{x}\geq 0$ nên $\frac{5-2m}{m}\geq 0$
Mà $m$ nguyên dương nên $5-2m\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow m\leq 2,5$.
$\Rightarrow m=1; 2$
$\Rightarrow x=9; x=\frac{1}{4}$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)