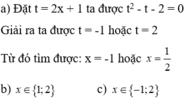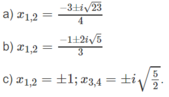Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tìm x, biết:
2
x
+
1
x
2
-
2
x
+
1
-
2
x
+
3
x
2
-
1...
Đọc tiếp
Tìm x, biết: 2 x + 1 x 2 - 2 x + 1 - 2 x + 3 x 2 - 1 = 0
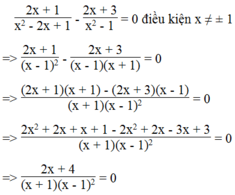
Biểu thức bằng 0 khi tử bằng 0 và mẫu khác 0
Ta có: 2x + 4 = 0 => x = - 2 (thỏa mãn điều kiện)
Vậy với x = - 2 thì giá trị của biểu thức bằng 0.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
b. 4x2 +4x+1=0 d. 5x2 6x1=0 a. 2x2-5x+1=0 c. -3x2 +2x+8=0 e. -3x2+ 14x - 8=0 g. -7x2 +4x-3=0
a. 2x2-5x+1=0
△= b2 - 4ac = (-5)2 - 4*2*1 = 17 ⇒√△ = √17
\(\Rightarrow x_1=\frac{5+\sqrt{17}}{4};x_2=\frac{5-\sqrt{17}}{4}\)
Vậy .... S={\(\frac{5\pm\sqrt{17}}{4}\)}
b. 4x2 +4x+1=0
⇔(2x+1)2 = 0 ⇔ x=\(\frac{-1}{2}\)
c. -3x2 +2x+8=0
△' = b'2 - ac = 12 - (-3)*8 = 25 ⇒√△ = 5
\(\Rightarrow x_1=\frac{-1+5}{-3}=-\frac{4}{3};x_2=\frac{-1-5}{-3}=2\)
Vậy... S={-\(\frac{4}{3}\);2}
d. 5x2 6x1=0 (thiếu dấu nên mk chưa giải được)
e. -3x2+ 14x - 8=0
△' = b'2 - ac = 72 - (-3)*(-8) = 25 ⇒ √△ = 5
⇒\(x_1=\frac{-7+5}{-3}=\frac{2}{3};x_2=\frac{-7-5}{-3}=4\)
Vậy .... S={\(\frac{2}{3};4\)}
g. -7x2 +4x-3=0
△' = b'2 - ac = 22 - (-7)*(-3) = -17<0
Vậy pt vô nghiệm , S=∅
Đúng 0
Bình luận (4)
Giải phương trình bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích :
3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0
x2 - 4x + 1 = 0
2x2 - 6x + 1 = 0
3x2 + 4x - 4 = 0
3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
=> 3x2 + 3x - x - 1 = 0
=> 3x(x + 1) - (x + 1) = 0
=> (3x - 1)(x + 1) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-1=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
=> x2 - 2x - 3x + 6 = 0
=> x(x - 2) - 3(x - 2) = 0
=> (x - 3)(x - 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0
=> 3x2 + 6x + x + 2 = 0
=> 3x(x + 2) + (x + 2) = 0
=> (3x + 1)(x + 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x+1=0\\x+2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{3}\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1, \(3x^2+2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+3x-x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
2, \(x^2-5x+6=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=3\end{cases}}}\)
3, \(3x^2+7x+2=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+6x+x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+2=0\\3x+1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=-\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(x^2-4x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt{3}+2;x=2-\sqrt{3}\)
\(2x^2-6x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-12x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)^2=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{\sqrt{7}+3}{2};x=\frac{3-\sqrt{7}}{2}\)
\(3x^2+4x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-2x+6x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2;x=\frac{2}{3}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x:
a) 5x+40x4=0
b) 8x2-2x-1=0
c) (3x2+x)2-(3x2+x)-2=0
a: Ta có: \(40x^4+5x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x\left(8x^3+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Ta có: \(8x^2-2x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x^2-4x+2x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(4x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x:
a) 3x2+ 6x = 0
b)x (x − 1) + 2x − 2 = 0
\(a,\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)+2\left(x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Câu 1: Giải hệ phương trình
a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3y=-5\\6x-5y=27\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) 3x2 + 4x = 0
c) x4 - 3x2 - 4 = 0
a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3y=-5\\6x-5y=27\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x+9y=-15\\6x-5y=27\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}14y=-42\\2x+3y=-5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\2x+3.\left(-3\right)=-5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\2x-9=-5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\2x=4\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(3x^2+4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\3x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là: \(S=\left\{0;-\dfrac{4}{3}\right\}\)
c) Đặt: \(x^2=t\left(t\ge0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Ta có phương trình mới:
\(t^2-3t-4=0\)
Ta có: a - b + c = 1 + 3 - 4 = 0
\(\Rightarrow t_1=-1\left(loại\right);t_2=4\left(TM\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\pm2\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là: S = {2; -2}
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a, \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3y=-5\\6x-5y=27\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x+9y=-15\left(1\right)\\6x-5y=27\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lấy (1) - (2) ta được : \(14y=-15-27=-42\Leftrightarrow y=-3\)
\(\Rightarrow6x-27=-15\Leftrightarrow6x=12\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(2;-3\right)\)
b, \(3x^2+4x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x+4\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=0;x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\)
c, \(x^4-3x^2-4=0\Leftrightarrow x^4+x^2-4x^2-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-4\right)+x^2-4=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm2;x^2+1>0\)
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là x = -2 ; x = 2
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Số nghiệm của phương trình
2
x
2
-
2
x
2
-
3
x
2
-
2
x
+
1
0
là A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
Đọc tiếp
Số nghiệm của phương trình 2 x 2 - 2 x 2 - 3 x 2 - 2 x + 1 = 0 là
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Đặt t = x2 – 2x. Khi đó, phương trình đã cho trở thành:
2t2 – 3t + 1 = 0 ⇔ [ t = 1 t = 1 2
* Với t= 1 thì x2 – 2x = 1 hay x2 – 2x – 1 =0 có ac < 0 nên phương trình này có 2 nghiệm.
* Với t = 1 2 thì x 2 - 2 x = 1 2 ⇔ x 2 - 2 x - 1 2 = 0 có ac < 0 nên phương trình này có 2 nghiệm.
Do đó, phương trình đã cho có 4 nghiệm.
Chọn D.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:a)
2
x
+
1
2
−
2
x
−
1
2
;
b)
x
2
−
3
x
2
+
5
x...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 2 x + 1 2 − 2 x − 1 = 2 ;
b) x 2 − 3 x 2 + 5 x 2 − 3 x + 6 = 0 ;
c) x 2 − x − 1 x 2 − x − 2 = 0 .
Giải các phương trình sau trên tập số phức:
a) 2x2 + 3x + 4 = 0
b) 3x2 + 2x + 7 = 0
c) 2x4 + 3x2 – 5 = 0