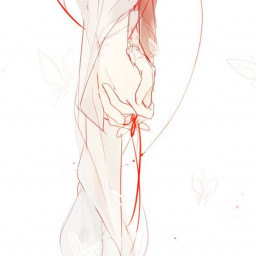
\(3x^2- 12+√145=0\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
tìm x
a)12:x=144
b)x-17=(-2).27
c)3x-125=145
a: 12:x=144
=>\(x=\dfrac{12}{144}\)
=>\(x=\dfrac{1}{12}\)
b: \(x-17=\left(-2\right)\cdot27\)
=>\(x-17=-54\)
=>\(x=-54+17=-37\)
c: \(3x-125=145\)
=>\(3x=125+145=270\)
=>\(x=\dfrac{270}{3}=90\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(a,12:x=144\\ x=\dfrac{12}{144}=\dfrac{1}{12}\\ ---\\ b,x-17=\left(-2\right).27\\ x-17=-54\\ x=-54+17=-37\\ ----\\ 3x-125=145\\ 3x=145+125=270\\ x=\dfrac{270}{3}=90\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a: 12:x=144
x=\(\dfrac{1}{12}\)
b: x−17=(−2)⋅27
x−17=−54
x=−54+17
−37
c: 3x−125=145
3x=125+145=270
x=90
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau bằng hai cách (chuyển số hạng tự do sang vế phải; bằng công thức nghiệm) và so sánh kết quả tìm được :
a) \(4x^2-9=0\)
b) \(5x^2+20=0\)
c) \(2x^2-2+\sqrt{3}=0\)
d) \(3x^2-12+\sqrt{145}=0\)
a: \(4x^2-9=0\)
=>(2x-3)(2x+3)=0
=>x=3/2 hoặc x=-3/2
b: \(5x^2+20=0\)
nên \(x^2+4=0\)(vô lý)
c: \(2x^2-2+\sqrt{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2=2-\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=\dfrac{4-2\sqrt{3}}{4}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1}{2};\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}+1}{2}\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình sau:
a. \(5x^2+10x=0\)
b. \(3x^2-12=0\)
c. \(3x^2+7=0\)
d. \(12x^2-3x=0\)
Tìm x
a) x2 - 145 = -64
b) (3x - 4) x (5x +15) = 0
Cần gấp và giải đầy đủ, theo cách học của lớp 6
a) x2 - 145 = -64
x2=-64+145
x2=81
x2=92
=>x=+9
Vậy x=+9
b) (3x - 4)(5x+15)=0
.\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-4=0\\5x+15=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x=4\Rightarrow x=\frac{4}{3}\\5x=-15\Rightarrow x=-15:5=-3\end{cases}}\)
Vậy..............................................
a) x2 - 145 = -64
x2 = -64 +145
x2= 81
=> x2= 92
=> x = 9
Vậy...
\(a,x^2-145=-64\)
\(x^2=81\)
\(x^2=9^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=9\\x=-9\end{cases}}\)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
a) Tính bằng cách thuận tiện nhất:
134 x 4 x 5;
5 x 36 x 2
42 x 2 x 7 x5
b) Tính (theo mẫu):
145 x2 + 145 x 98
= 145 x (2 + 98)
= 145 x 100 = 14 500
137 x 3 + 137 x 97
428 x 12 - 428 x 2
94 x 12 + 94 x 88
537 x 39 - 537 x 19
a) Tính bằng cách thuận tiện nhất:
134 x 4 x 5
= 134 x (4 x 5)
= 134 x 20 = 1680
5 x 36 x 2
= 36x (5 x 2)
= 36 x 10 = 360
42 x 2 x 7 x5
= (42 x 7) x (2 x5)
= 294 x 10 = 2940
b) 137 x 3 + 137 x 97
= 137 x (3 + 97)
= 137 x 100 = 13700
94 x 12 + 94 x 88
= 94 x (12 + 88)
= 94 x 100 = 9400
428 x 12 - 428 x 2
= 428 x (12 - 2) = 4280
537 x 39 - 537 x 19
= 537 x (39 - 19)
= 537 x 20 = 10740
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x biết:
a) [( x+ 32) -17] x2= 42
b) 125+(145-x)= 175
3X x(x-5)= 0
a) \(\left[\left(x+32\right)-17\right].2=42\)
\(\left[\left(x+32\right)-17\right]=42:2\)
\(\left[\left(x+32\right)-17\right]=21\)
\(\left(x+32\right)=21+17\)
\(\left(x+32\right)=38\)
\(x=38-32\)
\(x=6\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
b) \(125+\left(145-x\right)=175\)
\(\left(145-x\right)=175-125\)
\(\left(145-x\right)=50\)
\(x=145-50\)
\(x=95\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình
a) \(x^2-2x+1=0\)
b)\(1+3x+3x^2+x=0\)
c)\(x+x^4=0\)
d)\(x^3-3x^2+3x-1+x\left(x^2-x\right)=0\)
e)\(x^2+x-12=0\)
g)\(6x^2-11x-10=0\)
a) Ta có: \(x^2-2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\)hay x=1
Vậy: S={1}
c) Ta có: \(x+x^4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^3+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2-x+1>0\forall x\)
nên x(x+1)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={0;-1}
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
Bài 1: Tìm x biết a) x^3 - 4x^2 - x + 4= 0 b) x^3 - 3x^2 + 3x + 1=0 c) x^3 + 3x^2 - 4x - 12=0 d) (x-2)^2 - 4x +8 =0
a: \(x^3-4x^2-x+4=0\)
=>\(\left(x^3-4x^2\right)-\left(x-4\right)=0\)
=>\(x^2\left(x-4\right)-\left(x-4\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x-4\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=0\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4=0\\x^2-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x^2=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{2;1;-1\right\}\)
b: Sửa đề: \(x^3+3x^2+3x+1=0\)
=>\(x^3+3\cdot x^2\cdot1+3\cdot x\cdot1^2+1^3=0\)
=>\(\left(x+1\right)^3=0\)
=>x+1=0
=>x=-1
c: \(x^3+3x^2-4x-12=0\)
=>\(\left(x^3+3x^2\right)-\left(4x+12\right)=0\)
=>\(x^2\cdot\left(x+3\right)-4\left(x+3\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2-4\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x-2=0\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
d: \(\left(x-2\right)^2-4x+8=0\)
=>\(\left(x-2\right)^2-\left(4x-8\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x-2\right)^2-4\left(x-2\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x-2\right)\left(x-2-4\right)=0\)
=>(x-2)(x-6)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x-6=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1. Tính:
a) 12 - 6;
b) 23 - ( -35);
c) (-145)-(-254).
2. Tính:
a) [(-3)-4]+8;
b) (-2) - (-4)-5;
c) 0 - (-2)+6.
a) 12 - 6 = 6
b) 23 - (-35) = 58
c) = 109
Bài 2: a) = 1
b) -3
c) = 8
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)