Cho biểu thức f(x)=\(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{2}{x+4}-\frac{3}{x+3}\). Tập hợp tất cả các giá trị của x thỏa mãn bất phương trình f(x)<0 là?

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Cho biểu thức f(x) = (x + 5)(3 - x). Tập hợp tất cả các giá trị của x thỏa mãn bất phương trình f(x) ≤ 0 là
A. x ∈ (- ∞ ;5) ∪ (3;+ ∞ )
B. x ∈ (3;+ ∞ )
C. x ∈ (-5;3)
D. x ∈ (- ∞ ;-5] ∪ [3;+ ∞ )
Chọn D.
Để f(x) ≤ 0 thì (x + 5)(3 - x) < 0
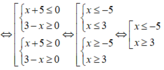
Vậy x ∈ (- ∞ ;-5] ∪ [3;+ ∞ ).
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1.cho biểu thức f(x) = \(\frac{4x-12}{x^2-4x}\) . tập hợp tất cả các giá trị của x thỏa mãn f(x) không dương
1. Cho biểu thức f(x) = 2x - 4. Tập hợp tất cả các giá trị của x để f(x) >= 0
2. Cho biểu thức f(x) = (x +5)(3-x). Tập hợp tất cả các giá trị của x thoả mãn bất phương trình f(x) <= 0
6. Cho biểu thức f(x) = 1/ 3x -6 . Tập hợp tất cả các giá trị của x để f(x) <= 0
1/ \(f\left(x\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow2x-4\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge2\)
2/ \(f\left(x\right)\le0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(3-x\right)\le0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge-5\\x\ge3\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le-5\\x\le3\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge3\\x\le-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
6/ ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne2\)
\(f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{3x-6}\le0\Leftrightarrow3x-6< 0\Leftrightarrow x< 2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho biểu thức f(x)=\(\frac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)}{x^2-1}\). Hỏi có tất cả bao nhiêu giá trị nguyên âm của x thỏa mãn bất phương trình f(x)<1?
Bài 1: Tìm tất cả các cặp số nguyên (x;y) thỏa mãn: x2 - 2xy - x + y + 3 = 0
Bài 2: Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên: ( y2+1 )( 2x2+x+1) = x+5
Bài 3: Cho các số thực dương a,b thỏa mãn a + b = 2.
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức : P = \(\frac{a}{\sqrt{4-a^2}}+\frac{b}{\sqrt{4-b^2}}\)
1. Ta có: \(x^2-2xy-x+y+3=0\)
<=> \(x^2-2xy-2.x.\frac{1}{2}+2.y.\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{4}+y^2-y^2-\frac{1}{4}+3=0\)
<=> \(\left(x-y-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-y^2=-\frac{11}{4}\)
<=> \(\left(x-2y-\frac{1}{2}\right)\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)=-\frac{11}{4}\)
<=> \(\left(2x-4y-1\right)\left(2x-1\right)=-11\)
Th1: \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x-4y-1=11\\2x-1=-1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=0\\y=-3\end{cases}}\)
Th2: \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x-4y-1=-11\\2x-1=1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\y=3\end{cases}}\)
Th3: \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x-4y-1=1\\2x-1=-11\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=-5\\y=-3\end{cases}}\)
Th4: \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x-4y-1=-1\\2x-1=11\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=6\\y=3\end{cases}}\)
Kết luận:...
2. \(y^2+1\ge1>0;2x^2+x+1>0\) với mọi x; y
=> x + 5 > 0
=> \(y^2+1=\frac{x+5}{2x^2+x+1}\ge1\)
<=> \(x+5\ge2x^2+x+1\)
<=> \(x^2\le2\)
Vì x nguyên => x = 0 ; x = 1; x = -1
Với x = 0 ta có: \(y^2+1=5\Leftrightarrow y=\pm2\)
Với x = 1 ta có: \(y^2+1=\frac{3}{2}\)loại vì y nguyên
Với x = -1 ta có: \(y^2+1=2\Leftrightarrow y=\pm1\)
Vậy Phương trình có 4 nghiệm:...
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Tập hợp tất cả các giá trị x thỏa mãn đồng thời hai bất phương trình 2x + 1 < x + 3 và \(5x\ge x-16\) là
Xem chi tiết
Ta có bất phương trình thứ nhất:
\(2x+1< x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-x< 3-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\cdot\left(2-1\right)< 2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 2\) (1)
Bất phương trình thứ hai:
\(5x\ge x-16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-x\ge-16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x\ge-16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge-4\) (2)
Từ (1) và (2) ta có:
\(-4\le x< 2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
2x+1<x+3 và 5x>=x-16
=>2x-x<3-1 và 5x-x>=-16
=>x<2 và x>=-4
=>-4<=x<2
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cho biểu thức:Pfrac{2+sqrt{x}}{2-sqrt{x}}-frac{2-sqrt{x}}{2+sqrt{x}}-frac{4x}{x-4}1, Tìm điều kiện xác định của biểu thức P. Rút gọn biểu thức P2, Tìm x để P 23, Tính giá trị của biểu thưc P tại x thỏa mãn left(sqrt{x}-2right)left(2sqrt{x}-1right)04. Tìm giá trị x để Pfrac{sqrt{x}+3}{2sqrt{x}-1}5. Tìm tất cả các giá trị nguyên của x để biểu thức P nhận giá trị nguyên
Đọc tiếp
Cho biểu thức:
\(P=\frac{2+\sqrt{x}}{2-\sqrt{x}}-\frac{2-\sqrt{x}}{2+\sqrt{x}}-\frac{4x}{x-4}\)
1, Tìm điều kiện xác định của biểu thức P. Rút gọn biểu thức P
2, Tìm x để P = 2
3, Tính giá trị của biểu thưc P tại x thỏa mãn \(\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(2\sqrt{x}-1\right)=0\)
4. Tìm giá trị x để \(P=\frac{\sqrt{x}+3}{2\sqrt{x}-1}\)
5. Tìm tất cả các giá trị nguyên của x để biểu thức P nhận giá trị nguyên
1) \(ĐKXĐ:\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge0\\x\ne4\end{cases}}\)
\(P=\frac{2+\sqrt{x}}{2-\sqrt{x}}-\frac{2-\sqrt{x}}{2+\sqrt{x}}-\frac{4x}{x-4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P=\frac{\left(2+\sqrt{x}\right)^2-\left(2-\sqrt{x}\right)^2+4x}{\left(2+\sqrt{x}\right)\left(2-\sqrt{x}\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P=\frac{4+4\sqrt{x}+x-4+4\sqrt{x}-x+4x}{\left(2+\sqrt{x}\right)\left(2-\sqrt{x}\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P=\frac{4x+8\sqrt{x}}{\left(2+\sqrt{x}\right)\left(2-\sqrt{x}\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P=\frac{4\sqrt{x}}{2-\sqrt{x}}\)
2) Để \(P=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{4\sqrt{x}}{2-\sqrt{x}}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\sqrt{x}=4-2\sqrt{x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6\sqrt{x}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=\frac{2}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{4}{9}\)
Vậy để \(P=2\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{4}{9}\)
3) Khi \(\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(2\sqrt{x}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\sqrt{x}-2=0\\2\sqrt{x}-1==0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\sqrt{x}=2\\\sqrt{x}=\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=4\left(ktm\right)\\x=\frac{1}{4}\left(tm\right)\end{cases}}\)
Thay \(x=\frac{1}{4}\)vào P, ta được :
\(\Leftrightarrow P=\frac{4\sqrt{\frac{1}{4}}}{2-\sqrt{\frac{1}{4}}}=\frac{4\cdot\frac{1}{2}}{2-\frac{1}{2}}=\frac{2}{\frac{3}{2}}=\frac{4}{3}\)
4) Để \(P=\frac{\sqrt{x}+3}{2\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{4\sqrt{x}}{2-\sqrt{x}}=\frac{\sqrt{x}+3}{2\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x-4\sqrt{x}=-x-\sqrt{x}+6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x-3\sqrt{x}-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-\sqrt{x}-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=3x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=9x^2-12x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2-13x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(9x-4\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}9x-4=0\\x-1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{4}{9}\\x=1\end{cases}}\)
Thử lại ta được kết quá : \(x=\frac{4}{9}\left(ktm\right)\); \(x=1\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy để \(P=\frac{\sqrt{x}+3}{2\sqrt{x}-1}\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
5) Để biểu thức nhận giá trị nguyên
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{4\sqrt{x}}{2-\sqrt{x}}\inℤ\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\sqrt{x}⋮2-\sqrt{x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4\left(2-\sqrt{x}\right)+8⋮2-\sqrt{x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8⋮2-\sqrt{x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2-\sqrt{x}\inƯ\left(8\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2;\pm4;\pm8\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\in\left\{1;3;0;4;-2;6;-6;10\right\}\)
Ta loại các giá trị < 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\in\left\{1;3;0;4;6;10\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{1;9;0;16;36;100\right\}\)
Vậy để \(P\inℤ\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{1;9;0;16;36;100\right\}\)
\(\)
1. Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức 7lx-3l-l4x+8l-l2-3xl2. Cho hàm số f(x) xác định với mọi x varepsilonQ. Cho f(a+b) f(a.b) với mọi a, b và f(2011) 11. Tìm f(2012)3.Cho hàm số f thỏa mãn f(1) 1; f(2) 3; f(n) +f(n+2) 2f(n+1) với mọi số nguyên dương n. Tính f(1) + f(2) + f(3)+...+f(30)4. Tính giá trị của biểu thức left(frac{3}{4}-81right)left(frac{^{3^2}}{5}-81right)left(frac{3}{6}^3-81right)...left(frac{3}{2014}^{2011}-81right)5. Đa thức P(x) cộng với đa thức Q(x) x^3-2x^2-1 được đa thức ^...
Đọc tiếp
1. Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức 7lx-3l-l4x+8l-l2-3xl
2. Cho hàm số f(x) xác định với mọi x \(\varepsilon\)Q. Cho f(a+b) =f(a.b) với mọi a, b và f(2011) = 11. Tìm f(2012)
3.Cho hàm số f thỏa mãn f(1) =1; f(2) = 3; f(n) +f(n+2) = 2f(n+1) với mọi số nguyên dương n. Tính f(1) + f(2) + f(3)+...+f(30)
4. Tính giá trị của biểu thức \(\left(\frac{3}{4}-81\right)\left(\frac{^{3^2}}{5}-81\right)\left(\frac{3}{6}^3-81\right)...\left(\frac{3}{2014}^{2011}-81\right)\)
5. Đa thức P(x) cộng với đa thức Q(x) = \(x^3-2x^2-1\) được đa thức \(^{x^2}\). Tìm hệ số tự do của P(x)
6. Cho a, b, c là các số thỏa mãn điều kiện \(\frac{2a-b}{a+b}=\frac{b-a+c}{2a-3}=\frac{2}{3}\). Tính \(\frac{\left(5b+4a\right)^5}{\left(5b+4a\right)^2\left(a+3c\right)^3}\)
4. (3/4-81)(3^2/5-81)(3^3/6-81)....(3^6/9-81).....(3^2011/2014-81)
mà 3^6/9-81=0 => (3/4-81)(3^2/5-81)....(3^2011/2014-81)=0
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm giá trị nguyên của \(x\)thỏa mãn cả 2 bất phương trình :
\(\frac{2x+1}{6}-\frac{x-2}{9}>x-3\)và \(x-\frac{x-3}{4}\ge3-\frac{x-3}{12}\)


















