Giải phương trình: x4-5x3-x2+8x+4 = 0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải các phương trình sau:a)
x
+
3
3
−
x
−
1
3
0
;
b)
x
4
+
x
2
−
2
0
;
c)
x
3...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) x + 3 3 − x − 1 3 = 0 ;
b) x 4 + x 2 − 2 = 0 ;
c) x 3 + 3 x 2 + 6 x + 4 = 0 ;
d) x 3 − 6 x 2 + 8 x = 0 .
a) Cách 1: Khai triển HĐT rút gọn được 3 x 2 + 6x + 7 = 0
Vì (3( x 2 + 2x + 1) + 4 < 0 với mọi x nên giải được x ∈ ∅
Cách 2. Chuyển vế đưa về ( x + 3 ) 3 = ( x - 1 ) 3 Û x + 3 = x - 1
Từ đó tìm được x ∈ ∅
b) Đặt x 2 = t với t ≥ 0 ta được t 2 + t - 2 = 0
Giải ra ta được t = 1 (TM) hoặc t = -2 (KTM)
Từ đó tìm được x = ± 1
c) Biến đổi được ![]()
d) Biến đổi về dạng x(x - 2) (x - 4) = 0. Tìm được x ∈ {0; 2; 4}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình sau:
a. (9x2-4)(x+1) = (3x+2) (x2-1)
b. (x-1)2-1+x2 = (1-x)(x+3)
c. (x2-1)(x+2)(x-3) = (x-1)(x2-4)(x+5)
d. x4+x3+x+1=0
e. x3-7x+6 = 0
f. x4-4x3+12x-9 = 0
g. x5-5x3+4x = 0
h. x4-4x3+3x2+4x-4 = 0
m.n jup vs
Giải các phương trình sau:a, (9x2 - 4)(x + 1) (3x +2)(x2 - 1)b, (x - 1)2 - 1 + x2 (1 - x)(x + 3)c, (x2 - 1)(x + 2)(x - 3) (x - 1)(x2 - 4)(x + 5)d, x4 + x3 + x + 1 0e, x3 - 7x + 6 0f, x4 - 4x3 + 12x - 9 0g, x5- 5x3 + 4x 0h, x4 - 4x3 + 3x2 + 4x - 4 0
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình sau:
a, (9x2 - 4)(x + 1) = (3x +2)(x2 - 1)
b, (x - 1)2 - 1 + x2 = (1 - x)(x + 3)
c, (x2 - 1)(x + 2)(x - 3) = (x - 1)(x2 - 4)(x + 5)
d, x4 + x3 + x + 1 = 0
e, x3 - 7x + 6 = 0
f, x4 - 4x3 + 12x - 9 = 0
g, x5- 5x3 + 4x = 0
h, x4 - 4x3 + 3x2 + 4x - 4 = 0
a, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(3x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(\left(9x^2-4\right)-\left(\left(3x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(9x^2-4-\left(3x^2-x-2\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(9x^2-4-3x^2+x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x^2+x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)=0;3x^2+x-2=0\)
=> x=-1
với \(3x^2+x-2=0\)
ta sử dụng công thức bậc 2 suy ra : \(x=\dfrac{2}{3};x=-1\)
Vậy ghiệm của pt trên \(S\in\left\{-1;\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1-1+x^2=x+3-x^2-3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-2x=-x^2-2x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2=3\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left[\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(x+5\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x-3-x^2-3x+10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(-5x+7\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;-2;\dfrac{7}{5}\right\}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Phương trình x 4 − 5 x 3 + 8 x 2 − 10 x + 4 = 0 có bao nhiêu nghiệm nguyên?
A. 4
B. 1
C. 2
D. 0
x 4 − 5 x 3 + 8 x 2 − 10 x + 4 = 0 ⇔ ( x 4 + 4 x 2 + 4 ) − 5 x 3 + 4 x 2 − 10 x = 0
⇔ x 2 + 2 2 − 5 x 3 + 10 x + 4 x 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 + 2 2 − 5 x x 2 + 2 + 4 x 2 = 0
Đặt t = x 2 + 2 ta được t 2 − 5 t x + 4 x 2 = 0 ⇔ t − x t − 4 x = 0
Hay phương trình đã cho ⇔ x 2 − x + 2 x 2 − 4 x + 2 = 0
⇔ x 2 − x + 2 = 0 ( V N ) x 2 − 4 x + 2 = 0 ⇔ x = 2 ± 2
Vậy phương trình không có nghiệm nguyên
Đáp án cần chọn là: D
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình:
a) 1,2x3 – x2 – 0,2x = 0;
b) 5x3 – x2 – 5x + 1 = 0.
a) 1,2x3 – x2 – 0,2x = 0
⇔ 0,2x.(6x2 – 5x – 1) = 0
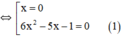
Giải (1): 6x2 – 5x – 1 = 0
có a = 6; b = -5; c = -1
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ (1) có hai nghiệm x1 = 1 và x2 = c/a = -1/6.
Vậy phương trình ban đầu có tập nghiệm 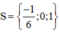
b) 5x3 – x2 – 5x + 1 = 0
⇔ x2(5x – 1) – (5x – 1) = 0
⇔ (x2 – 1)(5x – 1) = 0
⇔ (x – 1)(x + 1)(5x – 1) = 0
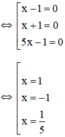
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 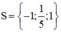
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình: 5x3 – x2 – 5x + 1 = 0
5x3 – x2 – 5x + 1 = 0
⇔ x2(5x – 1) – (5x – 1) = 0
⇔ (x2 – 1)(5x – 1) = 0
⇔ (x – 1)(x + 1)(5x – 1) = 0
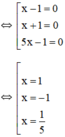
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 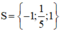
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình dưới đây1) x2 - 9 (x - 3)(5x +2)2) x3 - 1 (x - 1)(x2 - 2x +16)3) 4x2 (x - 1) - x + 1 04) x3 + 4x2 - 9x - 36 05) (3x + 5)2 (x - 1)26) 9 (2x + 1)2 4 (x - 5)27) x2 + 2x 158) x4 + 5x3 + 4x2 09) (x2 - 4) - (x - 2)(3 - 2x) 010) (3x + 2)(x2 - 1) (9x2 - 4) (x + 1)11) (3x - 1)(x2 + 2) (3x - 1)(7x - 10)12) (2x2 + 1) (4x - 3) (x - 12)(2x2 + 1)
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình dưới đây
1) x2 - 9 = (x - 3)(5x +2)
2) x3 - 1 = (x - 1)(x2 - 2x +16)
3) 4x2 (x - 1) - x + 1 = 0
4) x3 + 4x2 - 9x - 36 = 0
5) (3x + 5)2 = (x - 1)2
6) 9 (2x + 1)2 = 4 (x - 5)2
7) x2 + 2x = 15
8) x4 + 5x3 + 4x2 = 0
9) (x2 - 4) - (x - 2)(3 - 2x) = 0
10) (3x + 2)(x2 - 1) = (9x2 - 4) (x + 1)
11) (3x - 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x - 1)(7x - 10)
12) (2x2 + 1) (4x - 3) = (x - 12)(2x2 + 1)
1: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(5x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(-4x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{3;\dfrac{1}{4}\right\}\)
2: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1-x^2+2x-16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-15\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;5\right\}\)
3: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;\dfrac{1}{2};-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
4: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+4\right)-9\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-4;3;-3\right\}\)
5: \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+5=x-1\\3x+5=1-x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-6\\4x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
6: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3\right)^2-\left(2x-10\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3-2x+10\right)\left(6x+3+2x-10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+13\right)\left(8x-7\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{13}{4};\dfrac{7}{8}\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(5x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3=5x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=5\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
2.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+1=x^2-2x+16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=15\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
3.
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{1}{2};x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
7.
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
8.\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+x^3+4x^3+4x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x+1\right)+4x^2\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^3+4x^2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=0;x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
9.\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2=3-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Gi ải các phương trình sau
e) x3-7x+6=0
f) x4-4x3+12x-9=0
g)x5-5x3+4x=0
h) x4-4x3+3x2+4x-4=0
a.
\(x^3-7x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-3x^2+2x+3x^2-9x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-3x+2\right)+3\left(x^2-3x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x-2x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[x\left(x-1\right)-2\left(x-1\right)\right]\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
f.
\(x^4-4x^3+12x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-4x^3+3x^2-3x^2+12x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-4x+3\right)-3\left(x^2-4x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-4x+3\right)\left(x^2-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x-3x+3\right)\left(x^2-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[x\left(x-1\right)-3\left(x-1\right)\right]\left(x^2-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2-3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=3\\x=\pm\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
g.
\(x^5-5x^3+4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^4-5x^2+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^4-x^2-4x^2+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left[x^2\left(x^2-1\right)-4\left(x^2-1\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\pm1\\x=\pm2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Giải các phương trình: 2 x 4 + 2 2 x 3 + (1 - 3 2 ) x 2 - 3x - 4 = 0
Giải các phương trình trùng phương x 4 -8 x 2 – 9 =0
Đặt m = x 2 .Điều kiện m ≥ 0
Ta có: x 4 -8 x 2 – 9 =0 ⇔ m 2 -8m -9 =0
Phương trình m 2 - 8m - 9 = 0 có hệ số a = 1,b = -8,c = -9 nên có dạng a – b + c = 0
suy ra: m 1 = -1 (loại) , m 2 = -(-9)/1 =9
Ta có: x 2 =9 ⇒ x= ± 3
Vậy phương trình đã cho có 2 nghiệm : x 1 =3 ; x 2 =-3
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)














