2x2 (4x3 + 2x) + (x2 - 2) (-2x)3 = 20

Những câu hỏi liên quan
tìm x , biết
a, x ( x -1 ) - x2 + 2x = 5
b, 4x3 - 36x = 0
c, 2x2 - 2x = ( x - 1 )2
d, ( x - 7 ) ( x2- 9x + 20 ) ( x - 2 ) = 72
giúp emmm
a) \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-x^2+2x=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
b) \(\Leftrightarrow4x\left(x^2-9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0
\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=0\\x-3=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy x = 0 , x = 3 hoặc x = -3
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(a,\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-x^2+2x=5\\ \Leftrightarrow x=5\\ b,\Leftrightarrow4x\left(x^2-9\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x-x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\\ d,\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-9x+14\right)\left(x^2-9x+20\right)-72=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-9x+17\right)^2-3^2-72=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-9x+17\right)^2-81=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-9x+17-9\right)\left(x^2-9x+17+9\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-8\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-9x+26\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\x=1\\\left(x-\dfrac{9}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{23}{4}=0\left(vô.n_0\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
(6x4-4x3+x2+x):(2x2+2x+1)
\((6x^4-4x^3+x^2+x):(2x^2-2x+1)=3x^2+x\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1) tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của
D= 4x-x2+3
E=2x-2x2-5
F=-x2-4x+20
2) chứng minh biểu thức không phụ vào biến
A= (2x+3)(4x2-6x+9)-2(4x3-1)
B=(x+3)3-(x+9)(x2+27)
1. Đề bài sai, các biểu thức này chỉ có giá trị lớn nhất, không có giá trị nhỏ nhất
2.
\(A=\left(2x\right)^3-3^3-\left(8x^3+2\right)\)
\(=8x^3-27-8x^3-2\)
\(=-29\)
\(B=x^3+9x^2+27x+27-\left(x^3+9x^2+27x+243\right)\)
\(=27-243=-216\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
sửa đề lại thành tìm Max nhé1, vì mấy ý này ko có min
\(1,=>D=-\left(x^2-4x-3\right)=-\left(x^2-2.2x+4-7\right)\)
\(=-[\left(x-2\right)^2-7]=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\)
dấu"=" xảy ra<=>x=2
2, \(E=-2\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)=-2[x^2-2.\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{9}{4}]\)
\(=-2[\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{9}{4}]\le-\dfrac{9}{2}\) dấu"=" xảy ra<=>x=1/2
3, \(F=-\left(x^2+4x-20\right)=-\left(x^2+2.2x+4-24\right)\)
\(=-[\left(x+2\right)^2-24]\le24\) dấu"=" xảy ra<=>x=-2
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(D=-x^2+4x+3\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x-3\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x+4-7\right)\)
\(=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=2
c) Ta có: \(F=-x^2-4x+20\)
\(=-\left(x^2+4x-20\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2+4x+4-24\right)\)
\(=-\left(x+2\right)^2+24\le24\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=-2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Cho biểu thức P 1+ 3/x2+5x+6 : ( 8x2/ 4x3-8x2 - 3x/ 3x2-12 -1/x+2)A) Rút gọn PB) Tìm các giá trị của x để P 0; P 1C) Tìm cã giá trị của x để P 0Cho biểu thứcQ (2x-x2/ 2x2 +8 - 2x2/ 3x3-2x2+4x-8) (2/x2 + 1-x/x)A) Rút gọn QB) Tìm giá trị nguyên của x để Q có giá trị nguyên
Đọc tiếp
Cho biểu thức P= 1+ 3/x2+5x+6 : ( 8x2/ 4x3-8x2 - 3x/ 3x2-12 -1/x+2)
A) Rút gọn P
B) Tìm các giá trị của x để P= 0; P= 1
C) Tìm cã giá trị của x để P> 0
Cho biểu thức
Q= (2x-x2/ 2x2 +8 - 2x2/ 3x3-2x2+4x-8) (2/x2 + 1-x/x)
A) Rút gọn Q
B) Tìm giá trị nguyên của x để Q có giá trị nguyên
Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(P=1+\dfrac{3}{x^2+5x+6}:\left(\dfrac{8x^2}{4x^3-8x^2}-\dfrac{3x}{3x^2-12}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\left(\dfrac{8x^2}{4x^2\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{3x}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\left(\dfrac{4}{x-2}-\dfrac{x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\dfrac{4\left(x+2\right)-x-\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{4x+8-x-x+2}\)
\(=1+3\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)+3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+10x+6x+30+3x-6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+19x-6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
6). – x2 y(xy2 – 1/2 xy + 3/4 x2 y2 )7). (3xy – x2 + y). 2/3 x2 y8). (4x3 – 5xy + 2x)( – 1/2 xy)9). 2x2 (x2 + 3x + 1/2 )10). – 3/2 x4 y2 (6x4 − 10/9 x2 y3 – y5 )11). 2 3 x3 (x + x2 – 3/4 x5 )12). 2xy2 (xy + 3x2 y – 2/3 xy3 )13). 3x(2x3 – 1/3 x2 – 4x)14). 3/5 x3 y5 (7x4 + 5x2 y − 10/21 x4 y3 –y4 )
Đọc tiếp
6). – x2 y(xy2 – 1/2 xy + 3/4 x2 y2 )
7). (3xy – x2 + y). 2/3 x2 y
8). (4x3 – 5xy + 2x)( – 1/2 xy)
9). 2x2 (x2 + 3x + 1/2 )
10). – 3/2 x4 y2 (6x4 − 10/9 x2 y3 – y5 )
11). 2 3 x3 (x + x2 – 3/4 x5 )
12). 2xy2 (xy + 3x2 y – 2/3 xy3 )
13). 3x(2x3 – 1/3 x2 – 4x)
14). 3/5 x3 y5 (7x4 + 5x2 y − 10/21 x4 y3 –y4 )
6: \(-x^2y\left(xy^2-\dfrac{1}{2}xy+\dfrac{3}{4}x^2y^2\right)\)
\(=-x^3y^3+\dfrac{1}{2}x^3y^2-\dfrac{3}{4}x^4y^3\)
7: \(\dfrac{2}{3}x^2y\cdot\left(3xy-x^2+y\right)\)
\(=2x^3y^2-\dfrac{2}{3}x^4y+\dfrac{2}{3}x^2y^2\)
8: \(-\dfrac{1}{2}xy\left(4x^3-5xy+2x\right)\)
\(=-2x^4y+\dfrac{5}{2}x^2y^2-x^2y\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
9: \(2x^2\left(x^2+3x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=2x^4+6x^3+x^2\)
10: \(-\dfrac{3}{2}x^4y^2\left(6x^4-\dfrac{10}{9}x^2y^3-y^5\right)\)
\(=-9x^8y^2+\dfrac{5}{3}x^6y^5+\dfrac{3}{2}x^4y^7\)
11: \(\dfrac{2}{3}x^3\left(x+x^2-\dfrac{3}{4}x^5\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}x^3+\dfrac{2}{3}x^5-\dfrac{1}{2}x^8\)
12: \(2xy^2\left(xy+3x^2y-\dfrac{2}{3}xy^3\right)=2x^2y^3+6x^3y^3-\dfrac{4}{3}x^2y^5\)
13: \(3x\left(2x^3-\dfrac{1}{3}x^2-4x\right)=6x^4-x^3-12x^2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Thực hiện phép chia: (2x4 – 4x3 + 5x2 + 2x – 3):(2x2 - 1)
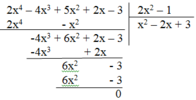
Vậy (2x4 – 4x3 + 5x2 + 2x – 3) : (2x2 – 1) = x2 – 2x + 3.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1) Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
a) 2x4-4x3+2x2
b) 2x2-2xy+5x-5y
2) Tìm x, biết:
a) 4x(x-3)-x+3=0
b)(2x-3)2-(x+1)2=0
1.
a) \(2x^4-4x^3+2x^2\)
\(=2x^2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(=2x^2\left(x-1\right)^2\)
b) \(2x^2-2xy+5x-5y\)
\(=\left(2x^2-2xy\right)+\left(5x-5y\right)\)
\(=2x\left(x-y\right)+5\left(x-y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\cdot\left(2x+5\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
2 .
a,
\(4x\left(x-3\right)-x+3=0\)
⇒\(4x\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-3\right)=0\)
⇒\(\left(x-3\right)\left(4x-1\right)=0\)
⇒\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\4x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\4x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy \(x\in\left\{3;\dfrac{1}{4}\right\}\)
b,
\(\)\(\left(2x-3\right)^2-\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
⇒\(\left(2x-3-x-1\right)\left(2x-3+x+1\right)\) = 0
⇒\(\left(x-4\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4=0\\3x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\3x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy \(x\in\left\{4;\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
CÂU1 f(x)=x5-4x3+x2-2x+1 CÂU 2 G(X)=X5-2X4+X2-5X+3 CÂU 3H(X)=X2-3X2+ 2X-5
Tính:
a) ( 5x3 - x - 1/2 )
b) ( 3xy - x2 + y ) 2/3 x2y
c) ( 4x3 - 5xy + 2x ) ( -1/2xy )
d) ( x2 - 2x + 1 ) ( x - 1)
`@` `\text {Ans}`
`\downarrow`
`a)`
`5x^3 - x - 1/2`
Đã thu gọn?
`b)`
`(3xy - x^2 + y) * 2/3x^2y`
`= 3xy * 2/3 x^2y - x^2* 2/3x^2y + y*2/3x^2y`
`= 2x^3y^2 - 2/3x^4y + 2/3x^2y^2`
`c)`
`(4x^3 - 5xy +2x) (-1/2xy)`
`= 4x^3* (-1/2xy) - 5xy* (-1/2xy) + 2x * (-1/2xy)`
`= -2x^4y + 5/2x^2y^2 - x^2y`
`d)`
`(x^2 - 2x +1) (x-1)`
`= x^2(x-1) - 2x(x-1) + x - 1`
`= x^3 - x^2 - 2x^2 + 2x + x -1`
`= x^3 -3x^2 + 3x - 1`
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
d: =(x-1)^3=x^3-3x^2+3x-1
c: =-2x^4y+5/2x^2y^2-x^2y
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)



























