Giải các pt sau: a,(x2+5x+6)(x2+9x+20)=24
b,x4-24x=32
Giải các phương trình sau:
1/x2+5x+6 + 1/x2+7x+12 + 1/x2+9x+20 + 1/x2+11x+30 = 1/8
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)}+...+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{1}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x+3}-\dfrac{1}{x+4}+...+\dfrac{1}{x+5}-\dfrac{1}{x+6}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>1/x+2-1/x+6=1/8
=>\(\dfrac{x+6-x-2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>x^2+8x+12=32
=>x^2+8x-20=0
=>(x+10)(x-2)=0
=>x=-10 hoặc x=2
Khi thảo luận nhóm, một bạn ra đề bài: Hãy phân tích đa thức x4 - 9x3 + x2 - 9x thành nhân tử
Bạn Thái làm như sau:
x4 - 9x3 + x2 – 9x = x(x3 - 9x2 + x – 9).
Bạn Hà làm như sau:
x4 - 9x3 + x2 – 9x = (x4 - 9x3) + (x2 – 9x)
= x3(x – 9) + x(x – 9) = (x – 9)(x3 + x).
Bạn An làm như sau:
x4 - 9x3 + x2 – 9x = (x4 + x2) - (9x3 + 9x) = x2(x2 + 1) – 9x(x2 + 1)
= (x2 – 9x) (x2 + 1)= x(x – 9)(x2 + 1).
Hãy nêu ý kiến của em về lời giải của các bạn
Lời giải của các bạn đều thỏa mãn yêu cầu đề bài là phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
Giải các pt sau:
a) 3X2 + 8X + 4 = 0
b) X2 + 9X + 18 = 0
c) X2 + 12 + 32 = 0
a) \(\text{Δ}=8^2-4.3.4=16\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-8+4}{2.3}=-\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=\dfrac{-8-4}{2.3}=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(\text{Δ}=9^2-4.1.18=9\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-9+3}{2}=-3\\x=\dfrac{-9-3}{2}=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(x^2+12+32=0\)
\(x^2=-44\)
mà \(x^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\) pt vô nghiệm
Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử:
a) x 2 - 5x + 6; b) 3 x 2 + 9x - 30;
c) 3 x 2 - 5x - 2; d) x 2 -7xy + 10 y 2 ;
e) x 3 -7x-6; g) x 4 + 2 x 3 + 6x - 9;
h) x 2 -2x - y 2 +4y - 3.
a) (x - 2)(x - 3). b) 3(x - 2)(x + 5).
c) (x - 2)(3x + 1). d) (x-2y)(x - 5y).
e) (x + l)(x + 2)(x - 3). g) (x-1)(x + 3)( x 2 + 3).
h) (x + y - 3)(x - y + 1).
Tìm X:
a) 16x2-24x+9=25
b) x2+10x+9=0
c) x2-4x-12=0
d) x2-5x-6=0
e) 4x2-3x-1=0
f) x4+4x2-5=0
`a)16x^2-24x+9=25`
`<=>(4x-3)^2=25`
`+)4x-3=5`
`<=>4x=8<=>x=2`
`+)4x-3=-5`
`<=>4x=-2`
`<=>x=-1/2`
`b)x^2+10x+9=0`
`<=>x^2+x+9x+9=0`
`<=>x(x+1)+9(x+1)=0`
`<=>(x+1)(x+9)=0`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=-9\\x=-1\end{array} \right.\)
`c)x^2-4x-12=0`
`<=>x^2+2x-6x-12=0`
`<=>x(x+2)-6(x+2)=0`
`<=>(x+2)(x-6)=0`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=-2\\x=6\end{array} \right.\)
`d)x^2-5x-6=0`
`<=>x^2+x-6x-6=0`
`<=>x(x+1)-6(x+1)=0`
`<=>(x+1)(x-6)=0`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=6\\x=-1\end{array} \right.\)
`e)4x^2-3x-1=0`
`<=>4x^2-4x+x-1=0`
`<=>4x(x-1)+(x-1)=0`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=1\\x=-\dfrac14\end{array} \right.\)
`f)x^4+4x^2-5=0`
`<=>x^4-x^2+5x^2-5=0`
`<=>x^2(x^2-1)+5(x^2-1)=0`
`<=>(x^2-1)(x^2+5)=0`
Vì `x^2+5>=5>0`
`=>x^2-1=0<=>x^2=1`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=1\\x=-1\end{array} \right.\)
Xét sự đồng biến, nghịch biến của các hàm số:
a) y = 3 x 2 − 8 x 3
b) y = 16x + 2 x 2 − 16 x 3 /3 − x 4
c) y = x 3 − 6 x 2 + 9x
d) y = x 4 + 8 x 2 + 5
a) TXĐ: R
y′ = 6x − 24 x 2 = 6x(1 − 4x)
y' = 0 ⇔ 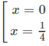
y' > 0 trên khoảng (0; 1/4) , suy ra y đồng biến trên khoảng (0; 1/4)
y' < 0 trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ; 0 ); (14; + ∞ ), suy ra y nghịch biến trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ;0 ); (14; + ∞ )
b) TXĐ: R
y′ = 16 + 4x − 16 x 2 − 4 x 3 = −4(x + 4)( x 2 − 1)
y' = 0 ⇔ 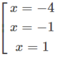
Bảng biến thiên:
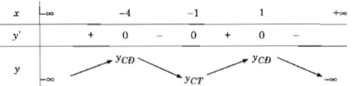
Vậy hàm số y đã cho đồng biến trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ; -4) và (-1; 1), nghịch biến trên các khoảng (-4; -1) và (1; + ∞ )
c) TXĐ: R
y′ = 3 x 2 − 12x + 9
y' = 0
y' > 0 trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ; 1), (3; + ∞ ) nên y đồng biến trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ; 1), (3; + ∞ )
y'< 0 trên khoảng (1; 3) nên y nghịch biến trên khoảng (1; 3)
d) TXĐ: R
y′ = 4 x 3 + 16 = 4x( x 2 + 4)
y' = 0 ⇔ 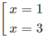
y' > 0 trên khoảng (0; + ∞ ) ⇒ y đồng biến trên khoảng (0; + ∞ )
y' < 0 trên khoảng ( - ∞ ; 0) ⇒ y nghịch biến trên khoảng ( - ∞ ; 0)
Bài 3: Giải phương trình:
a) x3+ 2x2 + x +2 = 0
b) x3 – x2 – 21x + 45 = 0
c) x3 + 3x2+4x + 2 = 0
d) x4+ x2 +6x – 8 = 0
e) (x2 + 1)2 = 4 ( 2x – 1 )
Bài 4: Giải phương trình:
a) ( x2-5x)2 + 10( x2 – 5x) + 24 = 0
b) ( x2 + 5x)2 - 2( x2 + 5x) = 24
c) ( x2 + x – 2)(x2 + x – 3) = 12
d) x ( x+1) (x2 + x + 1) = 42
Bài 1
a/ \(x\left(x^2+1\right)+2\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2+1\right)=0\Rightarrow x=-2\)
b/
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-6x^2+9x+5x^2-30x+45=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)^2+5\left(x-3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
1.
c/ \(\Leftrightarrow x^3+2x^2+2x+x^2+2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2+2x+2\right)+x^2+2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+2x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x^2+2x+2=0\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
d/
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+x^3-2x^2-x^3-x^2+2x+4x^2+4x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2+x-2\right)-x\left(x^2+x-2\right)+4\left(x^2+x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x+4\right)\left(x^2+x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-x+4=0\left(vn\right)\\x^2+x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 1:
e/ \(\Leftrightarrow x^4+2x^2-8x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-2x^3+x^2+2x^3-4x^2+2x+5x^2-10x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)^2+2x\left(x-1\right)^2+5\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+2x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+2x+5=0\left(vn\right)\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 2:
a/ Đặt \(x^2-5x=t\)
\(t^2+10t+24=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=-4\\t=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-5x=-4\\x^2-5x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-5x+4=0\\x^2-5x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=4\\x=2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 1: Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử
a. 1 - 4x2
b. 8 - 27x3
c. 27 + 27x + 9x 2 + x3
d. 2x3 + 4x2 + 2x
e. x2 - 5x - y2 + 5y
f. x2 - 6x + 9 - y2
g. 10x (x - y) - 6y(y - x)
h. x2 - 4x - 5
i. x4 - y4
Bài 2: Tìm x, biết
a. 5(x - 2) = x - 2
b. 3(x - 5) = 5 - x
c. (x +2)2 - (x+ 2) (x - 2) = 0
Bài 3: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức
a. A = x2 - 6x + 11
b. B = 4x2 - 20x + 101
c. C = -x2 - 4xy + 5y2 + 10x - 22y + 28
a.
\(1-4x^2=\left(1-2x\right)\left(1+2x\right)\)
b.
\(8-27x^3=\left(2\right)^3-\left(3x\right)^3=\left(2-3x\right)\left(4+6x+9x^2\right)\)
c.
\(27+27x+9x^2+x^3=x^3+3.x^2.3+3.3^2.x+3^3\)
\(=\left(x+3\right)^3\)
d.
\(2x^3+4x^2+2x=2x\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=2x\left(x+1\right)^2\)
e.
\(x^2-y^2-5x+5y=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)-5\left(x-y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y-5\right)\)
f.
\(x^2-6x+9-y^2=\left(x-3\right)^2-y^2=\left(x-3-y\right)\left(x-3+y\right)\)
g. 10x(x-y)-6y(y-x)
=10x(x-y)+6y(x-y)
=(x-y)(10x+6y)
h.x2-4x-5
=(x-5)(x+1)
i.x4-y4 = (x2-y2)(x2+y2)
B2.
a.5(x-2)=x-2
⇔5(x-2)-(x-2)=0
⇔4(x-2)=0
⇔x=2
b.3(x-5)=5-x
⇔3(x-5)+(x-5)=0
⇔4(x-5)=0
⇔x=5
c.(x+2)2-(x+2)(x-2)=0
⇔(x+2)[(x+2)-(x-2)]=0
⇔4(x+2)=0
⇔x=-2
Giải các phương trình sau:
a) 2 x + 5 6 − 1 3 2 x + 5 x − 10 = 0 ;
b) 4 x − 1 x + 5 = x 2 − 25 ;
c) 3 x − 3 2 − x − 3 x + 2 4 = 0 ;
d) x x + 3 3 − x 4 x + 3 = 0 .