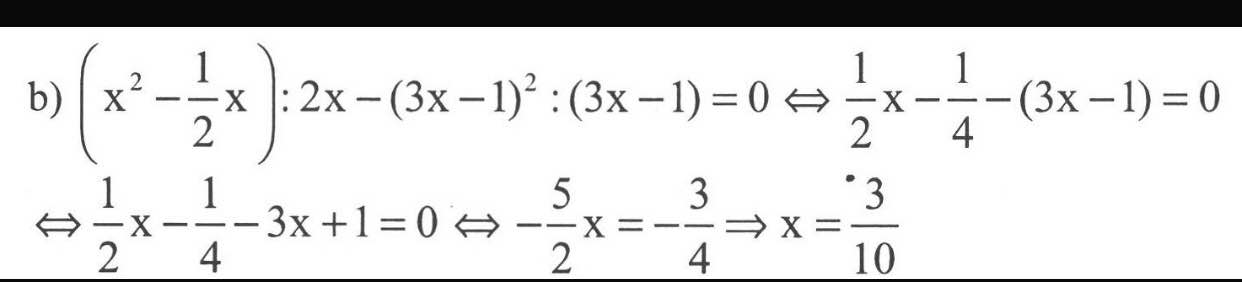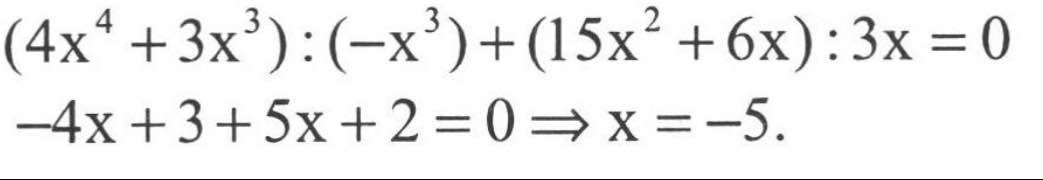(2x+1) (3x+2)-6x^2=0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
GIẢI CÁC PHƯƠNG TRÌNH SAU:
2x3+6x2+6x+1=0
X^3-3X^2+3X-3=0
2X^3+6X^2+6X+1=0
3X^3+18X^2+36X+23=0
Giai phường trình sau:a, 3x^2+2x-10 e, 4x^2-12x+50 i,2x^2+5x-30b,x^2-5x+60 f, 2x^2+5x+30 j,x^2+6x-160c,x^2-3x+20 g,x^2+x-20d,2x^2-6x+10 h, x^2-4x+30
Đọc tiếp
Giai phường trình sau:
a, \(3x^2+2x-1=0\) e, \(4x^2-12x+5=0\) i,\(2x^2+5x-3=0\)
b,\(x^2-5x+6=0\) f, \(2x^2+5x+3=0\) j,\(x^2+6x-16=0\)
c,\(x^2-3x+2=0\) g,\(x^2+x-2=0\)
d,\(2x^2-6x+1=0\) h, \(x^2-4x+3=0\)
a) Ta có: \(3x^2+2x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+3x-x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\3x=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-1;\dfrac{1}{3}\right\}\)
b) Ta có: \(x^2-5x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={2;3}
c) Ta có: \(x^2-3x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)-2\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={1;2}
d) Ta có: \(2x^2-6x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2-3x+\dfrac{1}{3}\right)=0\)
mà \(2\ne0\)
nên \(x^2-3x+\dfrac{1}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}+\dfrac{9}{4}-\dfrac{23}{12}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2=\dfrac{23}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{69}}{6}\\x-\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{-\sqrt{69}}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{9+\sqrt{69}}{6}\\x=\dfrac{9-\sqrt{69}}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{9+\sqrt{69}}{6};\dfrac{9-\sqrt{69}}{6}\right\}\)
e) Ta có: \(4x^2-12x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-10x-2x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(2x-5\right)-\left(2x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-5\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-5=0\\2x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=5\\2x=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{5}{2};\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
(x^2-1/2x):2x-(3x-1)^2.(3x-1)=0
(4x^4 + 3x3) : (-x^3) + (15x2 + 6x) : 3x =0
Ta có: \(\dfrac{4x^4+3x^3}{-x^3}+\dfrac{15x^2+6x}{3x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x-3+5x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\)
hay x=1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
I) THỰC HIỆN PHÉP TÍNH a) 2x(x^2-4y) b)3x^2(x+3y) c) -1/2x^2(x-3) d) (x+6)(2x-7)+x e) (x-5)(2x+3)+x II phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử a) 6x^2+3xy b) 8x^2-10xy c) 3x(x-1)-y(1-x) d) x^2-2xy+y^2-64 e) 2x^2+3x-5 f) 16x-5x^2-3 g) x^2-5x-6 IIITÌM X BIẾT a)2x+10 b) -3x-50 c) -6x+70 d)(x+6)(2x+1)0 e)2x^2+7x+30 f) (2x-3)(2x+1)0 g) 2x(x-5)-x(3+2x)26 h) 5x(x-1)x-1 IV TÌM GTNN,GTLN. a) tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất x^2-6x+10 2x^2-6x b) tìm giá trị lớn nhất 4x-x^2-5 4x-x^2+3
Đọc tiếp
I) THỰC HIỆN PHÉP TÍNH a) 2x(x^2-4y) b)3x^2(x+3y) c) -1/2x^2(x-3) d) (x+6)(2x-7)+x e) (x-5)(2x+3)+x II phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử a) 6x^2+3xy b) 8x^2-10xy c) 3x(x-1)-y(1-x) d) x^2-2xy+y^2-64 e) 2x^2+3x-5 f) 16x-5x^2-3 g) x^2-5x-6 IIITÌM X BIẾT a)2x+1=0 b) -3x-5=0 c) -6x+7=0 d)(x+6)(2x+1)=0 e)2x^2+7x+3=0 f) (2x-3)(2x+1)=0 g) 2x(x-5)-x(3+2x)=26 h) 5x(x-1)=x-1 IV TÌM GTNN,GTLN. a) tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất x^2-6x+10 2x^2-6x b) tìm giá trị lớn nhất 4x-x^2-5 4x-x^2+3
Giải như sau.
(1)+(2)⇔x2−2x+1+√x2−2x+5=y2+√y2+4⇔(x2−2x+5)+√x2−2x+5=y2+4+√y2+4⇔√y2+4=√x2−2x+5⇒x=3y(1)+(2)⇔x2−2x+1+x2−2x+5=y2+y2+4⇔(x2−2x+5)+x2−2x+5=y2+4+y2+4⇔y2+4=x2−2x+5⇒x=3y
⇔√y2+4=√x2−2x+5⇔y2+4=x2−2x+5, chỗ này do hàm số f(x)=t2+tf(x)=t2+t đồng biến ∀t≥0∀t≥0
Công việc còn lại là của bạn !
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(\left(x+6\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+6=0\\2x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-6\\x=-\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy....
hk tốt
^^
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a,4.|3x-1|=|6x-2|+|-1,5|
b,2024.|2x-1|=2025.|1-2x|-|-2|
c,|2x+1|+|3x-1|=0
c, |2\(x\) + 1| + |3\(x\) - 1| = 0
vì |2\(x\) + 1| ≥ 0; |3\(x\) - 1| = 0
⇒ |2\(x\) + 1| + |3\(x\) - 1| = 0
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=-1\\3x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(-\dfrac{1}{2}\) < \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Vậy \(x\) \(\in\) \(\varnothing\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a, Nếu 4.|3\(x\) - 1| = |6\(x\) - 2| + |-1,5|
4.|3\(x\) -1| - 2.|3\(x\) - 1| = 1,5
Nếu 3\(x\) - 1 ≥ 0 ⇒ \(x\) ≥ \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Ta có: 4.(3\(x\) - 1) - 2.(3\(x\) - 1) = 1,5
12\(x\) - 4 - 6\(x\) + 2 = 1,5
6\(x\) - 2 = 1,5
6\(x\) = 1,5 + 2
6\(x\) = 3,5
\(x\) = 3,5: 6
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{7}{12}\)
Nếu 3\(x\) - 1 < 0 ⇒ \(x\) < \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Ta có: - 4.(3\(x\) - 1) = - (6\(x\) - 2) + 1,5
-12\(x\) + 4 + 6\(x\) - 2 = 1,5
-6\(x\) + 2 = 1,5
6\(x\) = 2- 1,5
6\(x\) = 0,5
\(x\) = 0,5 : 6
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{1}{12}\)
Vậy \(x\) \(\in\) {\(\dfrac{1}{12}\); \(\dfrac{7}{12}\)}
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
b, 2024.|2\(x\) - 1| = 2025.|1 - 2\(x\)| - |-2|
2025.|1 - 2\(x\)| - 2024.|1 - 2\(x\)| = |-2|
|1 - 2\(x\)| = 2
Nếu 1 - 2\(x\) ≥ 0 ⇒ \(x\) ≥ \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
với \(x\) ≥ \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) ta có: 1 - 2\(x\) = 2 ⇒ 2\(x\) = -1 ⇒ \(x\) = - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) (1)
Nếu \(1-2x\) < 0 ⇒ 2\(x\) ≤ 1 ⇒ \(x\) < \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Với \(x\) < \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) ta có: -1 + 2\(x\) = 2 ⇒ 2\(x\) = 3 ⇒ \(x\) = \(\dfrac{3}{2}\) (2)
Kết hợp(1) và (2) ta có: \(x\) \(\in\) { - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\); \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
A=x+6x^2+7x^2-6x+1
A=(x^2)^2+2x^2.3x+9x^2-1x^2-6x+7
A=(x^2+3x)^2-2.(x^2+3x).1+1
A=(x^2+3x)^2>=0 với mọi x khi x^2=3x-1=0
Giải các phương trình sau
1. x^4+3x^3-2x^2-6x+4=0
2. x^4-3x^3-6x^2+3x+1=0
x4−3x3−2x2+6x+4=0x4−3x3−2x2+6x+4=0
⇔x4−2x3−2x2−x3+2x2+2x−2x2+4x+4=0⇔x4−2x3−2x2−x3+2x2+2x−2x2+4x+4=0
⇔x2(x2−2x−2)−x(x2−2x−2)−2(x2−2x−2)=0⇔x2(x2−2x−2)−x(x2−2x−2)−2(x2−2x−2)=0
⇔(x2−x−2)(x2−2x−2)=0⇔(x2−x−2)(x2−2x−2)=0
⇔(x+1)(x−2)(x−1−√3)(x−1+√3)=0⇔(x+1)(x−2)(x−1−3)(x−1+3)=0
⇔⎡⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢⎣x=−1x=2x=1+√3x=1−√3
tl
x4−3x3−2x2+6x+4=0x4−3x3−2x2+6x+4=0
⇔x4−2x3−2x2−x3+2x2+2x−2x2+4x+4=0⇔x4−2x3−2x2−x3+2x2+2x−2x2+4x+4=0
⇔x2(x2−2x−2)−x(x2−2x−2)−2(x2−2x−2)=0⇔x2(x2−2x−2)−x(x2−2x−2)−2(x2−2x−2)=0
⇔(x2−x−2)(x2−2x−2)=0⇔(x2−x−2)(x2−2x−2)=0
⇔(x+1)(x−2)(x−1−√3)(x−1+√3)=0⇔(x+1)(x−2)(x−1−3)(x−1+3)=0
⇔⎡⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢⎣x=−1x=2x=1+√3x=1−√3
^HT^
Ta thấy x=0 không là nghiệm của phương trình
chia cả 2 vế cho x^2 ta được:
PT <=> x^2-3x-6+3/x+1/(x^2)=0
<=> (x^2-2+1/(x^2))-3(x-1/x)-4=0
<=> (x-1/x)^2-3(x-1/x)-4=0
Đặt x-1/x=y
PT <=> y^2-3y-4=0
<=> y=-4 hoặc y=1
Tại y=-4 , ta có x+1/x+4=0
<=> x^2+4x+1=0
<=> x=-2+ √3 hoăc x=-2- √ 3
Tại y=1 ta có x^2-x-1=0
<=> x=(1- √ 5)/2 hoặc x=(1+ √5)/2
tim x bieta/(3x-5)(2x-1)-(x+2)(6x-1)0b/ (3x-5)(3x+2)-(3x-1)2-5c/(3x+2)(x-5)3(x-1)2-2d/ (x+1)2/3 - (x-2)2/2 2x+1/2 (x-3)2/6g/49x2(3x+2)2h/(3x-4)2-(2x-2)2-3(x-2)(2x-1)0i/ (x-2)(x2-2x+4)-x(x2+2)15k/ 6x2-7x-30m/(x+5)(x-3)+x2-250e/ x3+3x24x+12f/ (6x+7)2(3x+4)(x+1)6
Đọc tiếp
tim x biet
a/(3x-5)(2x-1)-(x+2)(6x-1)=0
b/ (3x-5)(3x+2)-(3x-1)2=-5
c/(3x+2)(x-5)=3(x-1)2-2
d/ (x+1)2/3 - (x-2)2/2 = 2x+1/2 (x-3)2/6
g/49x2=(3x+2)2
h/(3x-4)2-(2x-2)2-3(x-2)(2x-1)=0
i/ (x-2)(x2-2x+4)-x(x2+2)=15
k/ 6x2-7x-3=0
m/(x+5)(x-3)+x2-25=0
e/ x3+3x2=4x+12
f/ (6x+7)2(3x+4)(x+1)=6
giải pt:
a, \(2x^2-6x-1=\sqrt{4x+5}\)
b, \(18x^2+6x-29=\sqrt{12x+61}\)
c, \(4x^2-13x+5+\sqrt{3x+1}=0\)
c, \(4x^2-13x+5+\sqrt{3x+1}=0\)
c.
ĐLXĐ: \(x\ge-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(-\left(3x+1\right)+\sqrt{3x+1}+4x^2-10x+6=0\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{3x+1}=t\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow-t^2+t+4x^2-10x+6=0\)
\(\Delta=1+4\left(4x^2-10x+6\right)=\left(4x-5\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=\dfrac{-1+4x-5}{-2}=3-2x\\t=\dfrac{-1-4x+5}{-2}=2x-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{3x+1}=3-2x\left(x\le\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\\\sqrt{3x-1}=2x-2\left(x\ge1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+1=4x^2-12x+9\left(x\le\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\\3x-1=4x^2-8x+4\left(x\ge1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
b.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge-\dfrac{61}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow36x^2+12x-58-2\sqrt{12x+61}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(36x^2+24x+4\right)-\left(12x+61+2\sqrt{12x+61}+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+2\right)^2-\left(\sqrt{12x+61}+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+1-\sqrt{12x+61}\right)\left(6x+3+\sqrt{12x+61}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\) tương tự câu a
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge-\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-12x-2-2\sqrt{4x+5}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x^2-8x+4\right)-\left(4x+5+2\sqrt{4x+5}+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-2\right)^2-\left(\sqrt{4x+5}+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-2-\sqrt{4x+5}-1\right)\left(2x-2+\sqrt{4x+5}+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3-\sqrt{4x+5}\right)\left(2x-1+\sqrt{4x+5}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{4x+5}=2x-3\left(x\ge\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\\\sqrt{4x+5}=1-2x\left(x\le\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x+5=4x^2-12x+9\left(x\ge\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\\4x+5=4x^2-4x+1\left(x\le\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)