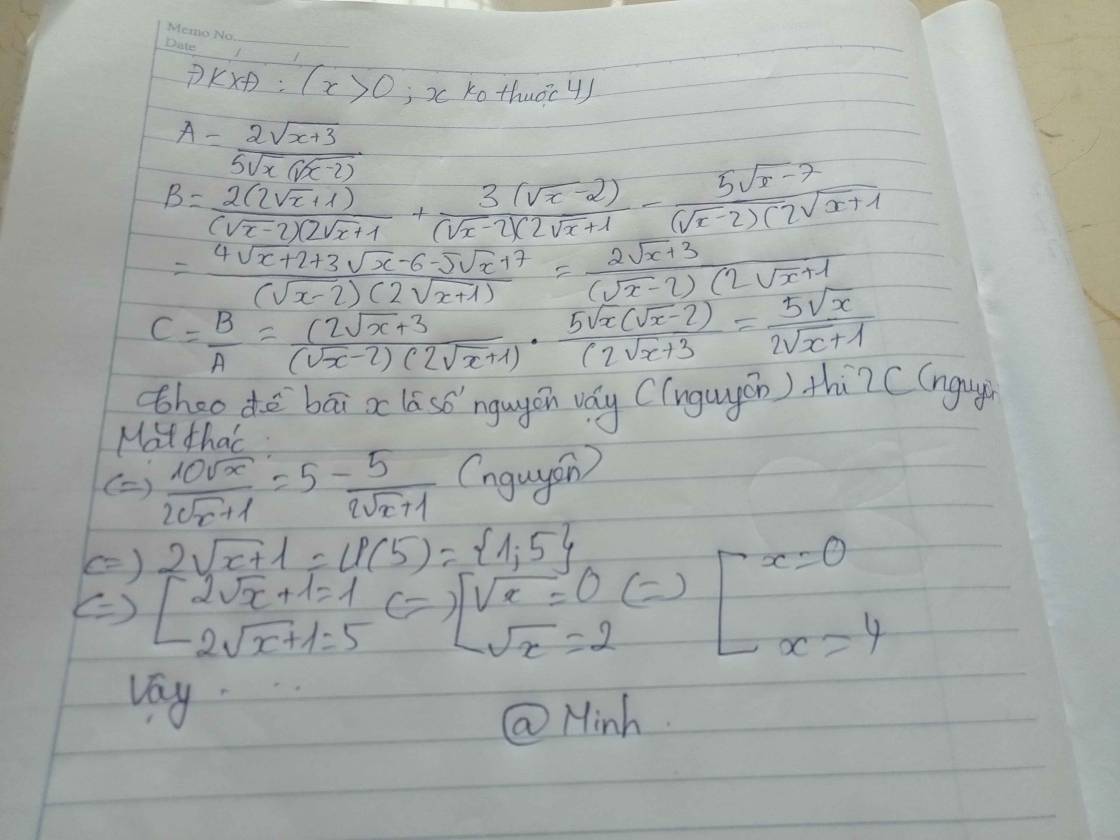Cho biểu thức \(A=\dfrac{2}{2+\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{2-\sqrt{x}}-\dfrac{2x}{4-x}\) (x ≥ 0 ; x = 4)
Rút gọn biểu thức A

Những câu hỏi liên quan
1.cho biểu thức A=\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}+3}-\dfrac{5}{x+\sqrt{x}-6}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)với(x≥0;x≠4)
a)rút gọn A
b)tính A khi x=6+4\(\sqrt{2}\)
2.cho biểu thức P=\(\left(\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}-\dfrac{8x}{x-4}\right):\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}-2}+3\right)\)với x≥0;x≠1;x≠4
a)rút gọn P
b)tìm x để P=-4
1)so sánh 2 số sau M=\(\sqrt{18}-\sqrt{8}\) và N=\(\dfrac{5+\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{5}+1}-\sqrt{6-2\sqrt{5}}\)
2)cho biểu thức A=\((\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{3+\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{2x}{9-x}):(\dfrac{x-4}{x-3\sqrt{x}}-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}})\) với x>0,\(x\ne4\),\(x\ne9\)
1) So sánh:
N = \(\dfrac{5+\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{5}+1}-\sqrt{6-2\sqrt{5}}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)}{\sqrt{5}+1}-\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\sqrt{5}-\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)=1\)
M = \(\sqrt{18}-\sqrt{8}\)
\(=3\sqrt{2}-2\sqrt{2}\)
\(=\sqrt{2}\)
Ta có: \(1=\sqrt{1}\)
Mà 1 < 2
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{1}< \sqrt{2}\)
Hay 1 \(< \sqrt{2}\)
Vậy N < M
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
2) Với \(x>0;x\ne4;x\ne9\), ta có:
A = \(\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{3+\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{2x}{9-x}\right):\left(\dfrac{x-4}{x-3\sqrt{x}}-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}}\right)\)
\(=\left[\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}-\dfrac{2x}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}\right]:\left[\dfrac{x-4}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}-\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}\right]\)
\(=\dfrac{x-3\sqrt{x}-2x}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}:\dfrac{x-4-2\sqrt{x}+6}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x-3}\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x-3\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}.\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}{x-2\sqrt{x}+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}.\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}{x-2\sqrt{x}+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x}{x-2\sqrt{x}+2}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
câu 2 rút gọn A và tìm các giá trị nguyên của x để A nhận giá trị âm
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1) cho biểu thức A= \(\dfrac{x^2-\sqrt{x}}{x-\sqrt{x}+1}\) - \(\dfrac{2x+\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}}\) + \(\dfrac{2.\left(x-1\right)}{\sqrt{x}-1}\) ( x>0; x ≠1)
a) Rút gọn biểu thức A
b) Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của 4
Lời giải:
a.
\(A=\frac{\sqrt{x}(\sqrt{x^3}-1)}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}-\frac{\sqrt{x}(2\sqrt{x}+1)}{\sqrt{x}}+\frac{2(\sqrt{x}-1)(\sqrt{x}+1)}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(=\frac{\sqrt{x}(\sqrt{x}-1)(x+\sqrt{x}+1)}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}-(2\sqrt{x}+1)+2(\sqrt{x}+1)\)
\(=\sqrt{x}(\sqrt{x}-1)-2\sqrt{x}-1+2\sqrt{x}+2\\ =x-\sqrt{x}-2\sqrt{x}-1+2\sqrt{x}+2\\ =x-\sqrt{x}+1\)
b.
$A=x-\sqrt{x}+1=(x-\sqrt{x}+\frac{1}{4})+\frac{3}{4}$
$=(\sqrt{x}-\frac{1}{2})^2+\frac{3}{4}\geq 0+\frac{3}{4}=\frac{3}{4}$
$\Rightarrow A_{\min}=\frac{3}{4}$
Giá trị này đạt tại $\sqrt{x}-\frac{1}{2}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{4}$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hai biểu thức \(A=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+3}{5x-10\sqrt{x}}\) và \(B=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}-2}+\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{x}+1}-\dfrac{5\sqrt{x}-7}{2x-3\sqrt{x}-2}\) với x>0, x≠4. Tìm x sao cho \(\dfrac{B}{A}\)nhận giá trị là một số nguyên.
Cho A = \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}-2}+\dfrac{2x+8}{2x-4}\) và B = \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}-6}\) với \(x\ge0;x\ne4;x\ne36\)
a) Rút gọn các biểu thức A
b) Tìm GTNN của biểu thức P = A : B
Bạn xem lại xem đã biết biểu thức đúng chưa vậy?
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hai biểu thứ A=\(\dfrac{\sqrt{X}+1}{\sqrt{X}-2}\);B=\(\dfrac{\sqrt{X}}{\sqrt{X}+1}+\dfrac{1-\sqrt{X}}{\sqrt{X}-2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+4}{x-\sqrt{x}-2}\)(với x≥0,x≠4)
a.Tính giá trị biểu thức A khi x=25
B.rút gọn biểu thức B
c.tìm x nguyên để p=B/A<-1
a: Khi x=25 thì \(A=\dfrac{5+1}{5-2}=\dfrac{6}{3}=2\)
b: \(B=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+1}+\dfrac{1-\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+4}{x-\sqrt{x}-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+1}+\dfrac{1-\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+4}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)+\left(1-\sqrt{x}\right)\left(1+\sqrt{x}\right)-\sqrt{x}-4}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2\sqrt{x}+1-x-\sqrt{x}-4}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-3\sqrt{x}-3}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}=-\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
c: P=B:A
\(=\dfrac{-3}{\sqrt{x}-2}:\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}=-\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
P<-1
=>P+1<0
=>\(\dfrac{-3+\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+1}< 0\)
=>\(\sqrt{x}-2< 0\)
=>\(\sqrt{x}< 2\)
=>0<=x<4
mà x nguyên
nên \(x\in\left\{0;1;2;3\right\}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Cho A = \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}-2}+\dfrac{2x+8}{2x-4}\) với \(x\ge0;x\ne4;x\ne36\)
Rút gọn biểu thức A
Sửa đề: x-4
\(A=\dfrac{x-2\sqrt{x}+x+4\sqrt{x}+4+2x+8}{x-4}=\dfrac{4x+2\sqrt{x}+12}{x-4}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Câu 1. Cho biểu thức Adfrac{2}{sqrt{x}-2} và Bdfrac{sqrt{x}}{sqrt{x}+2}+dfrac{4sqrt{x}}{x-4} với x ≥ 0 và x ≠ 4.1) Tính giá trị biểu thức A khi x 9.2) Chứng minh Bdfrac{sqrt{x}}{sqrt{x}-2}.3) Tìm x để A+Bdfrac{3x}{sqrt{x}-2}.Câu 2. Giải bài toán sau bằng cách lập phương trình hoặc hệ phương trình:Trong kì thi tuyển sinh vào lớp 10, hai trường A và B có tất cả 750 học sinh dự thi. Trong số học sinh trường A dự thi có 80% số học sinh trúng tuyển, còn trong số học sinh trường B dự thi có 70% số h...
Đọc tiếp

Câu 1.
Cho biểu thức \(A=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}-2}\) và \(B=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}+\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}}{x-4}\) với x ≥ 0 và x ≠ 4.
1) Tính giá trị biểu thức A khi x = 9.
2) Chứng minh \(B=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}.\)
3) Tìm x để \(A+B=\dfrac{3x}{\sqrt{x}-2}\).
Câu 2.
Giải bài toán sau bằng cách lập phương trình hoặc hệ phương trình:
Trong kì thi tuyển sinh vào lớp 10, hai trường A và B có tất cả 750 học sinh dự thi. Trong số học sinh trường A dự thi có 80% số học sinh trúng tuyển, còn trong số học sinh trường B dự thi có 70% số học sinh trúng tuyển. Biết tổng số học sinh trúng tuyển của cả hai trường là 560 học sinh. Tính số học sinh dự thi của mỗi trường?
Câu 3.
1) Giải hệ phương trình: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x-y}+\sqrt{y+1}=4\\\dfrac{1}{x-y}-3\sqrt{y+1}=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
2) Cho parabol (P): y = x2 và đường thẳng (d): y = 2(m - 1)x - m2 + 2m (m là tham số).
a) Tìm tọa độ giao điểm của parabol (P) và đường thẳng (d) khi m = 2.
b) Tìm m để (d) và (P) cắt nhau tại hai điểm phân biệt có hoành độ x1; x2 là hai số đối nhau.
Câu 4.
Cho nửa đường tròn (O; R) đường kính AB và điểm M thuộc nửa đường tròn đó (M khác A và B). Trên dây BM lấy điểm N (N khác B và M), tia AN cắt nửa đường tròn (O) tại điểm thứ hai là P. Tia AM và tia BP cắt nhau tại Q.
a) Chứng minh bốn điểm M, N, P, Q cùng thuộc một đường tròn.
b) Chứng minh tam giác MAB đồng dạng với tam giác MNQ.
c) Chứng minh MO là tiếp tuyến của đường tròn ngoại tiếp tam giác MNQ.
d) Dựng hình bình hành ANBC. Chứng minh \(QB=QC.\sin\widehat{QPM.}\)
1/ Cho hai biểu thức A=\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}}\) và B=\(\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+3}\)+ \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-3}\)-\(\dfrac{2x}{x-9}\) với x>0 , x≠9
a) Rút gọn biểu thức B
b) Tìm các giá trị nguyên của x để P<0 với P=A.B
Lời giải:
a.
\(B=\frac{2\sqrt{x}(\sqrt{x}-3)+\sqrt{x}(\sqrt{x}+3)-2x}{(\sqrt{x}+3)(\sqrt{x}-3)}=\frac{x-3\sqrt{x}}{(\sqrt{x}-3)(\sqrt{x}+3)}=\frac{\sqrt{x}(\sqrt{x}-3)}{(\sqrt{x}+3)(\sqrt{x}-3)}=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+3}\)
b.
\(P=AB=\frac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}}.\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+3}=\frac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}+3}\)
Để $P<0\Leftrightarrow \frac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}+3}<0$
Mà $\sqrt{x}+3>0$ nên $\sqrt{x}-2<0$
$\Leftrightarrow 0< x< 4$
Kết hợp với ĐKXĐ suy ra $0< x< 4$
Mà $x$ nguyên nên $x\in left\{1; 2; 3\right\}$
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)