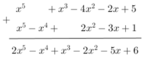Cho x3+x=1
Tính A=(x4-2x3+x2-3x+5)/(x5-x2-x+2)
Nhanh Nhé Các Bạn
Cho đa thức
F(x)=x5 - 3x2 -x3 - x2 - 2x + 5
G(x)+x5 - x4 + x2 - 3x + x2 + 1
Tính H(x) = F(x) + G(x)
\(H\left(x\right)=F\left(x\right)+G\left(x\right)=\left(x^5-3x^2-x^3-x^2-2x+5\right)+\left(x^5-x^4+x^2-3x+x^2+1\right)\\ =x^5-3x^2-x^3-x^2-2x+5+x^5-x^4+x^2-3x+x^2+1\\ =\left(x^5+x^5\right)-x^4-x^3-\left(3x^2+x^2-x^2-x^2\right)-\left(2x+3x\right)+5\\ =2x^5-x^4-x^3-2x^2-5x+5\)
Bài 1 : Cho a,b,c là các số hữu tỉ khác 0 sao cho a+b-c/c=a-b+c/b=(-a)+b+c/a
Tính giá trị của biểu thức A=(a+b).(b+c).(c+a)/abc
(LƯU Ý : DẤU / LÀ ...TRÊN.....)
Bài 2 : Cho x,x2,x3,x4,x5,x6 thỏa mãn :
(x2)^2=x1.x3
(x3)^2=x2.x4
(x4)^2=x3.x5
(x5)^2=x4.x6
Chứng minh rằng : x1/x6=(x1+x2+x3+x4+x5/x2+x3+x4+x5+x6)^5
Giusp mk vs nhé các bn !!!
Cho
f ( x ) = x 2 + 2 x 3 - 7 x 5 - 9 - 6 x 7 + x 3 + x 2 + x 5 - 4 x 2 + 3 x 7 g ( x ) = x 5 + 2 x 3 - 5 x 8 - x 7 + x 3 + 4 x 2 - 5 x 7 + x 4 - 4 x 2 - x 6 - 12 h ( x ) = x + 4 x 5 - 5 x 6 - x 7 + 4 x 3 + x 2 - 2 x 7 + x 6 - 4 x 2 - 7 x 7 + x
Thu gọn và sắp xếp các đa thức trên theo lũy thừa tăng của biến.
* f(x) = x2 + 2x3− 7x5 − 9 − 6x7 + x3 + x2 + x5 − 4x2 + 3x7
= (x2+ x2 – 4x2)+ (2x3 + x3 ) - (7x5 - x5 ) – 9 – (6x7 – 3x7)
= - 2x2 + 3x3 – 6x5 – 9 – 3x7
Sắp xếp theo thứ tự tăng của biến: f(x) = −9 − 2x2 + 3x3 − 6x5 − 3x7
* g(x) = x5 + 2x3 − 5x8 − x7 + x3 + 4x2 -5x7 + x4 − 4x2 − x6 – 12
= x5+ (2x3 + x3) - 5x8 – (x7+ 5x7) + (4x2 – 4x2 ) + x4 – x6 – 12
= x5 + 3x3 – 5x8 – 6x7 + x4 – x6 – 12
Sắp xếp theo thứ tự tăng của biến: g(x) = −12 + 3x3 + x4 + x5 – x6 − 6x7− 5x8
* h(x) = x + 4x5 − 5x6 − x7 + 4x3 + x2 − 2x7 + x6 − 4x2 − 7x7 + x.
= (x+ x) +4x5 – (5x6 – x6)- (x7 + 2x7+ 7x7) + 4x3+ (x2 – 4x2)
= 2x + 4x5 - 4x6 – 10x7 + 4x3 -3x2
Sắp xếp theo thứ tự tăng của biến: h(x) = 2x − 3x2 + 4x3 + 4x5 − 4x6 − 10x7
Cho
f ( x ) = x 2 + 2 x 3 - 7 x 5 - 9 - 6 x 7 + x 3 + x 2 + x 5 - 4 x 2 + 3 x 7 g ( x ) = x 5 + 2 x 3 - 5 x 8 - x 7 + x 3 + 4 x 2 - 5 x 7 + x 4 - 4 x 2 - x 6 - 12 h ( x ) = x + 4 x 5 - 5 x 6 - x 7 + 4 x 3 + x 2 - 2 x 7 + x 6 - 4 x 2 - 7 x 7 + x
Tính f(x) + g(x) – h(x)
Bài 1. Cho hai đa thức:
P(x) = 2x4 + 3x3 + 3x2 - x4 - 4x + 2 - 2x2 + 6x
Q(x) = x4 + 3x2 + 5x - 1 - x2 - 3x + 2 + x3
a) Thu gọn và sắp xếp các hạng tử của mỗi đa thức trên theo lũy thừa giảm
dần của biến.
b) Tính. P(x) + Q (x), P(x) - Q(x), Q(x) - P(x).
Bài 2. Cho hai đa thức:
P(x) = x5 + 5 - 8x4 + 2x3 + x + 5x4 + x2 - 4x3
Q(x) = (3x5 + x4 - 4x) - ( 4x3 - 7 + 2x4 + 3x5)
a) Thu gọn và sắp xếp các hạng tử của mỗi đa thức trên theo lũy thừa giảm
dần của biến.
b) Tính P(x) + Q(x), P(x) - Q(x)
Bài 5. Cho hai đa thức:
P(x) = 2x4 + 2x3 - 3x2 + x +6
Q(x) = x4 - x3 - x2 + 2x + 1
a) Tính P(x) + Q(x), P(x) - Q(x)
b) Tính và P(x) - 2Q(x).
Bài 6. Cho đa thức P(x) = 2x4 - x2 +x - 2.
Tìm các đa thức Q(x), H(x), R(x) sao cho:
a) Q(x) + P(x) = 3x4 + x3 + 2x2 + x + 1
b) P(x) - H(x) = x4 - x3 + x2 - 2
c) R(x) - P(x) = 2x3 + x2 + 1
Giải các phương trình sau:
a, (9x2 - 4)(x + 1) = (3x +2)(x2 - 1)
b, (x - 1)2 - 1 + x2 = (1 - x)(x + 3)
c, (x2 - 1)(x + 2)(x - 3) = (x - 1)(x2 - 4)(x + 5)
d, x4 + x3 + x + 1 = 0
e, x3 - 7x + 6 = 0
f, x4 - 4x3 + 12x - 9 = 0
g, x5- 5x3 + 4x = 0
h, x4 - 4x3 + 3x2 + 4x - 4 = 0
a, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(3x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(\left(9x^2-4\right)-\left(\left(3x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(9x^2-4-\left(3x^2-x-2\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(9x^2-4-3x^2+x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x^2+x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)=0;3x^2+x-2=0\)
=> x=-1
với \(3x^2+x-2=0\)
ta sử dụng công thức bậc 2 suy ra : \(x=\dfrac{2}{3};x=-1\)
Vậy ghiệm của pt trên \(S\in\left\{-1;\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1-1+x^2=x+3-x^2-3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-2x=-x^2-2x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2=3\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left[\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(x+5\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x-3-x^2-3x+10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(-5x+7\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;-2;\dfrac{7}{5}\right\}\)
Cho các đa thức f(x) = x5 – 3x2 + x3 – x2 - 2x + 5
g(x) = x5 – x4 + x2 - 3x + x2 + 1
a) Thu gọn và sắp xếp đa thức f(x) và g(x) theo luỹ thừa giảm dần.
b)Tính h(x) = f(x) + g(x)
a: \(F\left(x\right)=x^5-3x^2+x^3-x^2-2x+5\)
\(=x^5+x^3-4x^2-2x+5\)
\(G\left(x\right)=x^5-x^4+x^2-3x+x^2+1\)
\(=x^5-x^4+2x^2-3x+1\)
b: Ta có: \(H\left(x\right)=F\left(x\right)+G\left(x\right)\)
\(=x^5+x^3-4x^2-2x+5+x^5-x^4+2x^2-3x+1\)
\(=2x^5-x^4+x^3-2x^2-5x+6\)
Bài 1: Giải phương trình:
a) ( x+1)2 (x+2) + ( x – 1)2 ( x- 2) = 12
b) x4 + 3x3 + 4x2 + 3x + 1 = 0
c) x5 – x4 + 3x3 + 3x2 –x + 1 = 0
Bài 2: Chứng minh rằng các phương trình sau vô nghiệm
a) x4 – x3 + 2x2 – x + 1 = 0
b) x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1 = 0
c) x4 – 2x3 +4x2 – 3x +2 = 0
d) x6+ x5+ x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1 = 0
1.
a/ \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+3x+2\right)+\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-3x+2\right)-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)+3x\left(x+1\right)-3x\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x^2+2\right)+6x^2-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+3x^2+2x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+4x+6\right)=0\Rightarrow x=1\)
b/ Nhận thấy \(x=0\) ko phải nghiệm, chia 2 vế cho \(x^2\)
\(x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}+3\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)+4=0\)
Đặt \(x+\frac{1}{x}=t\Rightarrow x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}=t^2-2\)
\(t^2-2+3t+4=0\Rightarrow t^2+3t+2=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=-1\\t=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+\frac{1}{x}=-1\\x+\frac{1}{x}=-2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+x+1=0\left(vn\right)\\x^2+2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x=-1\)
1c/
\(\Leftrightarrow x^5+x^4-2x^4-2x^3+5x^3+5x^2-2x^2-2x+x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4\left(x+1\right)-2x^3\left(x+1\right)+5x^2\left(x+1\right)-2x\left(x+1\right)+x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^4-2x^3+5x^2-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x^4-2x^3+5x^2-2x+1=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow x^4-2x^3+x^2+x^2-2x+1+3x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x\right)^2+\left(x-1\right)^2+3x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-x=0\\x-1=0\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\) không tồn tại x thỏa mãn
Vậy pt có nghiệm duy nhất \(x=-1\)
2.
a. \(x^4-x^3+x^2+x^2-x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-x+1\right)+x^2-x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+1=0\left(vn\right)\\x^2-x+1=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}=0\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm
b.
\(x^4+x^3+x^2+x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^3+1\right)+x^3+1+x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^3+1\right)+x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x^2-x+1\right)+x^2=0\)
Mà \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x^2-x+1\right)\ge0\\x^2\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Nên dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ khi: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\) ko tồn tại x thỏa mãn
Tính f(x) + g(x) với:
f(x) = x5 – 3x2 + x3 – x2 – 2x + 5
g(x) = x2 – 3x + 1 + x2 – x4 + x5
Thu gọn, sắp xếp đa thức theo lũy thừa giảm của biến:
* Ta có: f(x) = x5 – 3x2 + x3 – x2 – 2x + 5
= x5 – (3x2 + x2 ) + x3 - 2x + 5
= x5 – 4x2 + x3 – 2x + 5
= x5 + x3 – 4x2 – 2x + 5
Và g(x) = x2 – 3x + 1 + x2 – x4 + x5
= (x2 + x2 ) – 3x + 1 – x4 + x5
= 2x2 – 3x + 1 – x4 + x5
= x5 – x4 + 2x2 – 3x + 1
* f(x) + g(x):