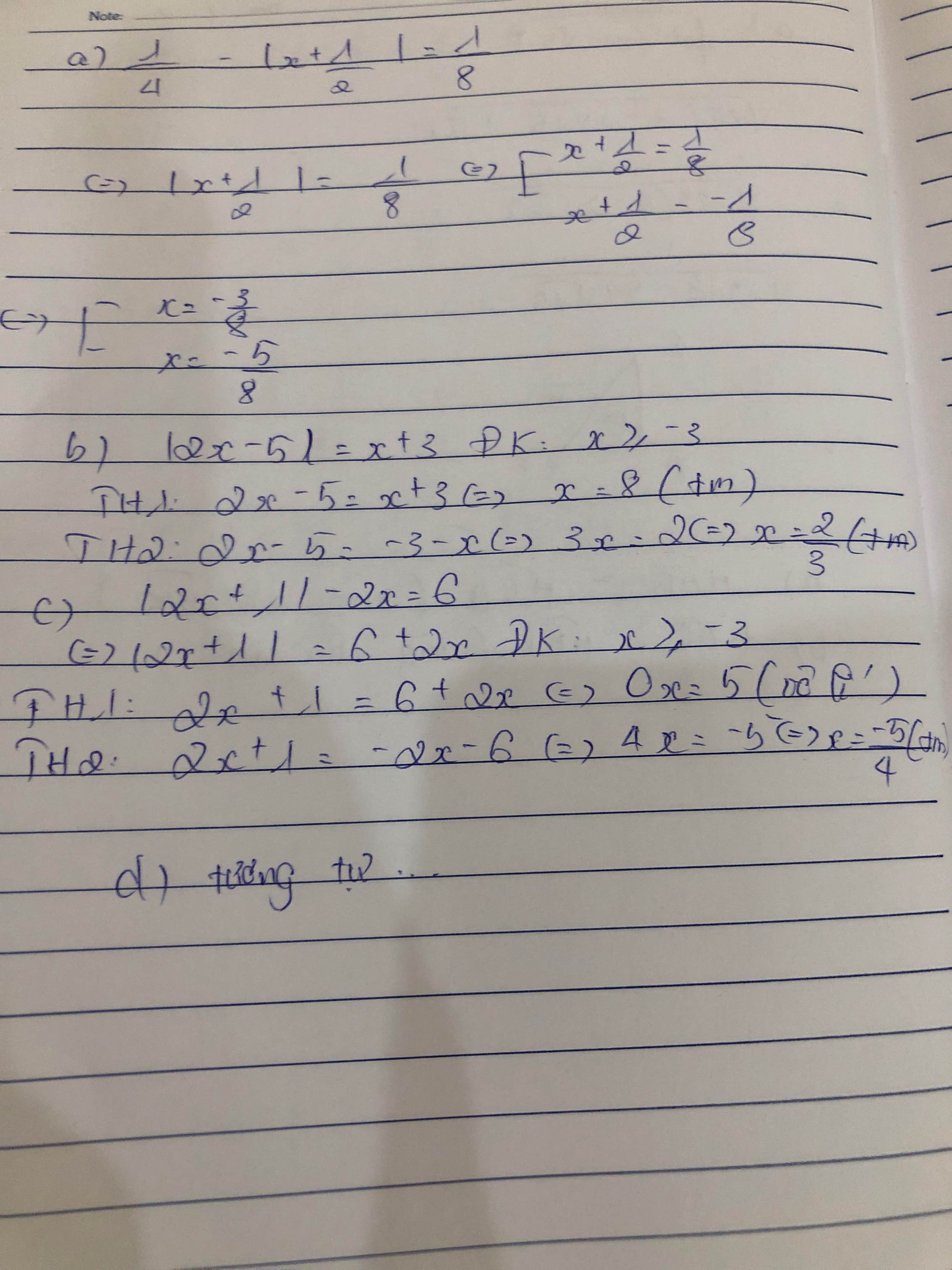Tìm x: x(5 - 2x) - (x - 1)(2x + 1)=7

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tìm x :
a, (2x-5).(x+2)-2x.(x-1)=15
b, (5-2x).(2x+7)=4\(x^2\)-25
c, x.(4x-5)-(2x+1)\(^2\)=0
M.n giúp em với
a: ta có: \(\left(2x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)-2x\left(x-1\right)=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+4x-5x-10-2x^2+2x=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=25\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(5-2x\right)\left(2x+7\right)=4x^2-25\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-25+\left(2x-5\right)\left(2x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-5\right)\left(2x+5+2x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-5\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: Ta có: \(x\left(4x-5\right)-\left(2x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-5x-4x^2-4x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x=1\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{9}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
. Tìm x, biết:
a) 6x.(x – 5) + 3x.(7 – 2x) = 18 b) 2x.(3x + 1) + (4 – 2x).3x = 7 c) 0,5x.(0,4 – 4x) + (2x + 5).x = -6,5 | d) (x + 3)(x + 2) – (x - 2)(x + 5) = 6 e) 3(2x - 1)(3x - 1) – (2x - 3)(9x - 1) = 0 |
a) Ta có: \(6x\left(x-5\right)+3x\left(7-2x\right)=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-30x+21x-6x^2=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x=18\)
hay x=-2
Vậy: S={-2}
b) Ta có: \(2x\left(3x+1\right)+\left(4-2x\right)\cdot3x=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+2x+12x-6x^2=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow14x=7\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
c) Ta có: \(0.5x\left(0.4-4x\right)+\left(2x+5\right)\cdot x=-6.5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0.2x-2x^2+2x^2+5x=-6.5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5.2x=-6.5\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{5}{4}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{5}{4}\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
d) Ta có: \(\left(x+3\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(x+5\right)=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+5x+6-\left(x^2+3x-10\right)=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+5x+6-x^2-3x+10=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+16=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-10\)
hay x=-5
Vậy: S={-5}
e) Ta có: \(3\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x-1\right)-\left(2x-3\right)\left(9x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(6x^2-5x+1\right)-\left(18x^2-29x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow18x^2-15x+3-18x^2+29x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow14x=0\)
hay x=0
Vậy: S={0}
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x \(\frac{7^{x+2}+7^{x+1}+7^x}{57}=\frac{5^{2x}+5^{2x+1}+5^{2x+3}}{131}\)
\(\frac{7^x\left(7^2+7+1\right)}{57}=\frac{5^{2x}\left(1+5+5^3\right)}{131}\)
\(\frac{7^x.57}{57}=\frac{5^{2x}.131}{131}\)
\(7^x=5^{2x}\)khi và chỉ khi x = 0.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
tìm x biết : \(\frac{7^{x+2}+7^{x+1}+7^x}{57}=\frac{5^{2x}+5^{2x+1}+5^{2x+3}}{131}\)
\(\frac{7^{x+2}+7^{x+1}+7^x}{57}=\frac{7^x.7^2+7^x.7+7^x}{57}=\frac{7^x.\left(7^2+7+1\right)}{57}=7^x\)
\(\frac{5^{2x}+5^{2x+1}+5^{2x+3}}{131}=\frac{5^{2x}+5^{2x}.5+5^{2x}.5^3}{131}=\frac{5^{2x}\left(1+5+5^3\right)}{131}=\frac{25^x.131}{131}=25^x\)
\(\Rightarrow7^x=25^x\Rightarrow x=0\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
ai tích mình mình tích lại cho
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Tìm x :
\(\frac{7^{x+2}+7^{x+1}+7^x}{57}=\frac{5^{2x}+5^{2x+1}+5^{2x+3}}{131}\)
\(\frac{7^{x+2}+7^{x+1}+7^x}{57}=\frac{5^{2x}+5^{2x+1}+5^{2x+3}}{131}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{7^x.7^2+7^x.7^1+7^x}{57}=\frac{5^{2x}+5^{2x}.5+5^{2x}.5^3}{131}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{7^x.\left(7^2+7+1\right)}{57}=\frac{5^{2x}.\left(1+5+5^3\right)}{131}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{7^x.57}{57}=\frac{5^{2x}.131}{131}\)
\(\Rightarrow7^x=5^{2x}\)
Bạn tự làm phần còn lại nhé
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x
\(\frac{7^{x+2}+7^{x+1}+7^x}{57}=\frac{5^{2x}+5^{2x+1}+5^{2x+3}}{131}\)
Biến đổi vế trái, ta được : \(\frac{7^{x+2}+7^{x+1}+7^x}{57}=\frac{7^x.7^2+7^x.7+7^x}{57}=\frac{7^x\left(7^2+7+1\right)}{57}=\frac{7^x.57}{57}=7^x\)\(=7^x\)
Biến đổi vế phải, ta được : \(\frac{5^{2x}+5^{2x+1}+5^{2x+3}}{131}=\frac{5^{2x}+5^{2x}.5+5^{2x}.5^3}{131}=\frac{5^{2x}.\left(1+5+5^3\right)}{131}=\frac{5^{2x}.131}{131}=5^{2x}=25^x\)
\(\Rightarrow7^x=25^x\)
Vì \(\left(7,25\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow7^x=25^x=1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=0\)
Vậy \(x=0\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x bt 2x/ 1 × 3 + 2x/ 3 x 5 + 2x / 5 x 7 +...+2x/2011×2013
Tìm x :
\(\frac{\left(7^{x+2}+7^{x+1}+7^x\right)^{57}}{57}=\frac{5^{2x}+5^{2x+1}+5^{2x+3}}{131}\)
BT1: cho -3x(x+5)=-3x2-15x
(x+3)(x+2)=x2+5x+6
Tìm x biết:
--3x(x+5)+(x+3)(x+2)=7
BT2:Cho(2x+1)2=4x2+4x+1
(2x+1)(2x-1)=4x2-1
Tìm x biết:
(2x+1)2-(2x+1)(2x-1)=19
BT3: Tìm x biết:
a)x(x+1)-x(x+5)=9
b)4x2(x+5)-8x(x+7)=13
7, Tìm x
a) \(\dfrac{1}{4}-\left|x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right|=\dfrac{1}{8}\) b) |2x-5|=x+3
c) |2x+1|-2x=6 d) |x-5|+x=5
a) Ta có: \(\dfrac{1}{4}-\left|x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right|=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right|=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{8}\\x+\dfrac{1}{2}=-\dfrac{1}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-3}{8}\\x=\dfrac{-5}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
b) Ta có: \(\left|2x-5\right|=x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-5=x+3\left(x\ge\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\\2x-5=-x-3\left(x< \dfrac{5}{2}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-x=3+5\\2x+x=-3+5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\left(nhận\right)\\x=\dfrac{2}{3}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời