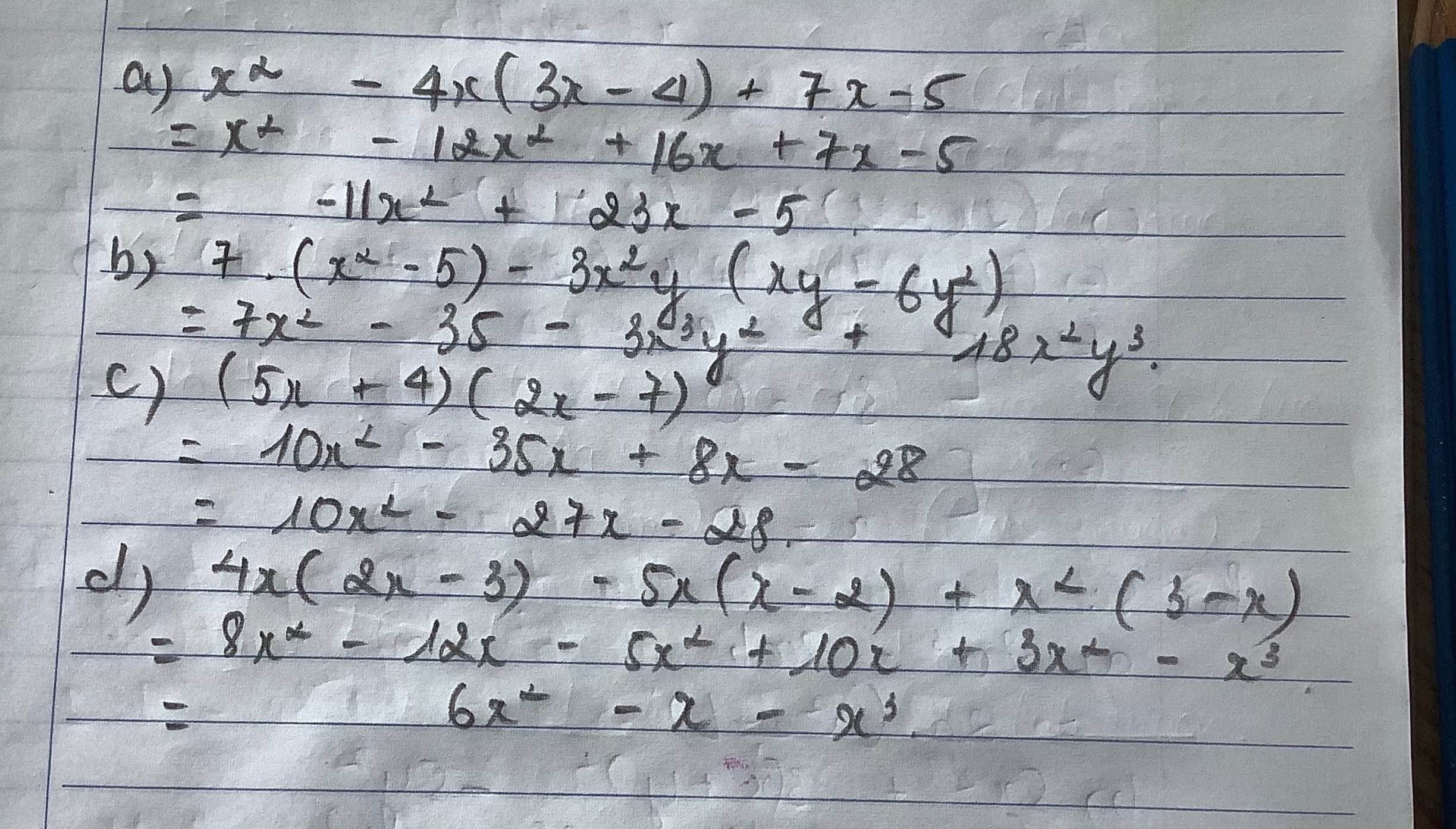thu gọn biểu thức (x^2-2)^2+(x-1)^2-(x-3)^2-(x+2)^2+5x

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Ai giúp em với ạ ;-;
Thu gọn biểu thức B = ( x - 3) ( x + 3 ) ( x + 2 ) - ( x - 1 ) ( x^2 - 3 ) - 5x ( x + 4 )^2 - ( x - 5)^2
Thu gọn các biểu thức sau :
A=2|x-3|+3|x+1|+2x-5
B=|x+7|+2|x-3|-x-4
C=8|x-1|+2|x-3|-5x-3
D=2|2-x|+3|3-x|+5x-2
a: Trường hợp 1: x<-1
A=3(-x-1)+2(-x+3)+2x-5
=-3x-3-2x+6+2x-5
=-3x-2
Trường hợp 2: -1<=x<3
A=3(x+1)+2(3-x)+2x-5
=3x+3+6-2x+2x-5
=3x+4
Trường hợp 3: x>=3
A=3(x+1)+2(x-3)+2x-5
=3x+3+2x-6+2x-5
=7x-8
b: Trường hợp 1: x<-7
B=-x-7+2(3-x)-x-4
=-2x-11+6-2x=-4x-5
TRường hợp 2: -7<=x<3
B=x+7+2(3-x)-x-4
=3+6-2x=-2x+9
Trường hợp 3: x>=3
B=x+7+2x-6-x-4=2x-3
c: Trường hợp 1: x<1
C=8(1-x)+2(3-x)-5x-3
=8-8x+6-2x-5x-3
=-15x+11
Trường hợp 2: 1<=x<3
C=8(x-1)+2(3-x)-5x-3
=8x-8+6-2x-5x-3
=x-5
TRường hợp 3: x>=3
C=8(x-1)+2(x-3)-5x-3
=8x-8+2x-6-5x-3
=5x-17
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Thu gọn các biểu thức sau :
A=2|x-3|+3|x+1|+2x-5
B=|x+7|+2|x-3|-x-4
C=8|x-1|+2|x-3|-5x-3
D=2|2-x|+3|3-x|+5x-2
a: Trường hợp 1: x<-1
A=2(3-x)+3(-x-1)+2x-5
=6-2x-3x-3+2x-5
=-3x-2
Trường hợp 2: -1<=x<3
A=2(3-x)+3(x+1)+2x-5
=6-2x+3x+3+2x-5
=3x+4
TRường hợp 3: x>=3
A=2(x-3)+3(x+1)+2x-5
=2x-6+3x+3+2x-5
=7x-8
b: Trường hợp 1: x<-7
B=7-x+2(3-x)-x-4
=3-2x+6-2x=-4x+9
Trường hợp 2: -7<=x<3
B=x+7+2(3-x)-x-4
=3+6-2x=-2x+9
Trường hợp 3: x>=3
B=x+7+2x-6-x-4=2x-3
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1) Cho biểu thức : Adfrac{4x^2}{x^2-4}+dfrac{1}{x+2}-dfrac{1}{x-2} (Với x≠2 và x≠ -2)a.Rút gọn biểu thức A.b. Tính giá trị của biểu thức A khi x4.2) Rút gọn biểu thức Adfrac{x}{x-1}+dfrac{3}{x+1}+dfrac{3-5x}{x^2-1} , với x≠ -1 và x≠13) Rút gọn biểu thức Pdfrac{2}{x-2}+dfrac{1}{x+2}dfrac{6+5x}{4-x^2}, với x≠ -2 và x≠ 24) Cho biểu thỨC : A dfrac{2x}{x^2-25}+dfrac{5}{5-x}-dfrac{1}{x+5}( với x≠5 và x≠ -5)a. Rút gọn biểu thức A b. Tính giá trị của biểu thức A khi xdfrac{4}{5}.5) Cho biểu thức : M dfr...
Đọc tiếp
1) Cho biểu thức : A=\(\dfrac{4x^2}{x^2-4}\)+\(\dfrac{1}{x+2}\)-\(\dfrac{1}{x-2}\) (Với x≠2 và x≠ -2)
a.Rút gọn biểu thức A.
b. Tính giá trị của biểu thức A khi x=4.
2) Rút gọn biểu thức A=\(\dfrac{x}{x-1}\)+\(\dfrac{3}{x+1}\)+\(\dfrac{3-5x}{x^2-1}\) , với x≠ -1 và x≠1
3) Rút gọn biểu thức P=\(\dfrac{2}{x-2}\)+\(\dfrac{1}{x+2}\)\(\dfrac{6+5x}{4-x^2}\), với x≠ -2 và x≠ 2
4) Cho biểu thỨC : A= \(\dfrac{2x}{x^2-25}\)+\(\dfrac{5}{5-x}\)-\(\dfrac{1}{x+5}\)( với x≠5 và x≠ -5)
a. Rút gọn biểu thức A
b. Tính giá trị của biểu thức A khi x=\(\dfrac{4}{5}\).
5) Cho biểu thức : M =\(\dfrac{x^2}{x^2+2x}\)+\(\dfrac{2}{x+2}\)+\(\dfrac{2}{x}\) ( với x ≠0 và x≠ -2)
a. Rút gọn biểu thức M
b. Tính giá trị của biểu thức M khi: x=\(-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
MN BIẾT LÀM CÂU NÀO THÌ LÀM CÂU ĐÓ CŨNG ĐƯỢC AH!
1,
\(A=\dfrac{4x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{x-2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{x+2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x^2+x-2-\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{4x^2-4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(x=4\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{4.x^2-4}{\left(4-2\right)\left(4+2\right)}=...\)
2.
\(A=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{3\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{3-5x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)+3\left(x-1\right)+3-5x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-2x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\)
3.
Đề lỗi, thiếu dấu trước \(\dfrac{6+5x}{4-x^2}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
4.
\(A=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}-\dfrac{5\left(x+5\right)}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}-\dfrac{x-5}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x-5\left(x+5\right)-\left(x-5\right)}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{-4x-20}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-4\left(x+5\right)}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{-4}{x-5}\)
\(x=\dfrac{4}{5}\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{-4}{\dfrac{4}{5}-5}=\dfrac{20}{21}\)
5.
\(M=\dfrac{x^2}{x\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{2x}{x\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x+2\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+4x+4}{x\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{x\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x+2}{x}\)
\(x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\Rightarrow M=\dfrac{-\dfrac{3}{2}+2}{-\dfrac{3}{2}}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Thu gọn các biểu thức : a) 6x^2y(3xy-2xy^2+y) b) (-3x+2)(5x^2-1/3x+4) c) (x+1)(x-2)+x(3-x) d) (2x+3)^2-(2x-5)(2x+5)-(x-1)(x^12+12)
a: =18x^3y^2-12x^3y^3+6x^2y^2
b: (-3x+2)(5x^2-1/3x+4)
=-12x^3+x^2-12x+10x^2-2/3x+8
=-12x^3+11x^2-38/3x+8
c: =x^2-x-2+3x-x^2
=2x-2
d: =4x^2+12x+9-4x^2+25-(x-1)(x^2+12)
=12x+34-x^3-12x+x^2+12
=-x^3+x^2+46
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Thu gọn biểu thức a)x^2-4x(3x-4)+7x-5 b)7x(x^2-5)-3x^2y(xy-6y^2) c)(5x+4)(2x-7) d)4x(2x-3)-5x(x-2)+x^2(3-x)
a: Ta có: \(x^2-4x\left(3x-4\right)+7x-5\)
\(=x^2-12x^2+16x+7x-5\)
\(=-11x^2+23x-5\)
b: Ta có: \(7x\left(x^2-5\right)-3x^2y\left(xy-6y^2\right)\)
\(=7x^3-35x-3x^3y^2+18x^2y^3\)
c: Ta có: \(\left(5x+4\right)\left(2x-7\right)\)
\(=10x^2-35x+8x-28\)
\(=10x^2-27x-28\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (2)
Câu 1: Thu gọn các biểu thức a) 6x²y(3xy - 2xy² + y) b) (-3x + 2) (5x² - 1 phần 3x + 4) c) ( x + 1)( x - 2) + x( 3 - x)
a: =12x^3y^2-12x^3y^3+6x^2y^2
b: =\(\left(-3x+2\right)\left(5x^2-\dfrac{1}{3}x+4\right)\)
=-15x^3+x^2-12x+10x^2-2/3x+8
=-15x^3+11x^2-38/3x+8
c: =x^2-x-2+3x-x^2
=2x-2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1. Tinh:
a) 4x^2 - x^2 + 8x^2
b) 1/2.x^2.y^2 - 3/4.x^2.y^2 + x^2y^2
c) 3y - 7y + 4y - 6y
2. Thu gọn biểu thức sau:
a) (-2/3.y^3) + 3y^2 - 1/2.y^3 - y^2
b) 5x^3 - 3x^2 + x- x^3 - 4x^2 - x
3. Cho đơn thức A = 5xy^2.(1/2)x^2y^2x
a) Thu gọn đơn thức trên
b) Tìm bậc. Xác định hệ số, phần biến
c) Tính giá trị của A khi x =1; y = -1
1 ) a) \(4x^2-x^2+8x^2\)
\(=\left(4+8\right).x^2+x^2-x^2\)
\(=12.x^3\)
b) \(\frac{1}{2}.x^2.y^2-\frac{3}{4}.x^2.y^2+x^2.y^2\)
\(\left(\frac{1}{2}-\frac{3}{4}\right).x^2.x^2.x^2.+y^2+y^2+y^2\)
\(=-\frac{1}{4}.x^6+y^6\)
c) \(3y-7y+4y-6y\)
\(=\left(3-7+4-6\right).y.y.y.y\)
\(=-6.y^4\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
2)
\(\left(-\frac{2}{3}.y^3\right)+3y^2-\frac{1}{2}.y^3-y^2\)
\(\left(-\frac{2}{3}+3-\frac{1}{2}\right).y^3.y^3-y\)
\(=\frac{25}{6}.y^5\)
b) \(5x^3-3x^2+x-x^3-4x^2-x\)
\(=\left(5-3-4\right).\left(x^3.x^2+x-x^3-x^2-x\right)\)
\(=-2.0=0\)
hông chắc
3)a) \(5xy^2.\frac{1}{2}x^2y^2x\)
\(\left(5.\frac{1}{2}\right).x^2.x^2.x.y^2.y^2\)
\(=\frac{5}{2}.x^5.y^4\)
b) Tổng các bậc của đơn thức là
5+4 = 9
Hệ số của đơn thức là \(\frac{5}{2}\)
Phần biến là x;y
Thay x=1;y=-1 vào đơn thức
\(\frac{5}{2}.1^5.\left(-1\right)^4\)
\(\frac{5}{2}.1.\left(-1\right)\)
\(\frac{5}{2}.\left(-1\right)=-\frac{5}{2}\)
Vậy ....
chắc không đúng đâu uwu
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a)Thu gọn biểu thức A=( 5x-3)^2-2(5x+3)( x+3) +(x+3)^2
b) Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử x^3 +5x^2 +6x
c) Tìm x cho biết :x^3 -3x^2 -4x +12=0
a) \(A=\left(5x-3\right)^2-2\left(5x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)+\left(x+3\right)^2\) ( \(5x-3\) chứ sao lại \(5x+3\) )
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\left[\left(5x-3\right)-\left(x+3\right)\right]^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\left(5x-3-x-3\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\left(4x-6\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\left(4x\right)^2-2.4x.6+6^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=16x^2-48x+36\)
b) \(x^3+5x^2+6x\)
\(=x\left(x^2+5x+6\right)\)
\(=x\left(x^2+3x+2x+6\right)\)
\(=x\left[\left(x^2+3x\right)+\left(2x+6\right)\right]\)
\(=x\left[x\left(x+3\right)+2\left(x+3\right)\right]\)
\(=x\left(x+3\right)\left(x+2\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)