Tìm điều kiện xác định của bất phương trình:
\(\dfrac{\sqrt{\text{x - 2}}}{\text{x}+1}-\sqrt{\text{4 - x}}\ge0\)
tìm điều kiện xác định của bất phương trình \(\sqrt{2-x}+x< 2+\sqrt{1-2x}\)
ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2-x\ge0\\1-2x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}\le x\le2\)
Giải các bất phương trình sau
1) \(\dfrac{\text{x - 2}}{x+1}-\dfrac{3}{x+2}>0\) 2) \(\dfrac{\text{x + 1}}{x+2}+\dfrac{x}{x-3}\le0\)
3) \(\dfrac{\text{x}^2+2x+5}{x+4}>x-3\) 4) \(\sqrt{\text{x^2}-3x+2}\ge3\)
\(\dfrac{x-2}{x+1}-\dfrac{3}{x+2}>0.\left(x\ne-1;-2\right).\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-4-3x-3}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}>0.\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-3x-7}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}>0.\)
Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x^2-3x-7}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}>0.\)
Ta có: \(x^2-3x-7=0.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2}.\\x=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2}.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x+1=0.\Leftrightarrow x=-1.\\ x+2=0.\Leftrightarrow x=-2.\)
Bảng xét dấu:
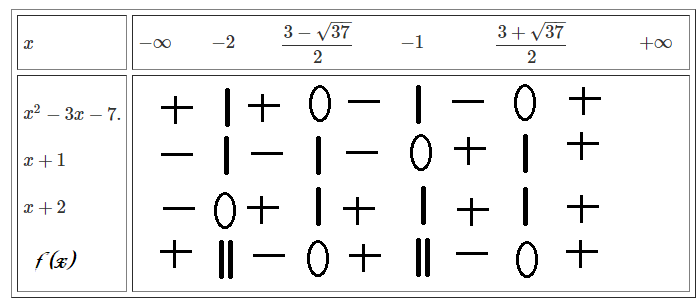
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)>0\Leftrightarrow x\in\left(-\infty-2\right)\cup\left(\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2};-1\right)\cup\left(\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2};+\infty\right).\)
\(\sqrt{x^2-3x+2}\ge3.\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2\ge9.\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-7\ge0.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2}.\\x=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2}.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=x^2-3x-7.\)
\(f\left(x\right)=x^2-3x-7.\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\in(-\infty;\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2}]\cup[\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2};+\infty).\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x^2-3x+2}\ge3\Leftrightarrow x\in(-\infty;\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2}]\cup[\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2};+\infty).\)
giải phương trình: \(\sqrt{\text{x}^2-\text{x}+1}+\sqrt{-2\text{x}^2+\text{x}+2}=\dfrac{\text{ }\text{x}^2-4\text{x}+7}{2}\)
Giải bằng bất đẳng thức Cô si: (ĐK: \(x^2-x+1\ge0;-2x^2+x+2\ge0;x^2-4x+7\)
Ta có: \(x^2-x+1+1\ge2\sqrt{x^2-x+1}\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2-x+1}\le\dfrac{x^2-x+2}{2}\left(1\right)\\ T,T:\sqrt{-2x^2+x+2}\le\dfrac{-2x^2+x+3}{2}\left(2\right)\\ \left(1\right);\left(2\right)\Rightarrow\sqrt{x^2-x+1}+\sqrt{-2x^2+x+2}\le\dfrac{x^2-x+2-2x^2+x+3}{2}=\dfrac{-x^2+5}{2}\\ \Rightarrow\sqrt{x^2-x+1}+\sqrt{-2x^2+x+2}-\dfrac{x^2-4x+7}{2}\le\dfrac{-x^2+5-x^2+4x-7}{2}\\
=\dfrac{-2x^2+4x-2}{2}\\
=-x^2+2x-1
\\
\Rightarrow-\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\)
Điều này chỉ thỏa 1 điều kiên khi x-1=0 ⇔x=1(nhận
Vậy x=1 là nghiệm cuả phương trình
Giải các bất phương trình sau:
1) \(\dfrac{\text{x}-1}{x-3}>1\) 2) \(\sqrt{\text{x}^2+x-12}< 8-x\)
1:
ĐKXĐ: x<>3
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x-3}>1\)
=>\(\dfrac{x-1-\left(x-3\right)}{x-3}>0\)
=>\(\dfrac{x-1-x+3}{x-3}>0\)
=>\(\dfrac{2}{x-3}>0\)
=>x-3>0
=>x>3
2: ĐKXĐ: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>=3\\x< =-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\sqrt{x^2+x-12}< 8-x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}8-x>=0\\x^2+x-12< \left(8-x\right)^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =8\\x^2+x-12-x^2+16x-64< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =8\\17x-76< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x< \dfrac{76}{17}\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}3< =x< \dfrac{76}{17}\\x< =-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 1: Cho bất phương trình \(4\sqrt{\left(x+1\right)\left(3-x\right)}\le x^2-2x+m-3\). Xác định m để bất phương trình nghiệm \(\forall x\in[-1;3]\)
Bài 2: Cho bất phương trình \(x^2-6x+\sqrt{-x^2+6x-8}+m-1\ge0\). Xác định m để bất phương trình nghiệm đúng \(\forall x\in[2;4]\)
cho A=\(\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
điều kiện xác định:\(x\ne1\) \(x\ge0\)
tìm \(mA=\sqrt{x}-2\)
để pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
Lời giải:
$mA=\sqrt{x}-2$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{m(2\sqrt{x}-1)}{\sqrt{x}+1}=\sqrt{x}-2$
$\Rightarrow m(2\sqrt{x}-1)=(\sqrt{x}+1)(\sqrt{x}-2)$
$\Leftrightarrow 2m\sqrt{x}-m=x-\sqrt{x}-2$
$\Leftrightarrow x-\sqrt{x}(2m+1)+(m-2)=0(*)$
Để pt ban đầu có 2 nghiệm pb thì $(*)$ phải có 2 nghiệm dương phân biệt.
Điều này xảy ra khi mà:
\(\left\{\begin{matrix}\
\Delta=(2m+1)^2-4(m-2)>0\\
S=2m+1>0\\
P=m-2>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix}
4m^2+9>0\\
m> \frac{-1}{2}\\
m>2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m>2\)
Tìm điều kiện của bất phương trình \(\sqrt{1-x}\) + \(\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{x+3}}\) < 0
(Chú thích: sqrt là căn bậc 2)
ĐKXĐ: -3 < x <= 1
Bpt --> sqrt(-x^2 - 2x + 3) + x < 0
<=> -3 <= x < (-1 - sqrt(7))/2
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ
--> -3 < x < (-1 - sqrt(7))/2
1, P=(\(\dfrac{\text{x-1}}{\text{x+3}\sqrt{\text{x-4}}}+\dfrac{\sqrt{\text{x}}+1}{1-\sqrt{\text{x}}}\)) : \(\dfrac{\text{x}+2\sqrt{\text{x}}+1}{x-1}\)+1
a, Rút gọn P
b, Tìm x để P<0
giải phương trình:
\(\sqrt{3\text{x}^{2^{ }}-5\text{x}+1}-\sqrt{\text{x}^2-2}=\sqrt{3\left(\text{x}^2-\text{x}-1\right)}-\sqrt{\text{x}^{2^{ }}-3\text{x}+4}\)
ĐKXĐ \(3x^2-5x+1\ge0;x^2-2\ge0;x^2-x-1\ge0\)
Ta có : \(\sqrt{3x^2-5x+1}-\sqrt{x^2-2}=\sqrt{3.\left(x^2-x-1\right)}-\sqrt{x^2-3x+4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{3x^2-5x+1}-\sqrt{3\left(x^2-x-1\right)}=\sqrt{x^2-2}-\sqrt{x^2-3x+4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x^2-5x+1-3.\left(x^2-x-1\right)}{\sqrt{3x^2-5x+1}+\sqrt{3\left(x^2-x-1\right)}}=\dfrac{x^2-2-x^2+3x-4}{\sqrt{x^2-2}+\sqrt{x^2-3x+4}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-2x+4}{\sqrt{3x^2-5x+1}+\sqrt{3\left(x^2-x-1\right)}}=\dfrac{3x-6}{\sqrt{x^2-2}+\sqrt{x^2-3x+4}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x^2-2}+\sqrt{x^2-3x+4}}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3x^2-5x+1}+\sqrt{3\left(x^2-x-1\right)}}=0\left(∗\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Xét phương trình (*) ta có VT > 0 \(\forall x\) mà VP = 0
nên (*) vô nghiệm
Vậy x = 2 là nghiệm phương trình