cho a,b,c là các số thực dương thỏa mãn a + b + c =3 .
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức P = a2 + b2 + c2 +\(\frac{ab+bc+ca}{a^2b+b^2c+c^2a}\)
cho a,b,c là các số thực thỏa mãn a,b≥0;0≤c≤1 và a2+b2+c2 =3.Tìm giá trị lớn nhất và giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức P=ab+bc+ca+3(a+b+c)
\(P\le a^2+b^2+c^2+3\sqrt{3\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)}=12\)
\(P_{max}=12\) khi \(a=b=c=1\)
Lại có: \(\left(a+b+c\right)^2=3+2\left(ab+bc+ca\right)\ge3\Rightarrow a+b+c\ge\sqrt{3}\)
\(a+b+c\le\sqrt{3\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)}=3\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{3}\le a+b+c\le3\)
\(P=\dfrac{\left(a+b+c\right)^2-\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)}{2}+3\left(a+b+c\right)\)
\(P=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(a+b+c\right)^2+3\left(a+b+c\right)-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Đặt \(a+b+c=x\Rightarrow\sqrt{3}\le x\le3\)
\(P=\dfrac{1}{2}x^2+3x-\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(x-\sqrt{3}\right)\left(x+6+\sqrt{3}\right)+3\sqrt{3}\ge3\sqrt{3}\)
\(P_{min}=3\sqrt{3}\) khi \(x=\sqrt{3}\) hay \(\left(a;b;c\right)=\left(0;0;\sqrt{3}\right)\) và hoán vị
Cho a, b, c là các số thực thỏa mãn a ≥ 3 và abc = 1. Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức P = \(\dfrac{2}{3}\).a2 + b2 + c2 - (ab + bc + ca).
Cho các số thực dương a,b,c thỏa mãn \(\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}+\sqrt{c}=1\) tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức \(P=\sqrt{2a^2+ab+2b^2}+\sqrt{2b^2+bc+2c^2}+\sqrt{2c^2+ca+2a^2}\)
\(\sqrt{2a^2+ab+2b^2}=\sqrt{\dfrac{3}{2}\left(a^2+b^2\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(a+b\right)^2}\ge\sqrt{\dfrac{3}{4}\left(a+b\right)^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(a+b\right)^2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(a+b\right)\)
Tương tự:
\(\sqrt{2b^2+bc+2c^2}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(b+c\right)\) ; \(\sqrt{2c^2+ca+2a^2}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(c+a\right)\)
Cộng vế với vế:
\(P\ge\sqrt{5}\left(a+b+c\right)\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\left(\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}+\sqrt{c}\right)^3=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(a=b=c=\dfrac{1}{9}\)
Cho các số thực a, b, c thỏa mãn a2 + b2 + c2 = 1 tìm giá trị lớn nhất và nhỏ nhất của biểu thức P = ab + bc + ca
\(\left(a-b\right)^2+\left(b-c\right)^2+\left(c-a\right)^2\ge0\) ; \(\forall a;b;c\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2+b^2+c^2\ge ab+bc+ca\)
\(\Rightarrow ab+bc+ca\le1\)
\(\Rightarrow P_{max}=1\) khi \(a=b=c\)
Lại có:
\(\left(a+b+c\right)^2\ge0\) ; \(\forall a;b;c\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2+b^2+c^2+2\left(ab+bc+ca\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow ab+bc+ca\ge-\dfrac{a^2+b^2+c^2}{2}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(P_{min}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\) khi \(a+b+c=0\)
Cho a, b, c là các số thực dương thay đổi thỏa mãn a+b+c=3. Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức:
\(P=a^2+b^2+c^2+\frac{ab+bc+ca}{a^2b+b^2c+c^2a}\)
(x−y)2=(x+y)2−4xy=2012−4xy" role="presentation" style="border:0px; direction:ltr; display:inline-block; float:none; font-size:16.38px; line-height:0; margin:0px; max-height:none; max-width:none; min-height:0px; min-width:0px; padding:1px 0px; position:relative; white-space:nowrap; word-spacing:normal; word-wrap:normal" class="MathJax_CHTML mjx-chtml">
xy" role="presentation" style="border:0px; direction:ltr; display:inline-block; float:none; font-size:16.38px; line-height:0; margin:0px; max-height:none; max-width:none; min-height:0px; min-width:0px; padding:1px 0px; position:relative; white-space:nowrap; word-spacing:normal; word-wrap:normal" class="MathJax_CHTML mjx-chtml">, tương đương với việc ta tìm GTLN,GTNN của hay cần tìm GTLN,GTNN của
x≥y" role="presentation" style="border:0px; direction:ltr; display:inline-block; float:none; font-size:16.38px; line-height:0; margin:0px; max-height:none; max-width:none; min-height:0px; min-width:0px; padding:1px 0px; position:relative; white-space:nowrap; word-spacing:normal; word-wrap:normal" class="MathJax_CHTML mjx-chtml"> thì: ;
|x−y|=x−y=x+y−2y=201−2y" role="presentation" style="border:0px; direction:ltr; display:inline-block; float:none; font-size:16.38px; line-height:0; margin:0px; max-height:none; max-width:none; min-height:0px; min-width:0px; padding:1px 0px; position:relative; white-space:nowrap; word-spacing:normal; word-wrap:normal" class="MathJax_CHTML mjx-chtml">
1≤y≤100" role="presentation" style="border:0px; direction:ltr; display:inline-block; float:none; font-size:16.38px; line-height:0; margin:0px; max-height:none; max-width:none; min-height:0px; min-width:0px; padding:1px 0px; position:relative; white-space:nowrap; word-spacing:normal; word-wrap:normal" class="MathJax_CHTML mjx-chtml"> nên:
Lập luận đi ngược lại thì tìm được các cực trị
Cho các số thực a, b, c thay đổi luôn thỏa mãn: a ≥ 1 , b ≥ 1 , c ≥ 1 và a b + b c + c a = 9 .Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất và giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức P = a 2 + b 2 + c 2 .
Áp dụng bất đẳng thức Cauchy cho 2 số dương ta có:
a 2 + b 2 ≥ 2 a b , b 2 + c 2 ≥ 2 b c , c 2 + a 2 ≥ 2 c a
Do đó: 2 a 2 + b 2 + c 2 ≥ 2 ( a b + b c + c a ) = 2.9 = 18 ⇒ 2 P ≥ 18 ⇒ P ≥ 9
Dấu bằng xảy ra khi a = b = c = 3 . Vậy MinP= 9 khi a = b = c = 3
Vì a , b , c ≥ 1 , nên ( a − 1 ) ( b − 1 ) ≥ 0 ⇔ a b − a − b + 1 ≥ 0 ⇔ a b + 1 ≥ a + b
Tương tự ta có b c + 1 ≥ b + c , c a + 1 ≥ c + a
Do đó a b + b c + c a + 3 ≥ 2 ( a + b + c ) ⇔ a + b + c ≤ 9 + 3 2 = 6
Mà P = a 2 + b 2 + c 2 = a + b + c 2 − 2 a b + b c + c a = a + b + c 2 – 18
⇒ P ≤ 36 − 18 = 18 . Dấu bằng xảy ra khi : a = 4 ; b = c = 1 b = 4 ; a = c = 1 c = 4 ; a = b = 1
Vậy maxP= 18 khi : a = 4 ; b = c = 1 b = 4 ; a = c = 1 c = 4 ; a = b = 1
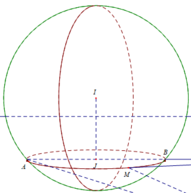
Cho ba số thực dương a,b,c thỏa mãn a 2 + b 2 + c 2 - 2 a + 4 b - 6 c = 10 và a + c=2 . Tính giá trị biểu thức P = 3a + 2b + c khi Q = a 2 + b 2 + c 2 - 14 a - 8 b + 18 c đạt giá trị lớn nhất.
A. 10
B. -10
C. 12
D. -12
Đáp án D

Bài toán trở thành: Tìm M nằm trên đường tròn giao tuyến của mặt cầu (S) và mặt phẳng (P) sao cho KM lớn nhất



Cho ba số dương a,b,c thỏa mãn điều kiện abc=1
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức :Q=\(\frac{bc}{a^2b+a^2c}+\frac{ca}{b^2c+b^2a}+\frac{ab}{c^2a+c^2b}\)
Cho ba số dương a,b,c thỏa mãn \(\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}+\sqrt{c}=\sqrt{3}\). Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức P= \(\sqrt{2a^2+ab+2b^2}+\sqrt{2b^2+bc+2c^2}+\sqrt{2c^2+ca+2a^2}\)