Mn ơi, hướng dẫn em cách để giống mẫu đi ạ!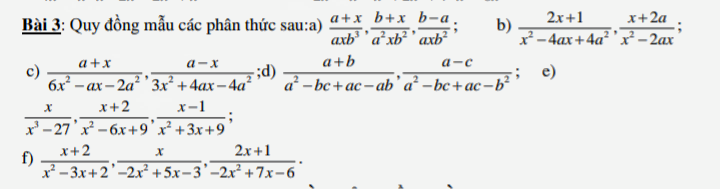

Những câu hỏi liên quan
mn ơi, hướng dẫn cho mik bài 1 đc k ạ! mik cảm ơn mn
mn hướng dẫn giúp em với ạ
anh chị gì ơi
hướng dẫn em lại cách làm với ( toán 7 toán số bài 22)
hướng dẫn nhé!
310;−56;−123=−53;413;0;" role="presentation" style="border:0px; direction:ltr; display:inline-block; float:none; font-size:20.32px; line-height:0; margin:0px; max-height:none; max-width:none; min-height:0px; min-width:0px; padding:1px 0px; position:relative; white-space:nowrap; word-spacing:normal; word-wrap:normal" class="MathJax_CHTML mjx-chtml">
310=39130;413=40130" role="presentation" style="border:0px; direction:ltr; display:inline-block; float:none; font-size:20.32px; line-height:0; margin:0px; max-height:none; max-width:none; min-height:0px; min-width:0px; padding:1px 0px; position:relative; white-space:nowrap; word-spacing:normal; word-wrap:normal" class="MathJax_CHTML mjx-chtml">
310<413" role="presentation" style="border:0px; direction:ltr; display:inline-block; float:none; font-size:20.32px; line-height:0; margin:0px; max-height:none; max-width:none; min-height:0px; min-width:0px; padding:1px 0px; position:relative; white-space:nowrap; word-spacing:normal; word-wrap:normal" class="MathJax_CHTML mjx-chtml">
−56=−2024;−53=−4024;−78=−2124⇒−4024<−2124<−2024(Do−40<−21<−20)⇒−53<−78<−56" role="presentation" style="border:0px; direction:ltr; display:inline-block; float:none; font-size:20.32px; line-height:0; margin:0px; max-height:none; max-width:none; min-height:0px; min-width:0px; padding:1px 0px; position:relative; white-space:nowrap; word-spacing:normal; word-wrap:normal" class="MathJax_CHTML mjx-chtml">
Vậy:
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
- sách bài tập hay giáo khoa thế?
- nếu là giáo khoa thì bạn hãy nhớ là số hữu tỉ âm luôn nhỏ hơn các số hữu tỉ dương. Do đó mình chỉ cần so sánh các số hữu tỉ âm với nhau và các số hữu tỉ dương với nhau.
- rồi quy đồng, đổi số thập phân -> phân số là được thôi.
- Ghi nhớ : Để so sánh hai số hữu tỉ ta viết chúng dưới dạng phân số cùng mẫu số dương rồi so sánh tử số của chúng.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
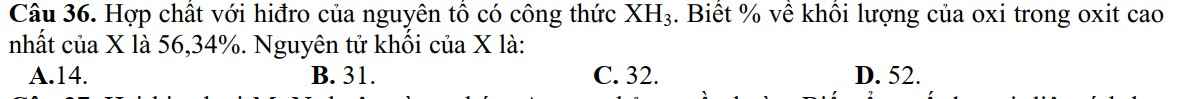
Mn có thể hướng dẫn em câu này dc không ạ?
Oxit cao nhất của X là X2O5
Ta có: \(\dfrac{16\cdot5}{2X+16\cdot5}=\dfrac{56,34}{100}\) \(\Leftrightarrow X=31\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
hãy biểu diễn lực kéo cái tủ với lực 200N theo phương nằm ngang, chiều từ phải sang trái.(viết cách giải và hướng dẫn cách biểu diễn lực có ...Newton)
MN KÍU EM GẤP Ạ, E ĐAG ÔN THI GẤP![]()
m.n hướng dẫn em cách nào để giải những bài gtnn gtln có hằng đẳng thức như này vs ạ
VD:3x2-5x+3
Phương trình bậc hai có dạng: a\(x^2\) + b\(x\) + c
Bước 1: Đưa nó về bình phương của một tổng hoặc một hiệu cộng với một số nào đó. nếu a > 0 thì em sẽ tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất; nếu a < 0 thì em sẽ tìm giá trị lớn nhất
Bước 2: lập luận chỉ ra giá trị lớn nhất hoặc nhỏ nhất
Bước 3: kết luận
Giải:
A = 3\(x^2\) - 5\(x\) + 3 Vì a = 3 > 0 vậy biểu thức A chỉ tồn tại giá trị nhỏ nhất
A = 3\(x^2\) - 5\(x\) + 3
A = 3.(\(x\)2 - 2.\(x\).\(\dfrac{5}{6}\) + \(\dfrac{25}{36}\)) + \(\dfrac{11}{12}\)
A = 3.(\(x\) - \(\dfrac{5}{6}\))2 + \(\dfrac{11}{12}\)
Vì (\(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\))2 ≥ 0 ⇒ 3.(\(x\) - \(\dfrac{5}{6}\))2 ≥ 0 ⇒ 3.(\(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\))2 + \(\dfrac{11}{12}\) ≥ \(\dfrac{11}{12}\)
Amin = \(\dfrac{11}{12}\) ⇔ \(x\) = \(\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
: " Sao giờ này chưa tới rước con ? "
a) Xác định lời dẫn . Cho biết lời dẫn trực tiếp hay gián tiếp
b) Hãy chuyển sang cách dẫn ngược lại
MẤY ANH CHỊ ƠI GIÚP EM ĐI Ạ . EM CẢM ƠN NHIỀU
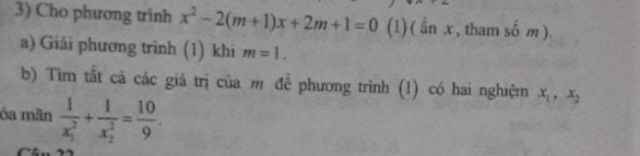 Hướng dẫn em cách làm phần b với ạ :
Hướng dẫn em cách làm phần b với ạ :
Lời giải:
Ta thấy
$\Delta'=(m+1)^2-(2m+1)=m^2\geq 0$ với mọi $m\in\mathbb{R}$ nên pt luôn có 2 nghiệm $x_1,x_2$
Áp dụng định lý Viet:
$x_1+x_2=2(m+1)$
$x_1x_2=2m+1$
$x_1,x_2\neq 0\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2=2m+1\neq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow m\neq \frac{-1}{2}$
Từ hệ thức Viet ta có:
$\frac{1}{x_1^2}+\frac{1}{x_2^2}=\frac{10}{9}$
$\Leftrightarrow (\frac{1}{x_1}+\frac{1}{x_2})^2-\frac{2}{x_1x_2}=\frac{10}{9}$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{(x_1+x_2)^2}{(x_1x_2)^2}-\frac{2}{x_1x_2}=\frac{10}{9}$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{4(m+1)^2}{(2m+1)^2}-\frac{2}{2m+1}=\frac{10}{9}$
$\Leftrightarrow 9(4m^2+4m+2)=10(4m^2+4m+1)$
$\Leftrightarrow m^2+m-2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (m-1)(m+2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow m=1$ hoặc $m=-2$ (tm)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Quy đồng mẫu 2 phân thức sau:
Mn ơi giúp em với ạ, 10h là em nộp bài rồi ạ!
Câu c mình làm rồi: Mn ơi, hướng dẫn em cách để giống mẫu đi ạ! - Hoc24
\(d,\dfrac{x}{x^3-27}=\dfrac{x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+3x+9\right)}=\dfrac{x\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)^2\left(x^2+3x+9\right)}\\ \dfrac{x+2}{x^2-6x+9}=\dfrac{x+2}{\left(x-3\right)^2}=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2+3x+9\right)}{\left(x-3\right)^2\left(x^2+3x+9\right)}\\ \dfrac{x-1}{x^2+3x+9}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2}{\left(x-3\right)^2\left(x^2+3x+9\right)}\)
\(f,\dfrac{x+2}{x^2-3x+2}=\dfrac{x+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(2x-3\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)}\\ \dfrac{x}{-2x^2+5x-3}=\dfrac{-x}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{-x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)}\\ \dfrac{2x+1}{-2x^2+7x-6}=\dfrac{-\left(2x+1\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)}=\dfrac{-\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(\dfrac{a+x}{6x^2-ax-2a^2}=\dfrac{\left(a+x\right)}{\left(2x+a\right)\left(3x-2a\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{a-x}{3x^2+4ax-4a^2}=\dfrac{a-x}{\left(x+2a\right)\left(3x-2a\right)}\)
Do đó ta quy đồng:
\(\dfrac{a+x}{6x^2-ax-2a^2}=\dfrac{\left(a+x\right)\left(x+2a\right)}{\left(x+2a\right)\left(2x+a\right)\left(3x-2a\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{a-x}{3x^2+4ax-4a^2}=\dfrac{\left(a-x\right)\left(2x+a\right)}{\left(x+2a\right)\left(2x+a\right)\left(3x-2a\right)}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)





















