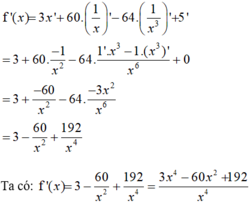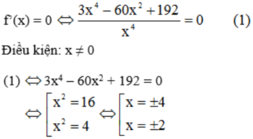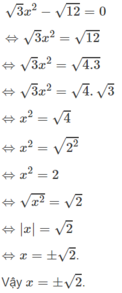Giải phương trình : 3x2+60x-900=0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải phương trình f ' x = 0 , biết rằng: f x = 3 x + 60 x - 64 x 3 + 5
Giải phương trình f'(x) = 0, biết rằng f ( x ) = 3 x + 60 x - 64 x 3 + 5
Giải phương trình: 7x4+60x3+70x2-100x+17=0
Giải phương trình : 48x4 + 144x3 + 148x2 + 60x + 7 = 0 .
Giải phương trình bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích :
3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0
x2 - 4x + 1 = 0
2x2 - 6x + 1 = 0
3x2 + 4x - 4 = 0
3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
=> 3x2 + 3x - x - 1 = 0
=> 3x(x + 1) - (x + 1) = 0
=> (3x - 1)(x + 1) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-1=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
=> x2 - 2x - 3x + 6 = 0
=> x(x - 2) - 3(x - 2) = 0
=> (x - 3)(x - 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0
=> 3x2 + 6x + x + 2 = 0
=> 3x(x + 2) + (x + 2) = 0
=> (3x + 1)(x + 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x+1=0\\x+2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{3}\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1, \(3x^2+2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+3x-x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
2, \(x^2-5x+6=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=3\end{cases}}}\)
3, \(3x^2+7x+2=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+6x+x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+2=0\\3x+1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=-\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(x^2-4x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt{3}+2;x=2-\sqrt{3}\)
\(2x^2-6x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-12x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)^2=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{\sqrt{7}+3}{2};x=\frac{3-\sqrt{7}}{2}\)
\(3x^2+4x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-2x+6x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2;x=\frac{2}{3}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình: 3x2 – 2 = 0.
3x2 - 2 = 0⇔ 3x2=2 ⇔ x2 = 2/3 ⇔ x = ±√(2/3)
Vậy phương trình có hai nghiệm
x1 = √(2/3); x2 = -√(2/3)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình: 3 x 2 – 2 = 0 .
3 x 2 − 2 = 0 ⇔ 3 x 2 = 2 ⇔ x 2 = 2 / 3 ⇔ x = ± ( 2 / 3
Vậy phương trình có hai nghiệm
x 1 = ( 2 / 3 ; x 2 = - ( 2 / 3
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình: 3 x 2 - 12 = 0
Giải các phương trình trùng phương: 2x4 – 3x2 – 2 = 0
2x4 – 3x2 – 2 = 0; (1)
Đặt x2 = t, điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 2t2 – 3t – 2 = 0 (2)
Giải (2) : Có a = 2 ; b = -3 ; c = -2
⇒ Δ = (-3)2 - 4.2.(-2) = 25 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm
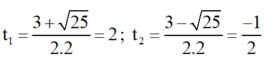
Chỉ có giá trị t1 = 2 thỏa mãn điều kiện.
+ Với t = 2 ⇒ x2 = 2 ⇒ x = √2 hoặc x = -√2;
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm S = {-√2 ; √2}.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)