Giải chi tiết giúp e vs

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải chi tiết giúp e vs 
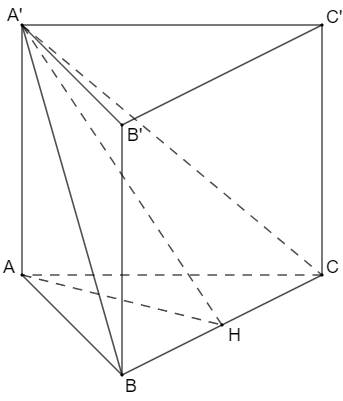
Góc giữa hai mặt phẳng (A'BC) và (ABC) bằng 600
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{A'HA}=60^\circ\)
Tam giác AA'H vuông tại A: \(AH=AA'.cot60^\circ=\dfrac{2a\sqrt{3}}{3}\)
Tam giác ABC đều nên \(AH=\dfrac{BC\sqrt{3}}{2}\) \(\Rightarrow BC=\dfrac{4a}{3}\)
Thể tích khối lăng trụ là: \(V=\dfrac{1}{2}AH\cdot BC\cdot AA'=\dfrac{8\sqrt{3}}{9}a^3\).
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải chi tiết giúp e vs 
\(g'\left(x\right)=f'\left(x\right)f\left(f\left(x\right)\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}f'\left(x\right)=0\\f\left(f\left(x\right)\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(f\left(f\left(x\right)\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}f\left(x\right)=x_1\left(x_1< -1\right)\\f\left(x\right)=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(f\left(x\right)=x_1\left(x_1< -1\right):\) phương trình có 1 nghiệm.
\(f\left(x\right)=1:\) phương trình có 3 nghiệm.
Số nghiệm của phương trình \(g'\left(x\right)=0\) là 6.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải chi tiết giúp e vs 
ĐKXĐ: \(x>1\)
\(2log_5\left(x-1\right)-log_5\left(4x+m\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow log_5\left(x-1\right)^2=log_5\left(4x+m\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=4x+m\)
\(\Rightarrow m=x^2-6x+1\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(x\right)=x^2-6x+1\) với \(x>1\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=2x-6=0\Rightarrow x=3\)
\(f\left(1\right)=-4\) ; \(f\left(3\right)=-8\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Pt có 2 nghiệm pb thỏa mãn \(x>1\) khi \(-8< m< -4\)
\(\Rightarrow m=\left\{-7;-6;-5\right\}\) có 3 giá trị nguyên
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải chi tiết giúp e vs 
\(f'\left(x\right)=x^2\left(x+2\right)\) có đúng 1 nghiệm bội lẻ \(x=-2\)
\(y=f\left(x^3-3x\right)\Rightarrow y'=\left(3x^2-3\right).f'\left(x^3-3x\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x^2-3=0\\x^3-3x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-1=0\\\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+2\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\left\{-1;1;-2\right\}\) hàm có 3 điểm cực trị
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
f
′
(
x
)
=
x
2
(
x
+
2
)
có đúng 1 nghiệm bội lẻ
x
=
−
2
y
=
f
(
x
3
−
3
x
)
⇒
y
′
=
(
3
x
2
−
3
)
.
f
′
(
x
3
−
3
x
)
=
0
⇒
[
3
x
2
−
3
=
0
x
3
−
3
x
=
−
2
⇒
[
x
2
−
1
=
0
(
x
−
1
)
2
(
x
+
2
)
=
0
⇒
x
=
{
−
1
;
1
;
−
2
}
hàm có 3 điểm cực trị
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải chi tiết giúp e vs 
Giải chi tiết giúp e vs 
Đặt \(3^x=t,\left(t>0\right)\)
Phương trình đã cho trở thành: \(t^2-2\left(m-1\right)t+2m+1=0\) (2)
Yêu cầu bài toán tương đương với phương trình (2) có hai nghiệm dương phân biệt
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta'=\left(m-1\right)^2-2m-1>0\\t_1+t_2=2\left(m-1\right)>0\\t_1\cdot t_2=2m+1>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}m< 0\\m>4\end{matrix}\right.\\m>1\\m< -\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m>4\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải chi tiết giúp e vs 
Hàm số có tập xác định là \(ℝ\) \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-m+1>0\forall x\inℝ\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=1-\left(-m+1\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m< 0\)
\(m\in\left(-2021;2021\right)\), m nguyên nên có 2020 giá trị của m thỏa mãn.
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải chi tiết giúp e vs 
\(y'=x^2+2mx+2m\)
Hàm đồng biến trên R khi và chỉ khi \(y'\ge0;\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=1>0\\\Delta'=m^2-2m\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow0\le m\le2\)
Có 2 giá trị nguyên dương của m thỏa mãn (1 và 2)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Giải chi tiết giúp e vs
Giả sử (P) cắt đáy nón theo đoạn thẳng AB
Độ dài AB là: \(2\left(1+\sqrt{5}\right)a-2.a\sqrt{5}=2a\)
Gọi H là trung điểm AB \(\Rightarrow OH\perp AB\)
\(AH=\dfrac{1}{2}AB=a\); \(SO=\sqrt{\left(a\sqrt{5}\right)^2-\left(2a\right)^2}=a\)
\(OH=\sqrt{R^2-AH^2}=a\sqrt{3}\)
Từ O kẻ \(OK\perp SH\Rightarrow OK=d\left(O;\left(P\right)\right)\)
Áp dụng hệ thức lượng trong tam giac vuông SOH:
\(\dfrac{1}{OK^2}=\dfrac{1}{SO^2}+\dfrac{1}{OH^2}=\dfrac{4}{3a^2}\Rightarrow OK=\dfrac{a\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)





