Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên:
a) x^3 - 8x^2 +2x= x^2y +y
a, giải phương trình : 4x²+√2x+3=8x+1
B, giải hệ phương trình :
{√x+y+1+(x+2y)=4(x+y) ²+√3*√x+y
X-4y-3=(2y)²-√2-x²
Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên:
a) \(x!+y!=\left(x+y\right)!\)
b) \(x^{17}+y^{17}=19^{17}\)
a, Khi \(x = 0 ⇔ 0! + y! = y! ⇔ \) Vô lý.
\(\rightarrow x \ne y\)\(\ne 0\)
Khi \(x = y \rightarrow 2 . x! = (2x)! \rightarrow 2x! = x(x+1)(x+2)...(2x)=>x(x+1)(x+2)...(2x) = 2 \rightarrow x = y = 1. \)
Nếu \(x \ne y \rightarrow\) Vì vai trò của \(x,y\) là bình đẳng nên giả sử \(x < y\)
\(\rightarrow x!+y!<2.y!≤(y+1).y!=(y+1)!<(x+y)!\)
Vì \(x \ne y \ne 1 => (x+y) \ne (y+1) \rightarrow (x+y)! \ne (y+1).\)
Vậy \((x,y) = {(1,1)}.\)
b, Chứng minh bằng phương pháp phản chứng:
Giả sử \(x^{17} + y^{17} = 19^{17} \) có nghiệm nguyên.
Không mất tổng quát, giả sử \(x < y\)
\(\rightarrow x^{17} < y^{17} ≤ 19^{17}\)
\(\rightarrow (y+1)^{17} ≤ 19^{17} \)
\(\rightarrow y^{17} + 17y^{16} = 19^{17}\)
Mà \(\rightarrow x > 17 \rightarrow x = y =18.\)
Thử lại không đúng, suy ra giả sử sai.
\(\rightarrow\) Không tồn tại số nguyên thỏa mãn.
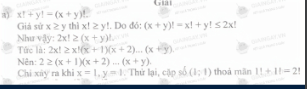

From : https://solvee.vn/r/baitap/812003032
Giải các phương trình và hệ phương trình sau:
1) \(\dfrac{x-1}{3}=x+1\)
2) \(\sqrt{16x^2+8x+1}-2=x\)
3)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=17\\x-2y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(1,\dfrac{x-1}{3}=x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1=3x+3\\ \Leftrightarrow3x-x=3+1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=2\)
PT có tập nghiệm S = {2}
\(2,\sqrt{16x^2+8x+1}-2=x\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(4x+1\right)^2}-2=x\\\Leftrightarrow 4x+1-2=x\\ \Leftrightarrow4x-x=2-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
PT có tập nghiệm S = {1/3}
\(3,\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=17\\x-2y=1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=17\\2x-4y=2\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+y\right)-\left(2x-4y\right)=17-2\\ \Leftrightarrow5y=15\\ \Leftrightarrow y=3\\ \Leftrightarrow2x+3=17\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=14\\ \Leftrightarrow x=7\)
PTHH có tập nghiệm (x; y) là (7; 3)
Giải hệ phương trình:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}y^3+\sqrt{8x^4-2y}=2\left(2x^4+3\right)\\\sqrt{2x^2+x+y}+2\sqrt{x+2y}=\sqrt{9x-2x^2+19y}\end{cases}}\)
Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên \(x^2+y^2+2x+2y=x^2y^2-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+y^2+2xy+2x+2y+1=x^2y^2+2xy+1-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y+1\right)^2=\left(xy+1\right)^2-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(xy+1\right)^2-\left(x+y+1\right)^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(xy+x+y+2\right)\left(xy-x-y\right)=1\)
Phương trình ước số cơ bản
Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên: (3x + 2y)(2x - y)2 = 7(x + y) -2
Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên: (3x + 2y)(2x - y)2 = 7(x + y) -2
\(\left(3x+2y\right)\left(2x-y\right)^2=7\left(x+y\right)-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2y\right)\left(2x-y\right)^2-7\left(x+y\right)+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2y\right)\left(2x-y\right)^2-7x-7y+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2y\right)\left(2x-y\right)^2-\left(9x+6x\right)+\left(2x-y\right)+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2y\right)\left(2x-y\right)^2-3\left(3x+2y\right)+\left(2x-y\right)+2=0\)
Đặt \(3x+2y\) = a ,đặt \(2x-y\) = b, ta có:
\(ab^2-3a+b+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a\left(b^2-3\right)=-2-b\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a=\dfrac{-2-b}{b^2-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a=\dfrac{b+2}{3-b^2}\\ \Leftrightarrow a\left(2-b\right)=\dfrac{4-b^2}{3-b^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a\left(2-b\right)=\dfrac{3-b^2+1}{3-b^2}\\ \Leftrightarrow a\left(2-b\right)=1+\dfrac{1}{3-b^2}\\ \Leftrightarrow1⋮3-b^2\\ \Leftrightarrow b^2-3\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow b^2\in\left\{4;2\right\}\\ \)
mà 2 không chính phương
\(\Rightarrow b\in\left\{2;-2\right\}\Rightarrow a=0\)
đến đây bạn tự giải tiếp
Biểu diễn miễn nghiệm của hệ phương trình:-2x+y=2; -x+2y=4; x+y=5 giải thích và vẽ miền nghiệm
Cho hệ phương trình {2x + y = 5m -1 và x - 2y=2 a) Giải HPT với m = 1 b) Tìm m để HPT có nghiệm ( x ; y) thoả mãn 2x - y = 3