giải pt dạng asinx + bscosx = c câu g,h,j

Giải pt dạng asinx+bcosx=c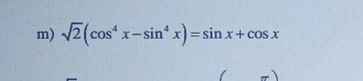
\(\sqrt{2}\left(cos^4x-sin^4x\right)=sinx+cosx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}\left(cos^2x+sin^2x\right)\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left(cosx+sinx\right)=sinx+cosx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(sinx+cosx\right)\left[\sqrt{2}\left(cosx-sinx\right)-1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}sin\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\left[2cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)-1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sin\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=0\\cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}=k\pi\\x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}=-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\) (\(k\in Z\)) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{12}+k2\pi\\x=-\dfrac{7\pi}{12}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)(\(k\in Z\))
Vậy...
Giải Pt dạng asinx+bcosx=c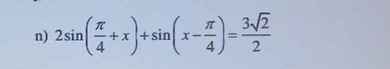
Lời giải:
PT \(\Leftrightarrow 2(\sin \frac{\pi}{4}\cos x+\cos \frac{\pi}{4}\sin x)+(\sin x\cos \frac{\pi}{4}-\cos x\sin \frac{\pi}{4})=\frac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{2}(\cos x+\sin x)+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\sin x-\cos x)=\frac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 2(\cos x+\sin x)+(\sin x-\cos x)=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \cos x+3\sin x=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{1}{\sqrt{10}}\cos x+\frac{3}{\sqrt{10}}\sin x=\frac{3}{\sqrt{10}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \sin t\cos x+\cos t\sin x=\cos t\) với \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{10}}=\sin t(t\in (0;\pi))\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \sin (t+x)=\cos t=\sin (\frac{\pi}{2}-t)\)
\(\Rightarrow t+x=\frac{\pi}{2}-t+2k\pi\) hoặc $t+x=\frac{\pi}{2}+t+2k\pi$ với $k$ nguyên.
Giải pt dạng asinx+bcosx =c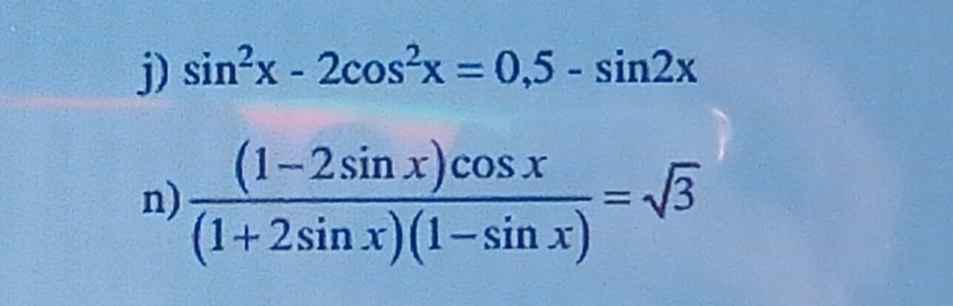
j)\(sin^2x-2cos^2x=0,5-sin2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin^2x-2cos^2x=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(sin^2x+cos^2x\right)-2.sinx.cosx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}sin^2x+2.sinx.cosx-\dfrac{5}{2}cos^2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}\left(sinx-cosx\right)\left(sinx+5cosx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx-cosx=0\left(1\right)\\sinx+5cosx=0\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Từ (1)\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}sin\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}=k\pi\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\) (\(k\in Z\))
Từ (2)\(\Leftrightarrow sinx=-5cosx\)
Xét \(cosx=0\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sinx=1\\sin2x=0\end{matrix}\right.\) thay vào pt ban đầu thấy ktm
=>\(cosx\ne0\)
Pt (2)\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}=-5\Leftrightarrow tanx=-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=arctan\left(-5\right)+k\pi\) (\(k\in Z\))
Vậy...
n) Đk:\(x\ne\dfrac{-\pi}{6}+k2\pi;x\ne\dfrac{7\pi}{6}+k2\pi;x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\) (\(k\in Z\))
PT \(\Rightarrow\left(1-2.sinx\right)cosx=\sqrt{3}\left(1+2sinx\right)\left(1-sinx\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-2.sinx.cosx=\sqrt{3}\left(1+sinx-2sin^2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-sin2x=\sqrt{3}\left(cos^2x+sin^2x+sinx-2sin^2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-sin2x=\sqrt{3}\left(cos^2x-sin^2x+sinx\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-sin2x=\sqrt{3}\left(cos2x+sinx\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-\sqrt{3}sinx=sin2x+\sqrt{3}cos2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2.cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=2.cos\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}-k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{-\pi}{18}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\) (k nguyên)
Kết hợp với đk => \(x=-\dfrac{\pi}{18}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{3}\) (k nguyên)
Giải pt asinx + bcosx =c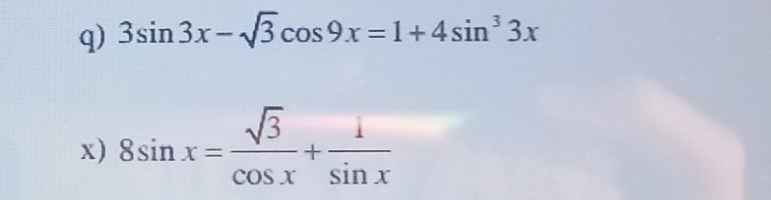
q) \(3sin3x-\sqrt{3}cos9x=1+4sin^33x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3sin3x-\sqrt{3}cos9x=1+3sin3x-sin9x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin9x-\sqrt{3}cos9x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin9x.cos\dfrac{\pi}{3}-cos9x.sin\dfrac{\pi}{3}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(9x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{18}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{9}\\x=\dfrac{7\pi}{54}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\) (\(k\in Z\))
Vậy...
x) \(8sinx=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{cosx}+\dfrac{1}{sinx}\)
(đk: \(cosx\ne0;sinx\ne0\) \(\Rightarrow sin2x\ne0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\);\(k\in Z\))
\(\Leftrightarrow8sinx=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}sinx+cosx}{cosx.sinx}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(8sinx.cosx.sinx=\sqrt{3}sinx+cosx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4sinx.sin2x=\sqrt{3}sinx+cosx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(cosx-cos3x\right)=\sqrt{3}sinx+cosx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-\sqrt{3}sinx=2cos3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx.cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)-sinx.sin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=cos3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=cos3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}-k\pi\\x=-\dfrac{\pi}{12}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)(\(k\in Z\)) (thỏa mãn)
Vậy...
giải pt asinx + bcosx = c

Pt \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{5}sin\left(x+1\right)+\dfrac{4}{5}cos\left(x+1\right)=1\)
Đặt \(cos\alpha=\dfrac{3}{5}\Rightarrow sin\alpha=\dfrac{4}{5}\) ( vì \(cos^2\alpha+sin^2\alpha=1\))
Pt tt: \(sin\left(x+1\right).cos\alpha+cos\left(x+1\right).sin\alpha=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(x+1+\alpha\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1+\alpha=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\) (\(k\in Z\))
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}-\alpha-1+k2\pi\) (\(k\in Z\))
`3sin(x+1)+4cos(x+1)=5`
`<=> 3/5 sin(x+1) + 4/5 cos (x+1)=1`
Vì `(3/5)^2 + (4/5)^2 = 1` nên ta có:
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sinα=\dfrac{3}{5}\\cosα=\dfrac{4}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
`sin α . sin(x+1)+cosa . cos(x+1)=1`
`<=> cos(α - x-1)=1`
`<=> α -x-1=k2π`
`<=> x=α-1+k2α (k \in ZZ)`
Nêu cách giải phương trình lượng giác cơ bản , cách giải phương trình a sin x + b cos x = c .
a) Cách giải các phương trình lượng giác cơ bản:
+ Phương trình sin x = a.
Nếu |a| > 1 ⇒ phương trình vô nghiệm.
Nếu |a| ≤ 1 ⇒ tìm một cung α sao cho sin α = a.
Khi đó phương trình trở thành sin x = sin α
⇒ Phương trình có nghiệm: 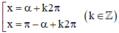
+ Phương trình cos x = a.
Nếu |a| > 1 ⇒ phương trình vô nghiệm.
Nếu |a| ≤ 1 ⇒ tìm một cung α sao cho cos α = a.
Khi đó phương trình trở thành cos x = cos α.
⇒ Phương trình có nghiệm: x = ±α + k2π (k ∈ Z).
+ Phương trình tan x = a.
Tìm một cung α sao cho tan α = a.
Khi đó phương trình trở thành tan x = tan α.
⇒ Phương trình có nghiệm x = α + kπ (k ∈ Z).
+ Phương trình cot x = a
Tìm một cung α sao cho cot α = a.
Khi đó phương trình trở thành cot x = cot α.
⇒ Phương trình có nghiệm x = α + kπ (k ∈ Z).
b) Cách giải phương trình a.sin x + b.cos x = c.
+ Nếu a = 0 hoặc b = 0 ⇒ Phương trình lượng giác cơ bản .
+ a ≠ 0 và b ≠ 0. Chia cả hai vế của phương trình cho  ta được:
ta được:

Ta giải phương trình trên như phương trình lượng giác cơ bản.
Ai giải được câu này thì cho 10 tỉ :a,s,d,f,g,h,j,...,l
Trả lời
a,s,d,f,g,h,j,k,l.
# Hok tốt #
cho ΔABC nhọn (AB < AC) đường cao AD,BE,CF cắt nhau tại H
a) C/mr : ΔAEB đồng dạng △AFC , △AEF đồng dạng △ABC
b) C/mr: HB.HE=HC.HF,từ đó suy ra △HEF đồng dạng △ HCB
c)C/mr ΔHDB đồng dạng △CDA
d) Từ D kẻ DI ⊥ AC ( I ϵ AC ) C/mr \(AD^2\)= AI. AC
e) C/mr EB là tia phân giác của góc FED
j)C/mr \(BC^2\)= BH.BE+CH.CF
g)Từ D kẻ DJ ⊥ AB( J ϵ AB ),DK⊥ CF (Kϵ CF)
C/mr 3 điểm I,J,K thẳng hàng
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình sau:
a) b) c) d) e) f) | g) h) i) j) k) l) |