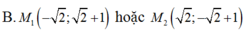Đường tròn (C) tâm \(I\left(1;-2\right)\) bán kính \(R=\sqrt{5}\)
Điểm M thuộc (C) thỏa mãn khoảng cách từ M tới \(\Delta\) lớn nhất khi M là giao điểm của (C) và đường thẳng d qua I và vuông góc \(\Delta\)
Phương trình d có dạng:
\(2\left(x-1\right)-1\left(y+2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow2x-y-4=0\)
Hệ pt tọa độ giao điểm (C) và d:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+y^2-2x+4y=0\\y=2x-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+\left(2x-4\right)^2-2x+4\left(2x-4\right)=0\\y=2x-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2x=0\\y=2x-4\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}M\left(0;-4\right)\\M\left(2;0\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(M\left(0;-4\right)\Rightarrow d\left(M;\Delta\right)=\dfrac{\left|-2.4+7\right|}{\sqrt{1^2+2^2}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\)
Với \(M\left(2;0\right)\Rightarrow d\left(M;\Delta\right)=\dfrac{\left|2+0+7\right|}{\sqrt{1^2+2^2}}=\dfrac{9}{\sqrt{5}}\)
Do \(\dfrac{9}{\sqrt{5}}>\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\) nên \(M\left(2;0\right)\) là điểm cần tìm