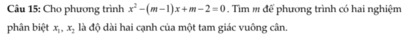x2-(m-1)x+m-2=0(1)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì Δ=(-m+1)2-4(m-2)
=m2-2m+1-4m+8
=m2-6m+9
=(m-3)2≥0 với mọi m
⇒phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt
Áp dụng định lý Vi-ét ta có:\(\begin{cases} x_1+x_2=m-2 \\ x_1.x_2=m-1 \end{cases}\)(2)
TH1:x1,x2 là hai cạnh góc vuông
⇒x1=x2
Từ (2)\(\begin{cases} x_1+x_1=m-2 \\ x_1^2=m-1 \end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\begin{cases} x_1=\frac{m-1}{2}\\ x_1=\sqrt{m-2} \end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\dfrac{m-1}{2}\)=\(\sqrt{m-2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\dfrac{m^2-2m+1}{4}\)=m-2
\(\Leftrightarrow\)m2-6m+9=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)(m-3)2=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)m=3
TH2:x1 là cạnh huyền,x2 là cạnh góc vuông
⇒x1=\(\sqrt{2}\)x2
Từ (2)⇒\(\begin{cases} \sqrt{2} x_2+x_2=m-1 \\ \sqrt{2} x_2^2=m-2 \end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\begin{cases} x_2= \frac{m-1}{1+\sqrt{2}} \\ x_2=\sqrt{\frac{m-2}{\sqrt{2}}} \end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\dfrac{m-1}{1+\sqrt{2}}\)=\(\sqrt{\dfrac{m-2}{\sqrt{2}}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\dfrac{m^2-2m+1}{3+2\sqrt{2}}\)=\(\dfrac{m-2}{\sqrt{2}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(3+2\sqrt{2}\right)\)\(m\)\(-6-2\sqrt{2}\)\(=\sqrt{2}m^2-2\sqrt{2}m+\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}m^2-\left(4\sqrt{2}+3\right)m+3\sqrt{2}+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)rồi m bằng bao nhiêu thì tự giải nhé mệt r