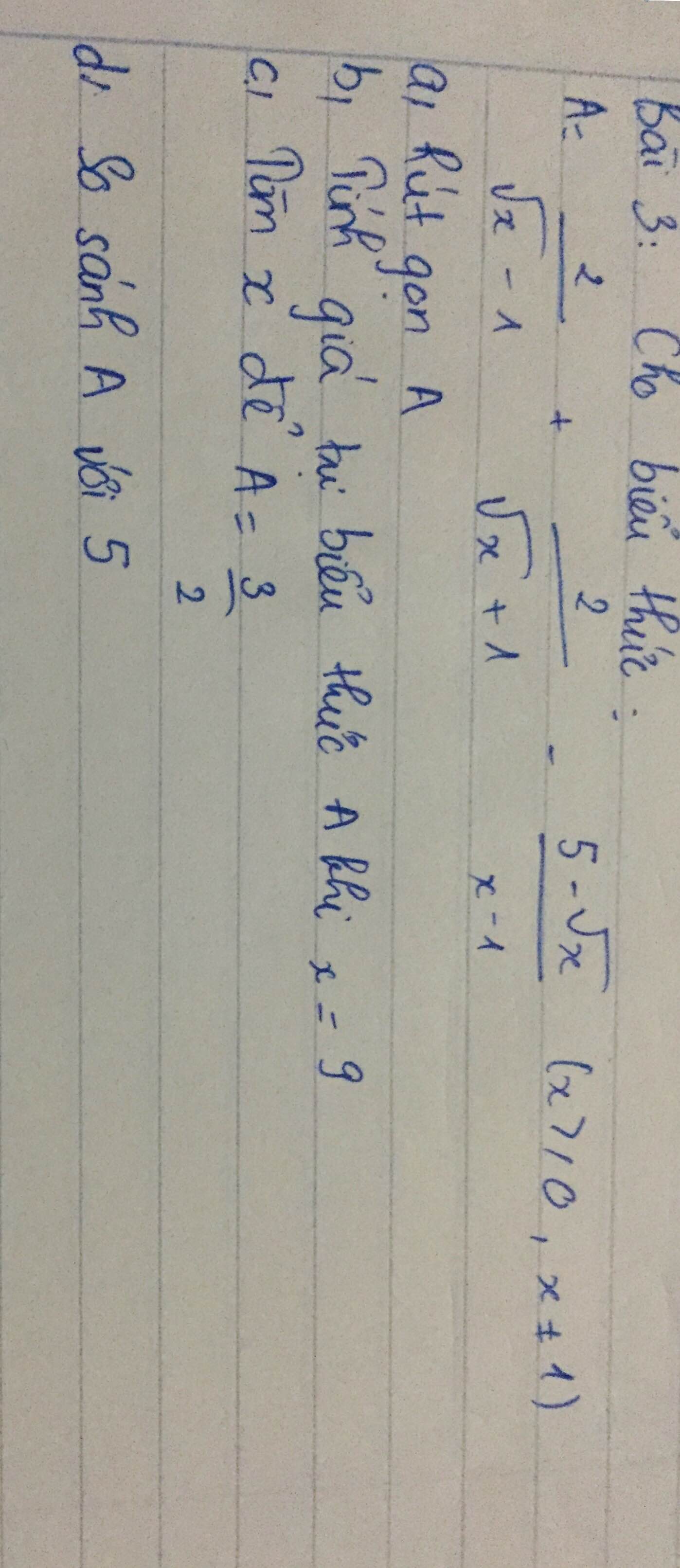A = \(\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)+2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)-\left(5-\sqrt{x}\right)}{x-1}\)
= \(\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt{x}+1+\sqrt{x}-1\right)-\left(5-\sqrt{x}\right)}{x-1}\)
= \(\dfrac{2.2\sqrt{x}-\left(5-\sqrt{x}\right)}{x-1}\)
= \(\dfrac{5\sqrt{x}-5}{x-1}\) = \(\dfrac{5\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{x-1}\) = \(\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
b) Tại x=9 ta có A = \(\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{9}+1}\) = \(\dfrac{5}{4}\)
c) A = \(\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+1}\) = \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)
⇒ 3\(\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\) = 10
⇒ \(\sqrt{x}\) = \(\dfrac{10}{3}\) - 1
⇒ x = \(\dfrac{49}{9}\)
d) ta có: \(\sqrt{x}\ge0\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{x}+1\ge1\)
⇒ \(\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+1}\le5\)
vậy A \(\le\) 5