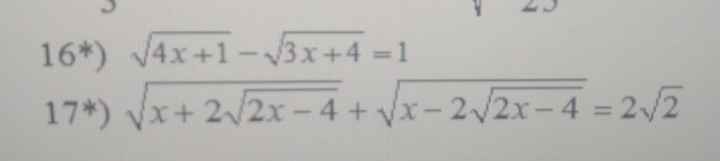\(a)\) Thay \(m=6\) vào phương trình (1), ta có:
\(x^2+x-6=0.\\ \Delta=1^2-4.1.\left(-6\right).\\ \Delta=25>0.\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt.
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{25}}{2.1}=\dfrac{-1+5}{2}=2.\\x_2=\dfrac{-1-\sqrt{25}}{2.1}=\dfrac{-1-5}{2}=-3.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b)\) Để phương trình (1) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt.
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta>0\\ .\Leftrightarrow1^2-4.1.\left(-m\right)>0.\\ \Leftrightarrow1+4m>0.\\ \Leftrightarrow4m>-1.\\ \Leftrightarrow m>\dfrac{-1}{4}.\)






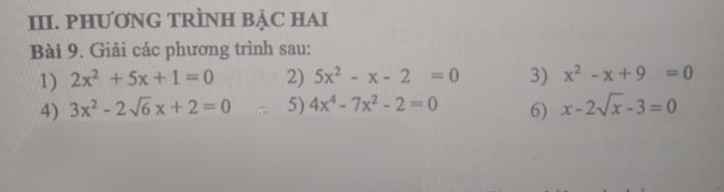

 giúp mk cau b vs
giúp mk cau b vs