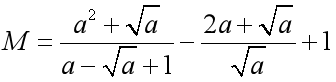Câu 1:
a. \(\sqrt{x+2}\) có nghĩa khi \(x+2\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge-2\)
Vậy biểu thức \(\sqrt{x+2}\) có nghĩa khi \(x\ge-2\)
b. \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=5\\x+2y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=5\\2x+4y=8\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3y=3\\2x+y=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (x; y) = (2; 1)
c. \(A=\left(\dfrac{3}{x-3\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+3}\right).\dfrac{x-9}{\sqrt{x}}\left(x>0;x\ne9\right)\)
\(=\left[\dfrac{3\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}{\sqrt{x}\left(x-9\right)}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}{\sqrt{x}\left(x-9\right)}\right].\dfrac{x-9}{\sqrt{x}}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}+9+x-3\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}\left(x-9\right)}.\dfrac{x-9}{\sqrt{x}}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+9}{\sqrt{x}\left(x-9\right)}.\dfrac{x-9}{\sqrt{x}}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+9}{x}\)






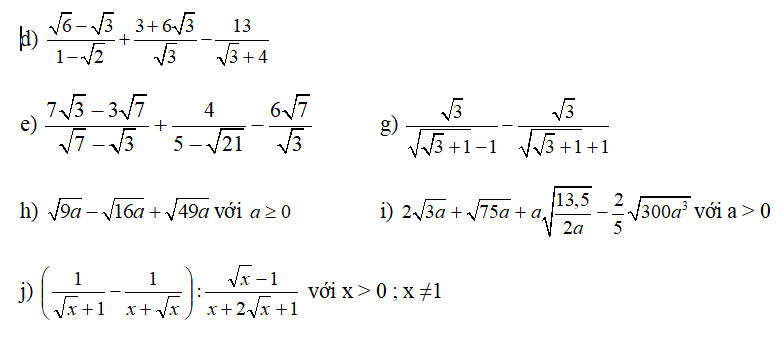





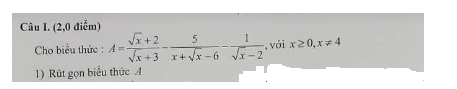 rút gọn biểu thức, giúp e với ạ :<
rút gọn biểu thức, giúp e với ạ :<