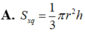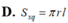\(f\left(x\right)=mx^2\left(x-1\right)+16\left(x-2\right)\)
Chỉ xét trên khoảng (1;2):
- Với \(m>0\) ta có:
\(f\left(1\right)=-16< 0\) ; \(f\left(2\right)=4m>0\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(1\right).f\left(2\right)< 0\) \(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) luôn có ít nhất 1 nghiệm thuộc \(\left(1;2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow y=\left|f\left(x\right)\right|\) không đơn điệu trên (1;2) (loại)
- Với \(m\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2\left(x-1\right)< 0\Rightarrow mx^2\left(x-1\right)\le0\\16\left(x-2\right)< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow mx^2\left(x-1\right)+16\left(x-2\right)< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow y=-mx^3+mx^2-16x+32\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=-3mx^2+2mx-16\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(3x^2-2x\right)\ge-16\), do \(3x^2-2x>0;\forall x\in\left(1;2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m\ge-\dfrac{16}{3x^2-2x}\)
Hàm \(f\left(x\right)=-\dfrac{16}{3x^2-2x}\) có \(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{32\left(3x-1\right)}{\left(3x^2-2x\right)^2}>0\) trên (1;2) nên đồng biến
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)< f\left(2\right)=-2\)
\(\Rightarrow m\ge-2\)
\(\Rightarrow-2\le m\le0\)
Có 3 giá trị nguyên của m