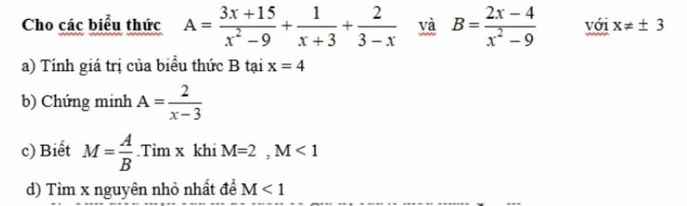a) Thay x=4 vào B, ta được:
\(B=\dfrac{2\cdot4-4}{4^2-9}=\dfrac{8-4}{16-9}=\dfrac{4}{7}\)
b) Ta có: \(A=\dfrac{3x+15}{x^2-9}+\dfrac{1}{x+3}+\dfrac{2}{3-x}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+15+x-3-2\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\cdot\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x+12-2x-6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x+6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2}{x-3}\)
c) Ta có: \(M=\dfrac{A}{B}\)
\(=\dfrac{2}{x-3}:\dfrac{2x-4}{x^2-9}\)
\(=\dfrac{2}{x-3}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}{2\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+3}{x-2}\)
Ta có: M<1
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+3}{x-2}-1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+3-x+2}{x-2}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2< 0\)
hay x<2
d) Để M<1 thì x<2
mà x là số nguyên nhỏ nhất
nên \(x\in Z;x< 2\)