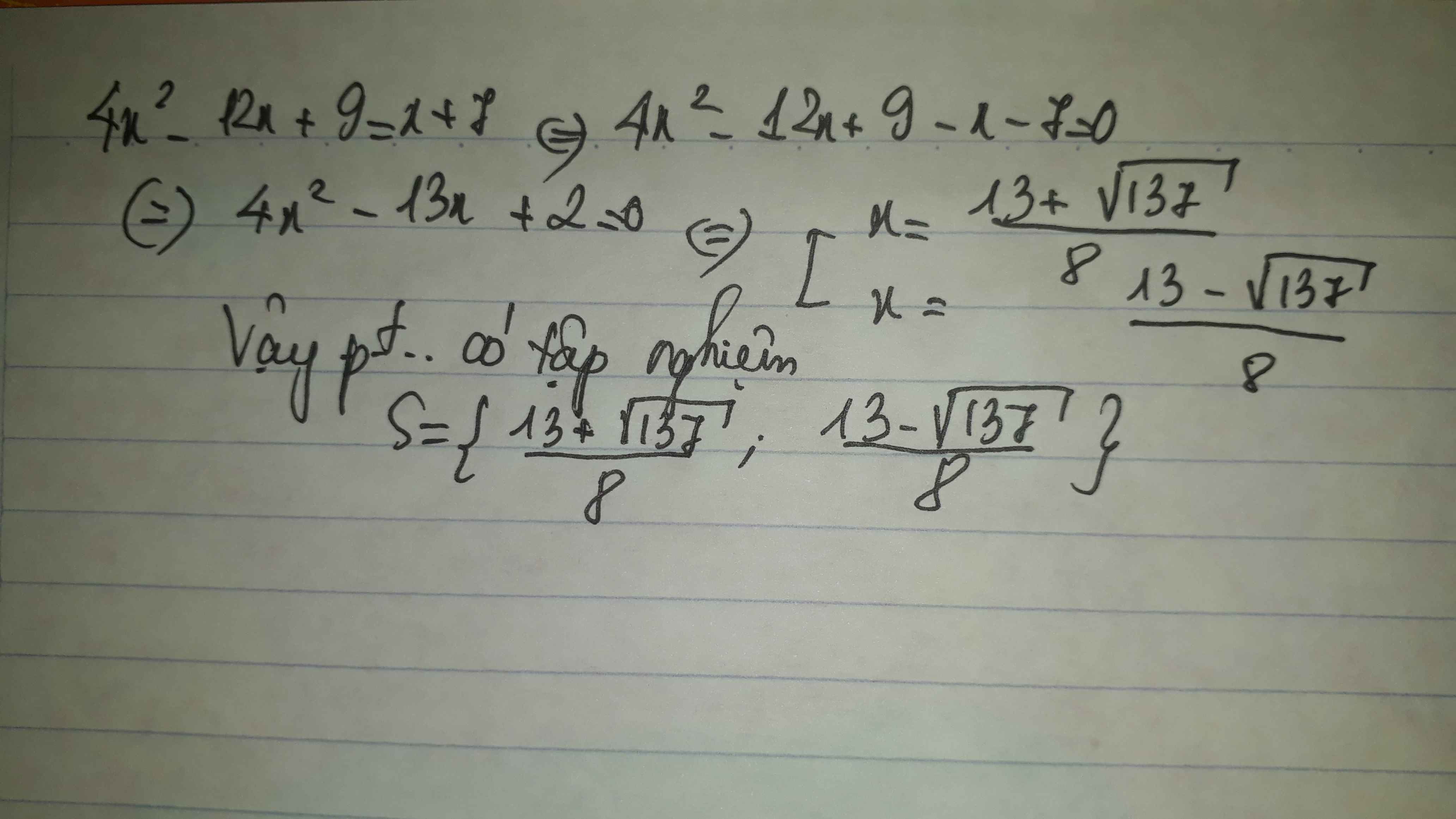4x2-12x+9

Những câu hỏi liên quan
giai phuong trinh: 6x+5/12x+9+3x-7/9-12x=4x2+10x-7/16x2-9
(2x+y)2 -4x2 +12x-9
(2x + y)2 - (2x - 3)2 = (2x + y - 2x + 3)(2x + y + 2x - 3) = (y + 3)(4x + y - 3)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(\left(2x+y\right)^2-4x^2+12x-9\)
\(=\left(2x+y\right)^2-\left(2x-3\right)^2\)
\(=\left(2x+y-2x+3\right)\left(2x+y+2x-3\right)\)
\(=\left(y+3\right)\left(4x+y-3\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình 4x2-12x+9=x+7
\(4\cdot2-12x+9=x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8-12x+9=x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-12x-x=7-8-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-13x=-10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{10}{13}\)
Vậy \(x=\dfrac{10}{13}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Ta có: \(4x^2-12x+9=x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-13x+2=0\)
\(\text{Δ}=\left(-13\right)^2-4\cdot4\cdot2=137\)
Vì Δ>0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{13-\sqrt{137}}{8}\\x_2=\dfrac{13+\sqrt{137}}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Đa thức 12x - 9 - 4x2 được phân tích thành:
=(4x2-12x+9)=[(2x)2-2.2x.3+32]=-(2x-3)2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức sau:
\(\sqrt{4x2-4x+1}+\sqrt{4x2-12x+9}\)
Đặt \(C=\sqrt{4x^2-4x+1}+\sqrt{4x^2-12x+9}\)
\(=\sqrt{\left(2x-1\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(2x-3\right)^2}\)
\(=\left|2x-1\right|+\left|2x-3\right|\)
\(=\left|2x-1\right|+\left|3-2x\right|\)
\(\ge\left|\left(2x-1\right)+\left(3-2x\right)\right|=\left|2\right|=2\)
Vậy \(C_{min}=2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
#)Giải :
\(\sqrt{4x^2-4x+1}+\sqrt{4x^2-12x+9}\)
\(=\sqrt{\left(2x-1\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(2x-3\right)^2}\)
\(=\left|2x-1\right|+\left|2x-3\right|\)
\(=\left|2x-1\right|+\left|3-2x\right|\ge\left|2x-1+3-2x\right|=2\)
Dấu ''='' xảy ra khi x = 1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
\(\sqrt{4x^2-4x+1}+\sqrt{4x^2-12x+9}\)
\(=\sqrt{\left(2x-1\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(2x-3\right)^2}\)
\(=|2x-1|+|2x-3|\)
\(=|2x-1|+|3-2x|\ge|2x-1+3-2x|=2\)
Dấu"=" xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(3-2x\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{2}\le x\le\frac{3}{2}\)
Chỉ là góp ý:V
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
Viết các biểu thức sau dưới dạng bình phương của một tổng
a) x2 + 3x +1
b) x2 + y2 + 2xy
c) 9x2 +12x +4
d) -4x2 - 9 - 12x
a) Sửa đề: \(x^2+3x+1\rightarrow x^2+2x+1\)
\(x^2+2x+1=\left(x+1\right)^2\)
b) \(x^2+y^2+2xy=\left(x+y\right)^2\)
c) \(9x^2+12x+4=\left(3x+2\right)^2\)
d) \(-4x^2-9-12x=-\left(4x^2+12x+9\right)=-\left(2x+3\right)^2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Thực hiện các phép tính sau:a)
P
(
4
x
2
−
1
)
1
2
x
−
1
−
1
2
x
+
1
−...
Đọc tiếp
Thực hiện các phép tính sau:
a) P = ( 4 x 2 − 1 ) 1 2 x − 1 − 1 2 x + 1 − 1 với x ≠ ± 1 2 ;
b) Q = 3 x + 3 − 9 x 2 + 6 x + 9 : 3 x 2 − 9 + 1 3 − x với x ≠ 0 và x ≠ ± 3
a) Ta có P = ( 4 x 2 − 1 ) ( 2 x + 1 ) − ( 2 x − 1 ) − ( 4 x 2 − 1 ) ( 2 x + 1 ) ( 2 x − 1 ) = 3 − 4 x 2
b) Ta có Q = 3 x ( x + 3 ) . ( x + 3 ) ( x − 3 ) − x = 9 − 3 x x + 3
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Số giao điểm của đường thẳng d: y = 12x − 9 và parabol (P): y = 4 x 2 là:
A. 2
B. 1
C. 0
D. 3
Xét phương trình hoành độ giao điểm 4 x 2 = 12 x – 9 ↔ 4 x 2 − 12 x + 9 có ∆’ = 0 nên phương trình có nghiệm kép hay đường thẳng tiếp xúc parabol tại một điểm.
Đáp án: B
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a)√16 -√x2+3x =0
b)3x-1-√4x2-12x+9 =0
c)√2x2-10x+11 = √x2-6x+8
a:
ĐKXĐ: \(x^2+3x>=0\)
=>x(x+3)>=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>=0\\x< =-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\sqrt{16}-\sqrt{x^2+3x}=0\)
=>\(\sqrt{x^2+3x}=\sqrt{16}\)
=>x^2+3x=16
=>x^2+3x-16=0
\(\text{Δ}=3^2-4\cdot1\cdot\left(-16\right)=9+64=73>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-3-\sqrt{73}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{-3+\sqrt{73}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\in R\)
\(3x-1-\sqrt{4x^2-12x+9}=0\)
=>\(\sqrt{\left(2x-3\right)^2}=3x-1\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-1>=0\\\left(3x-1\right)^2=\left(2x-3\right)^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=\dfrac{1}{3}\\\left(3x-1-2x+3\right)\left(3x-1+2x-3\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=\dfrac{1}{3}\\\left(x+2\right)\left(5x-4\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\left(loại\right)\\x=\dfrac{4}{5}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
c:
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-6x+8>=0\\2x^2-10x+11>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>=4\\x< =2\end{matrix}\right.\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< =\dfrac{5-\sqrt{3}}{2}\\x>=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{3}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< =\dfrac{5-\sqrt{3}}{2}\\x>=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\sqrt{2x^2-10x+11}=\sqrt{x^2-6x+8}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-10x+11=x^2-6x+8\)
=>\(x^2-4x+3=0\)
=>(x-1)(x-3)=0
=>x=3(loại) hoặc x=1(nhận)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)