a) x3 - 6x2 + 11x - 6
b) 6x3 - 295x -7
a) x3 + x2 + x + 1 = 0
b) x3 - 6x2 + 11x - 6 = 0
c) x3 - x2 - 21x + 45 = 0
d) x4 + 2x3 - 4x2 - 5x - 6 = 0
a) Ta có: \(x^3+x^2+x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2+1>0\forall x\)
nên x+1=0
hay x=-1
Vậy: S={-1}
b) Ta có: \(x^3-6x^2+11x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-x^2-5x^2+5x+6x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-5x\left(x-1\right)+6\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-5x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={1;2;3}
c) Ta có: \(x^3-x^2-21x+45=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-3x^2+2x^2-6x-15x+45=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-3\right)+2x\left(x-3\right)-15\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+2x-15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+5x-3x-15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2\cdot\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={3;-5}
d) Ta có: \(x^4+2x^3-4x^2-5x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-2x^3+4x^3-8x^2+4x^2-8x+3x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x-2\right)+4x^2\cdot\left(x-2\right)+4x\left(x-2\right)+3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^3+4x^2+4x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^3+3x^2+x^2+4x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left[x^2\left(x+3\right)+\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2+x+1>0\forall x\)
nên (x-2)(x+3)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={2;-3}
Bài 5; Tìm x
a) x2-4=0
b) 2x(x+5)-3(5+x)=0
c) x3-6x2+11x-6=0
a) x² - 4 = 0
x² = 4
x = 2 hoặc x = -2
b) 2x(x + 5) - 3(5 + x) = 0
(x + 5)(2x - 3) = 0
X + 5 = 0 hoặc 2x - 3 = 0
*) x + 5 = 0
x = -5
*) 2x - 3 = 0
2x = 3
x = 3/2
c) x³ - 6x² + 11x - 6 = 0
x³ - x² - 5x² + 5x + 6x - 6 = 0
(x³ - x²) - (5x² - 5x) + (6x - 6) = 0
x²(x - 1) - 5x(x - 1) + 6(x - 1) = 0
(x - 1)(x² - 5x + 6) = 0
(x - 1)(x² - 2x - 3x + 6) = 0
(x - 1)[(x² - 2x) - (3x - 6)] = 0
(x - 1)[x(x - 2) - 3(x - 2)] = 0
(x - 1)(x - 2)(x - 3) = 0
x - 1 = 0 hoặc x - 2 = 0 hoặc x - 3 = 0
*) x - 1 = 0
x = 1
*) x - 2 = 0
x = 2
*) x - 3 = 0
x = 3
Vậy x = 1; x = 2; x = 3
Diện tích hình phẳng giới hạn bởi các đường y = x 3 + 11 x - 6 , y = 6 x 2 , x = 0, x = 2. (Đơn vị diện tích)
A. 4 3
B. 5 2
C. 8 3
D. 18 23
Chọn B.
Đặt h x = x 3 + 11 x - 6 - 6 x 2 = x 3 - 6 x 2 + 11 x - 6 h x = 0 ⇔ x = 1 ∨ x = 2 ∨ x = 3 ( l o ạ i )
Bảng xét dấu
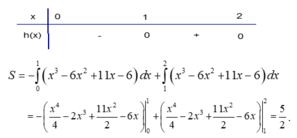
Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a/ y2 - 2y b/ 3x4 – 6x3 + 3x2
c/ 27x2 ( y – 1) – 9x3 ( 1 - y) d/y3 – 2y2 + y
e/ x3 + 6x2 + 9x f/ x3 – 2x2y + xy2
g/ x( 2- x) – x + 2 h/ 3x ( x – 1) + 6( 1 – x)
\(a,=y\left(y-2\right)\\ b,=3x\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=3x\left(x-1\right)^2\\ c,=\left(y-1\right)\left(27x^2+9x^3\right)=9x^2\left(x+3\right)\left(y-1\right)\\ d,=y\left(y^2-2y+1\right)=y\left(y-1\right)^2\\ e,=x\left(x^2+6x+9\right)=x\left(x+3\right)^2\\ f,=x\left(x^2-2xy+y^2\right)=x\left(x-y\right)^2\\ g,=\left(2-x\right)\left(x+1\right)\\ h,=\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-6\right)=3\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\)
a: =y(y-2)
b: \(=3x^2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=3x^2\left(x-1\right)^2\)
d: \(=y\left(y^2-2y+1\right)=y\left(y-1\right)^2\)
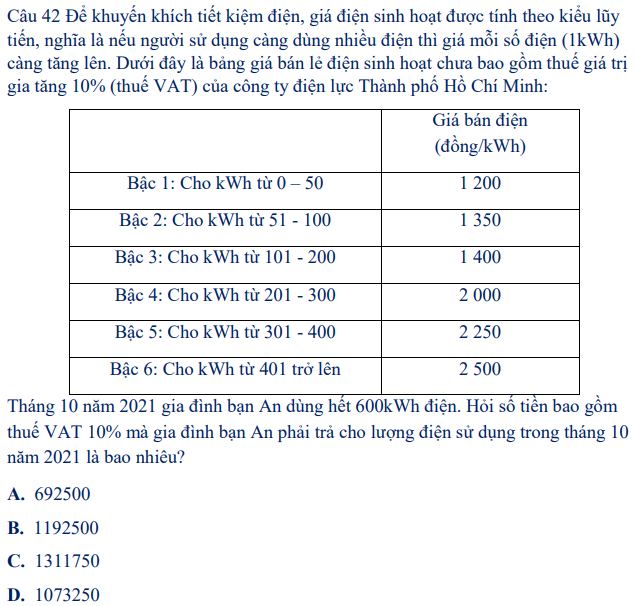
Cho hàm số f ( x ) = x 3 - 6 x 2 + 11 x - 6 k h i x ≠ 3 x - 3 m k h i x = 3 . Tìm giá trị của m để hàm số liên tục tại x=3?
A. ![]() .
.
B. ![]() .
.
C. ![]() .
.
D. ![]() .
.
Chọn B
Tập xác định của hàm số là ![]() .
.
Ta có: ![]() .
.
![]()
![]() .
.
Hàm số liên tục tại ![]() khi
khi
![]()
Cho hàm số f ( x ) = x 3 - 6 x 2 + 11 x - 6 x 2 - 9 k h i x ≠ ± 3 m - 2 3 k h i x = 3 . Tìm giá trị của m để hàm số liên tục tại x=3?
A.8/3
B.2/3
C.1
D.4/3
1 Một người đi bán hàng với giá 5x VND / món hàng và bán được ( x2 – 6) món hàng. Hãy viết biểu thức thể hiện số tiền người đó thu được ?
A. 6x3 – 11x (VND)
B. 5x3 – 30x (VND)
C. 5x2 – 11x (VND)
D. 6x3 + 30x (VND)
Bài 1 : phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử.
3x2 + 2x – 1
x3 + 6x2 + 11x + 6
x4 + 2x2 – 3
ab + ac +b2 + 2bc + c2
a3 – b3 + c3 + 3abc
Tính bằng cách thuận tiện
5/6x3+20/6x2-1:6/5
\(\dfrac{5}{6}\times3+\dfrac{20}{6}\times2-1:\dfrac{6}{5}\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{6}\times3-\dfrac{5}{6}+\dfrac{20}{6}\times2\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{6}\times\left(3-1\right)+\dfrac{20}{6}\times2\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{6}\times2+\dfrac{20}{6}\times2\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{5}{6}+\dfrac{20}{6}\right)\times2\)
\(=\dfrac{25}{6}\times2\)
\(=\dfrac{25}{3}\)
#DatNe
\(\dfrac{5}{6}\) \(\times\) 3 + \(\dfrac{20}{6}\) \(\times\) 2 - 1 : \(\dfrac{6}{5}\)
= \(\dfrac{5}{6}\) \(\times\) 3 + \(\dfrac{20}{6}\) \(\times\) 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{6}\)
= \(\dfrac{5}{6}\) \(\times\) 3 + \(\dfrac{5}{6}\) \(\times\) 8 - \(\dfrac{5}{6}\) \(\times\)1
= \(\dfrac{5}{6}\) \(\times\) ( 3 + 8 - 1)
= \(\dfrac{5}{6}\) \(\times\)10
= \(\dfrac{25}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{5}{6}\times3+\dfrac{20}{6}\times2-1:\dfrac{6}{5}\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{6}\times3+\dfrac{10}{3}\times2-1\times\dfrac{5}{6}\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{6}\times\left(3+8-1\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{6}\times10\)
\(=\dfrac{25}{3}\)