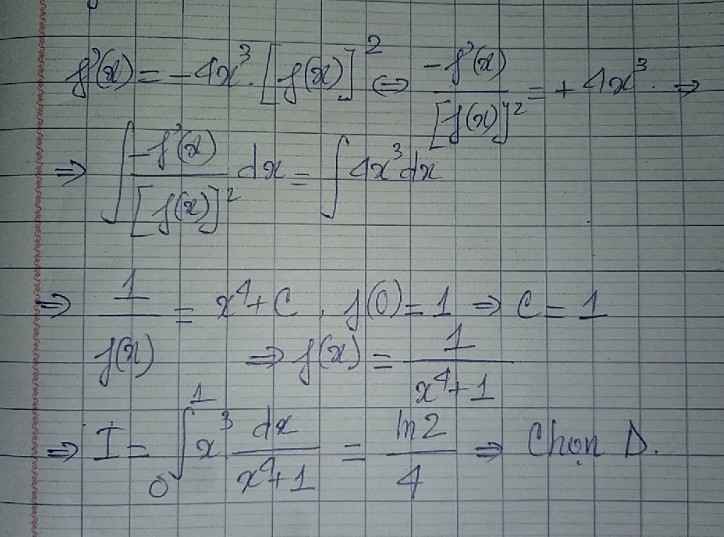Cho hàm số \(f\left(x\right)=\left(x+1\right)e^x\). Tính \(f'\left(0\right)\).

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Cho hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right) = - {x^2} + 1\). Tính \(f\left( { - 3} \right);f\left( { - 2} \right);f\left( { - 1} \right);f\left( 0 \right);f\left( 1 \right)\).
\(f\left( { - 3} \right) = - {\left( { - 3} \right)^2} + 1 = - 9 + 1 = - 8\);
\(f\left( { - 2} \right) = - {\left( { - 2} \right)^2} + 1 = - 4 + 1 = - 3\);
\(f\left( { - 1} \right) = - {\left( { - 1} \right)^2} + 1 = - 1 + 1 = 0\);
\(f\left( 0 \right) = - {0^2} + 1 = 0 + 1 = 1\);
\(f\left( 1 \right) = - {1^2} + 1 = - 1 + 1 = 0\);
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hàm số f(x) thỏa mãn \(\left[f'\left(x\right)\right]^2+f\left(x\right)f''\left(x\right)=15x^4+12x\) ∀x∈R biết
f(0)=f'(0)=1. Tính \(f^2\left(1\right)\)
Vẫn là đạo hàm của tích
Dễ dàng viết được:
\(\left[f'\left(x\right)\right]^2+f\left(x\right).f''\left(x\right)=\left[f\left(x\right)\right]'.f'\left(x\right)+f\left(x\right).\left[f'\left(x\right)\right]'=\left[f'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)\right]'\)
Do đó giả thiết biến đổi thành:
\(\left[f'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)\right]'=15x^4+12x\)
Nguyên hàm 2 vế:
\(f'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)=\int\left(15x^4+12x\right)dx=3x^5+6x^2+C\)
Thay \(x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(0\right).f\left(0\right)=C\Rightarrow C=1\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)=3x^5+6x^2+1\)
Tiếp tục nguyên hàm 2 vế:
\(\int f\left(x\right).f'\left(x\right)dx=\int\left(3x^5+6x^2+1\right)dx\) với chú ý \(\int f\left(x\right).f'\left(x\right)dx=\int f\left(x\right).d\left[f\left(x\right)\right]=\dfrac{1}{2}f^2\left(x\right)+C\)
Nên:
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}f^2\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}x^6+2x^3+x+C\)
Thay \(x=0\Rightarrow C=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}f^2\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}x^6+2x^3+x+\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow f^2\left(1\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hàm số \(f\left( x \right) = {x^2}{e^x}.\) Tính \(f''\left( 0 \right).\)
`f'(x) = (x^2)'e^x + x^2.(e^x)'`
`= 2xe^x + x^2.e^x`
`= (2x + x^2).e^x`
Tính đạo hàm lần 2 của f(x):
`f''(x) = ((2x + x^2).e^x)'`
`= (2x + x^2)'.e^x + (2x + x^2).(e^x)'`
`= (2 + 2x).e^x + (2x + x^2).e^x`
`= (2 + 4x + x^2).e^x`
Ta thay x = 0 vào công thức trên:
`f''(0) = (2 + 4.0 + 0^2).e^0`
`= 2.1`
`= 2`
Vậy, f''(0) = 2.
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Cho hàm số fleft(xright) có đạo hàm fleft(xright) liên tục trên R và thỏa mãn các điều kiện fleft(xright)0,forall xin R, fleft(0right)1 và fleft(xright)-4x^3.left(fleft(xright)right)^2,forall xin R. Tính Iint_0^1x^3fleft(xright)dxA.Idfrac{1}{6} B. Iln2 C. Idfrac{1}{4} D. Idfrac{ln2}{4}Mình cần bài giải ạ, mình cảm ơn nhiều♥
Đọc tiếp
Cho hàm số \(f\left(x\right)\) có đạo hàm \(f'\left(x\right)\) liên tục trên \(R\) và thỏa mãn các điều kiện \(f\left(x\right)>0,\forall x\in R\), \(f\left(0\right)=1\) và \(f'\left(x\right)=-4x^3.\left(f\left(x\right)\right)^2,\forall x\in R\). Tính \(I=\int_0^1x^3f\left(x\right)dx\)
A.\(I=\dfrac{1}{6}\) B. \(I=ln2\) C. \(I=\dfrac{1}{4}\) D. \(I=\dfrac{ln2}{4}\)
Mình cần bài giải ạ, mình cảm ơn nhiều♥
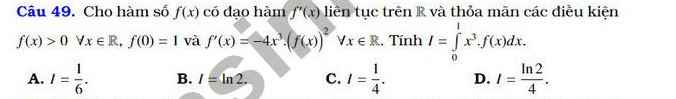
\(f'\left(x\right)=-4x^3\left(f\left(x\right)\right)^2\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{f'\left(x\right)}{\left(f\left(x\right)\right)^2}=4x^3\)
Lấy nguyên hàm hai vế
\(\int-\dfrac{f'\left(x\right)}{\left(f\left(x\right)\right)^2}dx=\int4x^3dx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{f\left(x\right)}=x^4+c\)
Thay x=0 vào tìm được c=1 \(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{x^4+1}\)
\(I=\int\limits^1_0\dfrac{x^3}{x^4+1}dx=\dfrac{1}{4}\int\limits^1_0\dfrac{\left(x^4+1\right)'}{x^4+1}dx=\dfrac{ln2}{4}\)
Chọn D
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cho hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right) = {x^2} + 4\). Tính \(f\left( { - 3} \right);f\left( { - 2} \right);f\left( { - 1} \right);f\left( 0 \right);f\left( 1 \right)\)
\(f\left( { - 3} \right) = {\left( { - 3} \right)^2} + 4 = 9 + 4 = 13\);
\(f\left( { - 2} \right) = {\left( { - 2} \right)^2} + 4 = 4 + 4 = 8\);
\(f\left( { - 1} \right) = {\left( { - 1} \right)^2} + 4 = 1 + 4 = 5\);
\(f\left( 0 \right) = {0^2} + 4 = 0 + 4 = 4\);
\(f\left( 1 \right) = {1^2} + 4 = 1 + 4 = 5\).
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
cho hàm số \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{\left(sinx+2x\right)\left[\left(x^2+1\right)sinx-x\left(cosx+2\right)\right]}{\left(cosx+2\right)^2\sqrt{\left(x^2+1\right)^3}}\). Biết F(x) là một nguyên hàm của f(x) và F(0)=2021. Tính giá trị biểu thức T=F(-1) + F(1).
Cho hàm số \(f\left(x\right)=e^{\sqrt{x^2+1}}\left(e^x-e^{-x}\right)\). Có bao nhiêu số nguyên dương m thỏa mãn bất phương trình \(f\left(m-7\right)+f\left(\dfrac{12}{m+1}\right)< 0\) ?
Lời giải:
Đặt $\sqrt{x^2+1}+x=a$ thì:
$f(a)=e^a-e^{\frac{1}{a}}$
$f'(a)=e^a+\frac{1}{a^2}.e^{\frac{1}{a}}>0$ với mọi $a$
Do đó hàm $f(a)$ là hàm đồng biến hay $f(x)$ là hàm đồng biến trên R
$\Rightarrow f(x)> f(0)=0$ với mọi $x>0$
$\Rightarrow f(\frac{12}{m+1})>0$ với $m$ nguyên dương
Do đó để $f(m-7)+f(\frac{12}{m+1})<0$ thì $f(m-7)<0$
$\Rightarrow m-7<0$
Mặt khác, dễ thấy: $f(x)+f(-x)=0$. Bây h xét:
$m=1$ thì $f(m-7)+f(\frac{12}{m+1})=f(-6)+f(6)=0$ (loại)
$m=2$ thì $f(m-7)+f(\frac{12}{m+1})=f(-5)+f(4)=f(4)-f(5)<0$ (chọn)
$m=3$ thì $f(m-7)+f(\frac{12}{m+1})=f(-4)+f(3)=f(3)-f(4)<0$ (chọn)
$m=4$ thì $f(m-7)+f(\frac{12}{m+1})=f(-3)+f(2,4)=f(2,4)-f(3)<0$ (chọn)
$m=5$ thì $f(m-7)+f(\frac{12}{m+1})=f(-2)+f(2)=0$ (loại)
$m=6$ thì $f(m-7)+f(\frac{12}{m+1})=f(-1)+f(12/7)>f(-1)+f(1)=0$ (loại)
Vậy có 3 số tm
Đúng 4
Bình luận (1)
cho hàm số f(x) = \(\dfrac{\left(sinx+2x\right)\left[\left(x^2+1\right)sinx-x\left(cosx+2\right)\right]}{\left(cosx+2\right)^2\sqrt{\left(X^2+1\right)^3}}\). Biết F(x) là một nguyên hàm của f(x) và F(0)=2021. Tính giá trị biểu thức T=F(-1) + F(1).
Cho a là một số thực dương. Biết rằng F(x) là 1 nguyên hàm của \(f\left(x\right)=e^x\left(ln\left(ax\right)+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)\) thỏa mãn \(F\left(\dfrac{1}{a}\right)=0\) và \(F\left(2020\right)=e^{2020}\). Tìm a.
\(F\left(x\right)=\int\left(e^x.ln\left(ax\right)+\dfrac{e^x}{x}\right)dx=\int e^xln\left(ax\right)dx+\int\dfrac{e^x}{x}dx=\int e^xlnxdx+\int\dfrac{e^x}{x}dx+\int e^x.lna.dx\)
Xét \(I=\int e^xlnxdx\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=lnx\\dv=e^xdx\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}du=\dfrac{dx}{x}\\v=e^x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow I=lnx.e^x-\int\dfrac{e^x}{x}dx\)
\(\Rightarrow F\left(x\right)=e^x.lnx+e^x.lna+C\)
\(F\left(\dfrac{1}{a}\right)=e^{\dfrac{1}{a}}ln\left(\dfrac{1}{a}\right)+e^{\dfrac{1}{a}}.lna+C=0\Rightarrow C=0\)
\(F\left(2020\right)=e^{2020}ln\left(2020\right)+e^{2020}.lna=e^{2020}\)
\(\Rightarrow ln\left(2020a\right)=1\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{e}{2020}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cho hàm số fleft(xright)left{{}begin{matrix}2sin^2x+1,x 02^x;xge0end{matrix}right.. Giả sử Fleft(xright) là một nguyên hàm của hàm số fleft(xright) trên R và thỏa mãn điều kiện Fleft(1right)dfrac{2}{ln2}. Tính Fleft(-piright) A. Fleft(-piright)-2pi+dfrac{1}{ln2} B. Fleft(-piright)-2pi-dfrac{1}{ln2}C. Fleft(-piright)-pi-dfrac{1}{ln2} D. Fleft(-piright)-2piMình cần bài giải ạ, mình cảm ơn nhiều ♥
Đọc tiếp
Cho hàm số \(f\left(x\right)=\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\sin^2x+1,x< 0\\2^x;x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\). Giả sử \(F\left(x\right)\) là một nguyên hàm của hàm số \(f\left(x\right)\) trên \(R\) và thỏa mãn điều kiện \(F\left(1\right)=\dfrac{2}{ln2}\). Tính \(F\left(-\pi\right)\)
A. \(F\left(-\pi\right)=-2\pi+\dfrac{1}{ln2}\) B. \(F\left(-\pi\right)=-2\pi-\dfrac{1}{ln2}\)
C. \(F\left(-\pi\right)=-\pi-\dfrac{1}{ln2}\) D. \(F\left(-\pi\right)=-2\pi\)
Mình cần bài giải ạ, mình cảm ơn nhiều ♥
Xem thêm câu trả lời