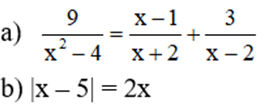giải bất phương trình ( x2 -x -2)(x2 +x)<0

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Giải bất phương trình sau
(x+2)(x2-2x+4)-x(x2+2)> hoặc = 5
=>x^3+8-x^3-2x>=5
=>-2x>=-3
=>x<=3/2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải các bất phương trình sau
a) (x2+2)2-(x+2)(x-2)(x2+4)-4x(x+1)< hoặc = 20
b) (x+2)(x2-2x+4)-x(x2+2)> hoặc = 15
a) \(\left(x^2+2\right)^2-\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)-4x\left(x+1\right)\le20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+4x^2+4-x^4+16-4x^2-4x\le20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^4-x^4\right)+\left(4x^2-4x^2\right)-4x+4+16\le20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x+20\le20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x\le20-20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x:-4\ge0:-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge0\)
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là: \(x\ge0\)
b) \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-x\left(x^2+2\right)\ge15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+8-x^3-2x\ge15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3-x^3\right)+8-2x\ge15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8-2x\ge15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x\ge15-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x\ge7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x:-2\le7:-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\le-\dfrac{7}{2}\)
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(x\le-\dfrac{7}{2}\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)
a: =>x^4+4x^2+4-x^4+16-4x^2-4x<=20
=>-4x+20<=20
=>-4x<=0
=>x>=0
b: =>x^3+8-x^3-2x>=15
=>-2x>=7
=>x<=-7/2
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải phương trình và bất phương trình:
(x – 2)2 + 2(x – 1) ≤ x2 + 4
cứuu lẹ
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+4+2x^2-4x+2-x^2< =4\)
=>-8x<=-2
hay x>=1/4
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải bất phương trình
x2-2x+1<9
(x-1)(4-x2)≥0
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}\)<0
\(x^2-2x+1< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 4\)
\(\left(x-1\right)\left(4-x^2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2-x=0\\2+x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a)\(x^2-2x+1< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2-9< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1-3\right)\left(x-1+3\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+2\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4< 0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4>0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 4\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>4\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\)(vô lý)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(-2< x< 4\).
b) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(4-x^2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2-x\right)\left(x+2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1< 0\\x-2>0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1>0\\x-2< 0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1>0\\x-2 >0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1< 0\\x-2< 0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x>2\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.\) (vô lí) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x< 2\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra) hay
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x>2\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\) (vô lí) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x< 2\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(x< -2\) hay \(1< x< 2\).
c) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne5\)
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}< 0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2< 0\\x-5>0\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2>0\\x-5< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< -2\\x>5\end{matrix}\right.\)(vô lí) hay
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>-2\\x< 5\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(-2< x< 5\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
Bài 1: Giải các bất phương trình sau
a) x+1/x+3 > 1
b) 2x-1/x-3 ≤ 2
c) x2+2x+2/x2+3 ≥ 1
d) 2x+1/x2+2 ≥ 1
a, \(\dfrac{x+1}{x+3}>1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+1}{x+3}-1>0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+1-x-3}{x+3}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow x+3< 0\)do -2 < 0
\(\Rightarrow x< -3\)Vậy tập nghiệm BFT là S = { x | x < -3 }
b, \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x-3}\le2\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-1}{x-3}-2\le0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-1-2x+6}{x-3}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-3\le0\)do 5 > 0
\(\Rightarrow x\le3\)Vậy tập nghiệm BFT là S = { x | x \(\le\)3 }
c, \(\dfrac{x^2+2x+2}{x^2+3}\ge1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2+2x+2}{x^2+3}-1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2+2x+2-x^2-3}{x^2+3}\ge0\Rightarrow2x-1\ge0\)do x^2 + 3 > 0
\(\Rightarrow x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\)Vậy tập nghiệm BFT là S = { x | x \(\ge\)1/2 }
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
mình ko chắc nên mình đăng sau :>
d, \(\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+2}\ge1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+2}-1\ge0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+1-x^2-2}{x^2+2}\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow-x^2+2x-1\ge0\Rightarrow-\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\)vô lí
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Giải các bất phương trình: 3(x – 2)(x + 2) < 3 x 2 + x
Ta có: 3(x – 2)(x + 2) < 3 x 2 + x
⇔ 3( x 2 – 4) < 3 x 2 + x
⇔ 3 x 2 – 12 < 3 x 2 + x
⇔ 3 x 2 – 3 x 2 – x < 12
⇔ -x < 12
⇔ x > -12
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là S = {x|x > -12}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải bất phương trình: (x – 3)2 < x2 – 3
(x – 3)2 < x2 – 3
⇔ x2 – 6x + 9 < x2 – 3
⇔ x2 – 6x – x2 < -3 – 9
⇔ -6x < -12
⇔ x > 2 (Chia cả hai vế cho -6 < 0, BPT đổi chiều)
Vậy BPT có nghiệm x > 2.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải bất phương trình
g
(
x
)
≤
0
với
g
(
x
)
x
2
+
3
x
−
9
x
−
2
A. S (1; 3) B.
S
...
Đọc tiếp
Giải bất phương trình g ' ( x ) ≤ 0 với g ( x ) = x 2 + 3 x − 9 x − 2
A. S = (1; 3)
B. S = 1 ; 3 / 2
C. S = − ∞ ; 1 ∪ ( 3 ; + ∞ )
D. S = − ∞ ; 1
Ta có
g ' ( x ) = ( 2 x + 3 ) . ( x − 2 ) − 1. ( x 2 + 3 x − 9 ) ( x − 2 ) 2 = x 2 − 4 x + 3 ( x − 2 ) 2
Mà g ' ( x ) ≤ 0
⇔ x 2 − 4 x + 3 ≤ 0 x − 2 ≠ 0 ⇔ 1 ≤ x ≤ 3 x ≠ 2 ⇔ x ∈ 1 ; 3 \ 2
Vậy tập nghiệm bất phương trình là: S=[1 ; 3]\{2}
Chọn đáp án B
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: (3 điểm) Giải phương trình và bất phương trình:
C) x – 2)2 + 2(x – 1) ≤ x2 + 4
Tham Khảo nào
a) Điều kiện: x + 2 ≠ 0 và x – 2 ≠ 0 ⇔ x ≠ ± 2
(Khi đó: x2 – 4 = (x + 2)(x – 2) ≠ 0)
Vậy tập nghiệm của pt là: S = {-1; 1}
b) Điều kiện: 2x ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≥ 0
Khi đó: |x – 5| = 2x ⇔ x – 5 = 2x hoặc x – 5 = -2x
⇔ x = -5 hoặc x = 5/3
Vì x ≥ 0 nên ta lấy x = 5/3 . Tập nghiệm : S = {5/3}
c) x – 2)2 + 2(x – 1) ≤ x2 + 4
⇔ x2 – 4x + 4 + 2x – 2 ≤ x2 + 4
⇔ -2x ≤ 2
⇔ x ≥ -1
Tập nghiệm S = {x | x ≥ -1}
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Giải phương trình và bất phương trình:
a
)
9
x
2
-
4
x
-
1
x
+
2
+
3
x
-
2
b
)
x
-
5
2
x...
Đọc tiếp
Giải phương trình và bất phương trình:
a ) 9 x 2 - 4 = x - 1 x + 2 + 3 x - 2 b ) x - 5 = 2 x c ) x - 2 2 + 2 x - 1 ≤ x 2 + 4
a) Điều kiện: x + 2 ≠ 0 và x – 2 ≠ 0 ⇔ x ≠ ± 2
(Khi đó: x2 – 4 = (x + 2)(x – 2) ≠ 0)
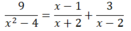
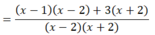
![]()
![]()
Vậy tập nghiệm của pt là: S = {-1; 1}
b) Điều kiện: 2x ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≥ 0
Khi đó: |x – 5| = 2x ⇔ x – 5 = 2x hoặc x – 5 = -2x
⇔ x = -5 hoặc x = 5/3
Vì x ≥ 0 nên ta lấy x = 5/3 . Tập nghiệm : S = {5/3}
c) x – 2)2 + 2(x – 1) ≤ x2 + 4
⇔ x2 – 4x + 4 + 2x – 2 ≤ x2 + 4
⇔ -2x ≤ 2
⇔ x ≥ -1
Tập nghiệm S = {x | x ≥ -1}
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)