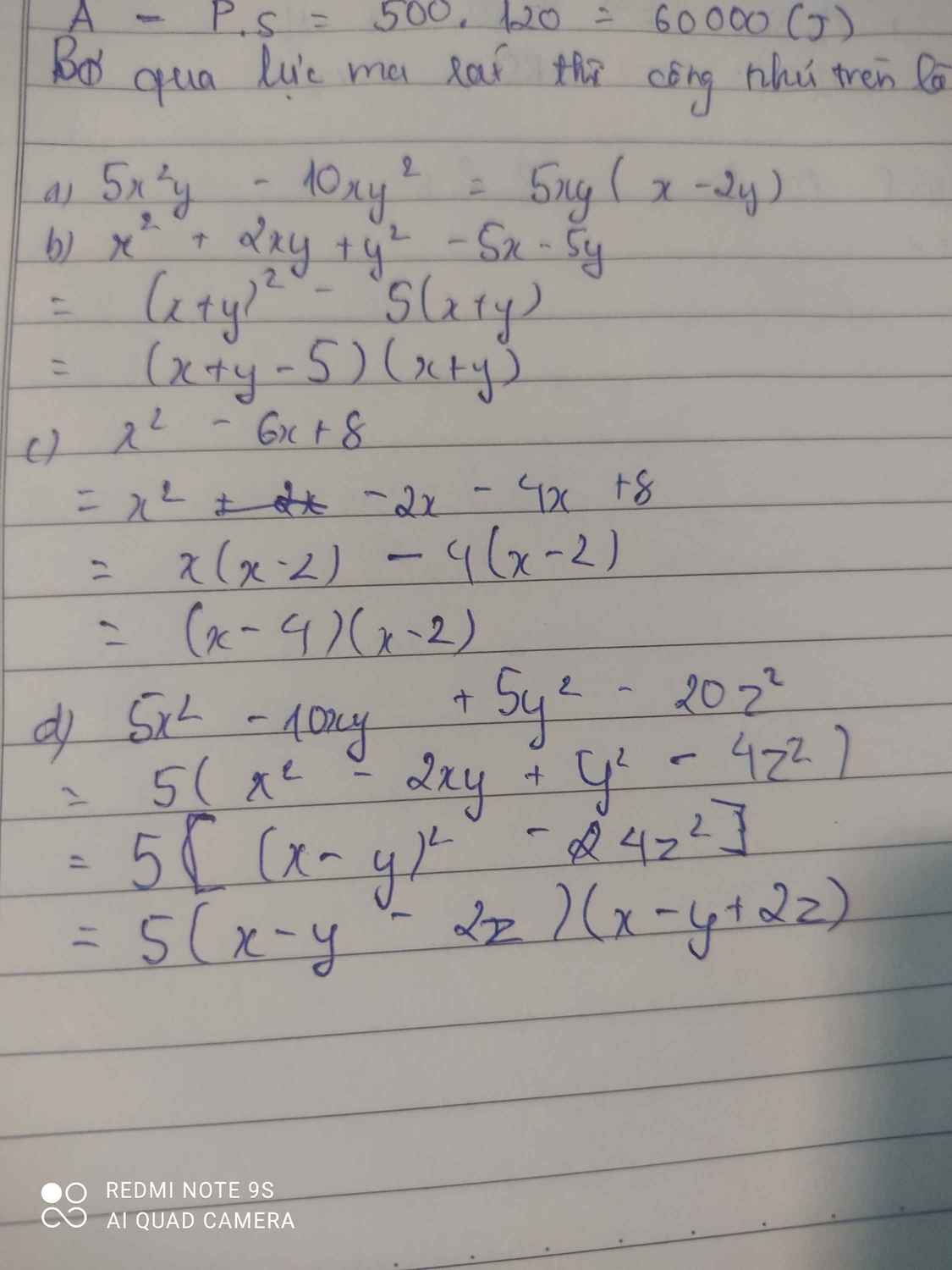Bài 1:
a) 5x2-10xy+5y2-20z2
b) x2+4x+3
Bài 2: Tính
a. (2x-3y)2

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Bài 9: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử1, 5x2 – 10xy + 5y2 – 20z2 2, 16x – 5x2 – 3 3, x2 – 5x + 5y – y24, 3x2 – 6xy + 3y2 – 12z25, x2 + 4x + 3 6, (x2 + 1)2 – 4x2 7, x2 – 4x – 5
Đọc tiếp
Bài 9: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
1, 5x2 – 10xy + 5y2 – 20z2 2, 16x – 5x2 – 3 3, x2 – 5x + 5y – y2 | 4, 3x2 – 6xy + 3y2 – 12z2 5, x2 + 4x + 3 6, (x2 + 1)2 – 4x2 7, x2 – 4x – 5
|
1.\(=5\left(x^2-2xy+y^2-4z^2\right)=5\left[\left(x+y\right)^2-\left(2z\right)^2\right]=5\left(x+y-2z\right)\left(x+y+2z\right)\)
2. \(=\left(-5x^2+15x\right)+\left(x-3\right)=-5x\left(x-3\right)+\left(x-3\right)=\left(1-5x\right)\left(x-3\right)\)
3. \(=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)-5\left(x-y\right)=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y-5\right)\)
4.\(=3\left(x^2-2xy+y^2-4z^2\right)=3\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-\left(2z\right)^2\right]=3\left(x-y-2z\right)\left(x-y+2z\right)\)
5. \(=\left(x^2+x\right)+\left(3x+3\right)=x\left(x+1\right)+3\left(x+1\right)=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)\)
6. \(=\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)^2\)
7. \(=\left(x^2+x\right)-\left(5x+5\right)=x\left(x+1\right)-5\left(x+1\right)=\left(x-5\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(1,=5\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-4z^2\right]=5\left(x-y-2z\right)\left(x-y+2z\right)\\ 2,=-5x^2+15x+x-3=\left(x-3\right)\left(1-5x\right)\\ 3,=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)-5\left(x-y\right)=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y-5\right)\\ 4,=3\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-4z^2\right]=3\left(x-y-2z\right)\left(x-y+2z\right)\\ 5,=x^2+x+3x+3=\left(x+3\right)\left(x+1\right)\\ 6,=\left(x^2+2x+1\right)\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)^2\\ 7,=x^2+x-5x-5=\left(x+1\right)\left(x-5\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử
a) 5x2 - 10xy + 5y2 - 20z
b) x2 - z2 + y2 - 2xy
c) a3 - ay - a2x + xy
d) x2 + 4x + 3
b: \(x^2-2xy+y^2-z^2\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)^2-z^2\)
\(=\left(x-y-z\right)\left(x-y+z\right)\)
d: \(x^2+4x+3=\left(x+3\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
=x4−2x3+2x3−4x2+4x2−8x+7x−14=x4−2x3+2x3−4x2+4x2−8x+7x−14
=(x−2)(x3+2x2+4x+7)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của các biểu thứca ) A x2 – 2x+5b) B x2 –x +1c) C ( x -1). ( x +2). ( x+3). ( x+6)d) D x2 + 5y2 – 2xy+ 4y+3Bài 2: Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của các biểu thức sau:a) A -x2 – 4x – 2 b) B -2x2 – 3x +5c) C ( 2- x). ( x +4)d) D -8x2 + 4xy - y2 +3Bài 3 : Chứng minh rằng các giá trị của các biểu thức sau luôn dương với mọi giá trị của biếna) A 25x – 20x+7b) B 9x2 – 6xy + 2y2 +1c) E x2 – 2x + y2 + 4y+6d) D x2 – 2x +2Giúp mình nha. Cần gấp ạ Chi tiết nha
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của các biểu thức
a ) A= x2 – 2x+5
b) B= x2 –x +1
c) C= ( x -1). ( x +2). ( x+3). ( x+6)
d) D= x2 + 5y2 – 2xy+ 4y+3
Bài 2: Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của các biểu thức sau:
a) A= -x2 – 4x – 2
b) B= -2x2 – 3x +5
c) C= ( 2- x). ( x +4)
d) D= -8x2 + 4xy - y2 +3
Bài 3 : Chứng minh rằng các giá trị của các biểu thức sau luôn dương với mọi giá trị của biến
a) A= 25x – 20x+7
b) B= 9x2 – 6xy + 2y2 +1
c) E= x2 – 2x + y2 + 4y+6
d) D= x2 – 2x +2
Giúp mình nha. Cần gấp ạ <Chi tiết nha>
Bài 3:
a) Ta có: \(A=25x^2-20x+7\)
\(=\left(5x\right)^2-2\cdot5x\cdot2+4+3\)
\(=\left(5x-2\right)^2+3>0\forall x\)(đpcm)
d) Ta có: \(D=x^2-2x+2\)
\(=x^2-2x+1+1\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)^2+1>0\forall x\)(đpcm)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(A=x^2-2x+5\)
\(=x^2-2x+1+4\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)^2+4\ge4\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=1
b) Ta có: \(B=x^2-x+1\)
\(=x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
b) (3x + 1)2 – (2x + 1)2
c) - 5x2 + 10xy – 5y2 + 20z2
\(a,=\left(3x+1-2x-1\right)\left(3x+1+2x+1\right)=x\left(5x+2\right)\\ b,=5\left[4z^2-\left(x-y\right)^2\right]=5\left(2z-x+y\right)\left(2z+x-y\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(b,\left(3x+1\right)^2-\left(2x+1\right)^2\\ =\left[\left(3x+1\right)+\left(2x+1\right)\right]\left[\left(3x+1\right)-\left(2x+1\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(3x+1+2x+1\right)\left(3x+1-2x-1\right)\\ =x\left(5x+2\right)\)
\(c,-5x^2+10xy-5y^2+20z^2\\ =-5\left(x^2-2xy+y^2-4z^2\right)\\ =-5\left[\left(x^2-2xy+y^2\right)-\left(2z\right)^2\right]\\ =-5\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-\left(2z\right)^2\right]\\ =-5\left(x-y+2z\right)\left(x-y-2z\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Phân tích đa thức rồi tính giá trị của biểu thức:
a. 5x2+10xy+5-5y2 tại x=1,y=2
b. 7x-7y-x2+2xy-y2 tại x=2,y=2
\(a,=5\left(x^2+2xy+y^2\right)-10y^2+5=5\left(x+y\right)^2-10y^2+5\\ =5\left(1+2\right)^2-10\cdot4+5=45-40+5=10\\ b,=7\left(x-y\right)-\left(x-y\right)^2=\left(x-y\right)\left(7-x+y\right)\\ =\left(2-2\right)\left(7-2+2\right)=0\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
b: \(=7\left(x-y\right)-\left(x-y\right)^2\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\left(7-x+y\right)=0\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử a) a/ x2 – 2xb) 2bx – 3ay – 6by + ax c) x3 +2x2y + xy2 – 4x d) 4 - x2 – 2xy – y2 đ) 5x2 + 3(x + y)2 – 5y2 e/ 6x2y – 9x b/ 4x3 – 4x2y + xy2 – 16 xf) x2 + (2x +y)y – z2
Đọc tiếp
Bài 1: Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
a) a/ x2 – 2x
b) 2bx – 3ay – 6by + ax
c) x3 +2x2y + xy2 – 4x
d) 4 - x2 – 2xy – y2
đ) 5x2 + 3(x + y)2 – 5y2
e/ 6x2y – 9x
b/ 4x3 – 4x2y + xy2 – 16 x
f) x2 + (2x +y)y – z2
\(a,=x\left(x-2\right)\\ b,=2b\left(x-3y\right)+a\left(x-3y\right)=\left(a+2b\right)\left(x-3y\right)\\ c,=x\left(x^2+2xy+y^2-4\right)=x\left[\left(x+y\right)^2-4\right]=x\left(x+y+2\right)\left(x+y-2\right)\\ d,=4-\left(x+y\right)^2=\left(2-x-y\right)\left(2+x+y\right)\\ đ,=5\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)+3\left(x+y\right)^2=\left(x+y\right)\left(5x-5y+3x+3y\right)\\ =\left(x+y\right)\left(8x-2y\right)=2\left(4x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)\\ e,=3x\left(2xy-3\right)\\ b,=x\left(4x^2-4xy+y^2-4\right)=x\left[\left(2x-y\right)^2-4\right]=x\left(2x-y-2\right)\left(2x-y+2\right)\\ f,=\left(x+y\right)^2-z^2=\left(x+y-z\right)\left(x+y+z\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a,=x(x−2)b,=2b(x−3y)+a(x−3y)=(a+2b)(x−3y)c,=x(x2+2xy+y2−4)=x[(x+y)2−4]=x(x+y+2)(x+y−2)d,=4−(x+y)2=(2−x−y)(2+x+y)đ,=5(x−y)(x+y)+3(x+y)2=(x+y)(5x−5y+3x+3y)=(x+y)(8x−2y)=2(4x−y)(x+y)e,=3x(2xy−3)b,=x(4x2−4xy+y2−4)=x[(2x−y)2−4]=x(2x−y−2)(2x−y+2)f,=(x+y)2−z2=(x+y−z)(x+y+z)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
chứng minh rằng
a)A=x2+4xy+5y2+2x-10y+14>0
b)B=5x2+10y2-(xy-4x-2y+3)>0
c)C=(x2+2x+3)(x2+2x+4)+3>0
11,18y2 - 12xy + 2x2 12,(x2+x)2 + 3(x2+x) + 213,5x2 - 10xy + 5y2 - 20z2 14,x3 - 9x + 2x2 - 1815,x2 - 2x - 4y2 - 4y16,a2 + 2ab + b2 - 2a - 2b + 117,x3 - x + 3x2 y + 3xy2 + y3 - y 18,x3 + y3 + z3 - 3xyz19,x2 + 4x - 520,2x2 - 6x - 821,x2 - 10xy + 9y222,5xz - 5xy - x2 + 2xy - y223,(x2 + x + 1) ( x2 + x + 2) - 1224,(x+1) (x+2) (x+3) (x+4) - 2425,x3 + 2x2 - 2x - 12
Đọc tiếp
11,18y2 - 12xy + 2x2
12,(x2+x)2 + 3(x2+x) + 2
13,5x2 - 10xy + 5y2 - 20z2
14,x3 - 9x + 2x2 - 18
15,x2 - 2x - 4y2 - 4y
16,a2 + 2ab + b2 - 2a - 2b + 1
17,x3 - x + 3x2 y + 3xy2 + y3 - y
18,x3 + y3 + z3 - 3xyz
19,x2 + 4x - 5
20,2x2 - 6x - 8
21,x2 - 10xy + 9y2
22,5xz - 5xy - x2 + 2xy - y2
23,(x2 + x + 1) ( x2 + x + 2) - 12
24,(x+1) (x+2) (x+3) (x+4) - 24
25,x3 + 2x2 - 2x - 12
11: \(2x^2-12xy+18y^2\)
\(=2\left(x^2-6xy+9y^2\right)\)
\(=2\left(x-3y\right)^2\)
12: \(\left(x^2+x\right)^2+3\left(x^2+x\right)+2\)
\(=\left(x^2+x+2\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
.Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử:
a) 5x2y- 10xy2
b) x2 + 2xy + y2 - 5x - 5y
c) x2 – 6x + 8
d)5x2 – 10xy + 5y2 – 20z2
\(a,5x^2y-10xy^2=5xy\left(x-2y\right)\\ b,x^2+2xy+y^2-5x-5y=\left(x+y\right)^2-5\left(x+y\right)=\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y-5\right)\\ c,x^2-6x+8=\left(x^2-2x\right)-\left(4x-8\right)=x\left(x-2\right)-4\left(x-2\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(x-4\right)\\ d,5x^2-10xy+5y^2-20z^2=5\left(x^2-2xy+y^2-4z^2\right)=5\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-\left(2z\right)^2\right]=5\left(x-y-2z\right)\left(x-y+2z\right)\)
Đúng 3
Bình luận (0)