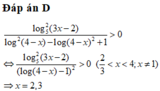tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình x^2+3x+1=y^4

Những câu hỏi liên quan
tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình x^6 + 3x^2 + 1 = y^4
-Tham khảo:
https://hoc24.vn/hoi-dap/tim-kiem?id=45441263315&q=T%C3%ACm%20nghi%E1%BB%87m%20nguy%C3%AAn%20c%E1%BB%A7a%20ph%C6%B0%C6%A1ng%20tr%C3%ACnh%20sau%C2%A0%5C%28x%5E6%203x%5E2%201%3Dy%5E4%5C%29
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình
\(x^2+x=y^4+y^3+y^2+y\)
2 Tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình :
\(3x^2+4y^2+6x+3y-4=0\)
Tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình: \(x^6+3x^2+1=y^4\)
Ta có:
\(x^6+3x^2+1=y^4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^6+12x^3+4=4y^4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^6+12x^3+9=4y^4+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^3+3\right)^2-4y^4=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^3+2y^2+3\right)\left(2x^3-2y^2+3\right)=5\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x^3+2y^2+3=5\\2x^3-2y^2+3=1\end{cases}}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0;y=1\\x=0;y=-1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x^3+2y^2+3=-1\\2x^3-2y^2+3=-5\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt[3]{-6}}\) (loại)
Vậy PT có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(0;1\right);\left(0;-1\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1. Tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình : x^2 + ( x+ 1)^2 = y^4 + (y+1)^4
2.tìm ngiệm nguyên của phương trình : x^2 - 3y^2 =17
Tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình: x6 + 3x2 + 1 = y4
Tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình sau \(x^6+3x^2+1=y^4\)
Có x6+3x2+1=y3>x6x6+3x2+1=y3>x6 (1)(1)
x6+3x2+1=y3\leqx6+3x4+3x2+1=(x2+1)3(2)x6+3x2+1=y3\leqx6+3x4+3x2+1=(x2+1)3(2)
(1);(2)(1);(2) suy ra x6+3x2+1=(x2+1)3x6+3x2+1=(x2+1)3 suy ra x=0;y=1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Đây là đáp án đúng nhất :
Ta có :
(x2+1)3=x6+3x4+3x2+1≥x6+3x2+1>(x3)2(x2+1)3=x6+3x4+3x2+1≥x6+3x2+1>(x3)2
Mà : x6+3x2+1=y3x6+3x2+1=y3
⇒x6+3x2+1=(x2+1)3⇒x=0⇒y=1⇒x6+3x2+1=(x2+1)3⇒x=0⇒y=1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Tìm số nghiệm nguyên của bất phương trình
log
5
2
(
3
x
-
2
)
log
2
(
4
-
x...
Đọc tiếp
Tìm số nghiệm nguyên của bất phương trình log 5 2 ( 3 x - 2 ) log 2 ( 4 - x ) - log ( 4 - x ) 2 + 1 > 0
A. 3
B. 1
C. 0
D. 2
tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình x2+xy+y2 = 3x +y -1
a:giải phương trình x³-3x²+3x-2=0
b:tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình
(x+y)²=(x-1)(y+1)
a/ \(x^3-3x^2+3x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-2x^2-x^2+2x+x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-2\right)-x\left(x-2\right)+\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\x^2-x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\left(tm\right)\\\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}=0\left(ktm\right)\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x = 2 là nghiệm của phương trình.
b/ \(\left(x+y\right)^2=\left(x-1\right)\left(y+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x+y\right)^2=2\left(x-1\right)\left(y+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+4xy+2y^2=2xy+2x-2y-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2y^2+2xy-2x+2y+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+\left(y^2+2y+1\right)+\left(x^2+2xy+y^2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y+1\right)^2+\left(x+y\right)^2=0\)
Mà \(\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\left(y+1\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\left(x+y\right)^2\ge0\)
Dấu " = " xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\y=-1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(x=1;y=-1\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y\right)^2=\left(x-1\right)\left(y+1\right)\)