tìm hệ số của x3 và x2: ( x3-3x2+2x+1)*(-x2)-x(2x-3x+1)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
a)A=3x(2/3x2-3x4)+(3x2)(x3-1)+(-2+9).x2-12
b)B=x(2x3+x+2)-2x2(x2+1)+x2-2x+1
c)C=x.(2x+1)-x2(x+2)+x3-x+3
a, \(A=2x^3-9x^5+3x^5-3x^2+7x^2-12=-6x^5+2x^3+4x^2-12\)
b, \(B=2x^4+x^2+2x-2x^3-2x^2+x^2-2x+1=2x^4-2x^3+1\)
c, \(C=2x^2+x-x^3-2x^2+x^3-x+3=3\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm x biết
a) x2-2x=-1
b) x3+3x2=-3x-1
a) x2-2x=-1
<=> x2-2x+1=0
<=> (x - 1)2 = 0
=> x = 1
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a: Ta có: \(x^2-2x=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\)
hay x=1
b: Ta có: \(x^3+3x^2=-3x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+3x^2+3x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1=0\)
hay x=-1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Thực hiện phép tính:
1)(x3-8):(x-2)
2)(x3-1):(x2+x+1)
3)(x3+3x2+3x+1):(x2+2x+1)
4)(25x2-4y2):(5x-2y)
1) \(\left(x^3-8\right):\left(x-2\right)=\left[\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+4\right)\right]:\left(x-2\right)=x^2+2x+4\)
2) \(\left(x^3-1\right):\left(x^2+x+1\right)=\left[\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\right]:\left(x^2+x+1\right)=x-1\)
3) \(\left(x^3+3x^2+3x+1\right):\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=\left(x+1\right)^3:\left(x+1\right)^2=x+1\)
4) \(\left(25x^2-4y^2\right):\left(5x-2y\right)=\left[\left(5x-2y\right)\left(5x+2y\right)\right]:\left(5x-2y\right)=5x+2y\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Tìm hệ số a,b,c biết
a, −3x2(2ax2−bx+c)=6x5+9x4−3c2∀x−3x2(2ax2−bx+c)=6x5+9x4−3c2∀x
b,(x2+cx+2)(a+b)=x3+x2−2∀x(x2+cx+2)(a+b)=x3+x2−2∀x
c,(ax2+bx+c)+(x+3)=x2+2x−3x∀x(ax2+bx+c)+(x+3)=x2+2x−3x∀x
Help me!!
bạn ghi lại đề đi mình chả hiểu cái mô tê gì cả
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
ài 6.Cho 2 đa thức: C(x) 2x3 -x + 7 - x3 + 3x2 - 1 ; D(x) - x3 - 8- x2 + 2x - x2 + 2 a) Thu gọn và sắp xếp các hạng tử của mỗi đa thức theo lũy thừa giảm dần của biến. b) Tìm bậc của C(x) và hệ số tự do của D(x) c) Tính C (2); D(- 1) d) Tính C(x) + D(x); C(x) - D (x) e) Tìm x biết C(x) - D (x)
Đọc tiếp
ài 6.Cho 2 đa thức: C(x) = 2x3 -x + 7 - x3 + 3x2 - 1 ; D(x) = - x3 - 8- x2 + 2x - x2 + 2
a) Thu gọn và sắp xếp các hạng tử của mỗi đa thức theo lũy thừa giảm dần của biến.
b) Tìm bậc của C(x) và hệ số tự do của D(x) c) Tính C (2); D(- 1)
d) Tính C(x) + D(x); C(x) - D (x) e) Tìm x biết C(x) = - D (x)
a: \(C\left(x\right)=x^3+3x^2-x+6\)
\(D\left(x\right)=-x^3-2x^2+2x-6\)
b: Bậc của C(x) là 3
Hệ số tự do của D(x) là -6
c: \(C\left(2\right)=8+3\cdot4-2+6=20-2+6=24\)
d: \(C\left(x\right)+D\left(x\right)=x^2+x\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a.
b. Bậc của C(x) là 3
Hệ số tự do của D(x) là -6
c.
d.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a. 12x3y – 24x2y2 + 12xy3 b. x2 – 6 x +xy – 6yc. 2x2 + 2xy x – y d. x3– 3x2 + 3x – 1 e. 3x2 – 3y2 – 12x – 12yf. x2 – 2xy – x2 + 4y2 g. x2 + 2x + 1 – 16 h.x2 – 2x – 4y2 + 1i. x2 – 2x –3j. x2 + 4x –12 k. x2 – 8 x – 9l. x2 + x – 6 a. 12x3y – 24x2y2 + 12xy3 b. x2 – 6 x +xy – 6yc. 2x2 + 2xy x – y d. x3– 3x2 + 3x – 1 e. 3x2 – 3y2 – 12x – 12yf. x2 – 2xy – x2 + 4y2 g. x2 + 2x + 1 – 16 h.x2 – 2x – 4y2 + 1i. x2 – 2x –...
Đọc tiếp
a. 12x3y – 24x2y2 + 12xy3 b. x2 – 6 x +xy – 6y c. 2x2 + 2xy x – y d. x3– 3x2 + 3x – 1 e. 3x2 – 3y2 – 12x – 12y f. x2 – 2xy – x2 + 4y2
| g. x2 + 2x + 1 – 16 h.x2 – 2x – 4y2 + 1 i. x2 – 2x –3 j. x2 + 4x –12 k. x2 – 8 x – 9 l. x2 + x – 6
|
a.
$12x^3y-24x^2y^2+12xy^3=12xy(x^2-2xy+y^2)=12xy(x-y)^2$
b.
$x^2-6x+xy-6y=(x^2+xy)-(6x+6y)=x(x+y)-6(x+y)=(x-6)(x+y)$
c.
$2x^2+2xy-x-y=2x(x+y)-(x+y)=(x+y)(2x-1)$
d.
$x^3-3x^2+3x-1=(x-1)^3$
e.
$3x^2-3y^2-12x-12y=(3x^2-3y^2)-(12x+12y)$
$=3(x-y)(x+y)-12(x+y)=(x+y)[3(x-y)-12]=3(x-y)(x-y-4)$
f.
$x^2-2xy-x^2+4y^2=4y^2-2xy=2y(2y-x)$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
g.
$x^2+2x+1=(x+1)^2$
h. Không phân tích được thành nhân tử
i.
$x^2-2x-3=(x^2-3x)+(x-3)=x(x-3)+(x-3)=(x+1)(x-3)$
j.
$x^2+4x-12=(x^2-2x)+(6x-12)=x(x-2)+6(x-2)=(x-2)(x+6)$
k.
$x^2-8x-9=(x^2+x)-(9x+9)=x(x+1)-9(x+1)=(x+1)(x-9)$
l.
$x^2+x-6=(x^2+3x)-(2x+6)=x(x+3)-2(x+3)=(x-2)(x+3)$
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1. (x3 – 3x2 + x – 3) : (x – 3) 2. (2x4 – 5x2 + x3 – 3 – 3x) : (x2 – 3) 3. (x – y – z)5 : (x – y – z)3 4. (x2 + 2x + x2 – 4) : (x + 2) 5. (2x3 + 5x2 – 2x + 3) : (2x2 – x + 1) 6. (2x3 – 5x2 + 6x – 15) : (2x – 5)
1: \(=x^2+1\)
3: \(=\left(x-y-z\right)^2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Viết theo hằng đẳng thức
a) x3- 3x2+ 3x –1
b) 1 - 4x2
c) (x2+ 2x + 4)(x - 2)
d) 27x3– 1
e) x3+ 8
g) x2- 4x + 4
h) (x - 2y)(x + 2y)
j) x2- 8x + 16
\(a,=\left(x-1\right)^3\\ b,=\left(1-2x\right)\left(1+2x\right)\\ c,=x^3-8\\ d,=\left(3x-1\right)\left(9x^2+3x+1\right)\\ e,=\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)\\ g,=\left(x-2\right)^2\\ h,=x^2-4y^2\\ j,=\left(x-4\right)^2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1) (1-x)(5x+3)=(3x-7)(x-1)
2) (x-2)(x+1)=x2-4
3) 2x3+3x2-32x=48
4) x2+2x-15=0
5) 2x(2x-3)=(3-2x)(2-5x)
6) x3-5x2+6x=0
7) (x2-5)(x+3)=0
8) (x+7)(3x-1)=49-x2
\(\left(1-x\right)\left(5x+3\right)=\left(3x-7\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
\(< =>\left(1-x\right)\left(5x+3+3x-7\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(1-x\right)\left(8x-4\right)=0\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}1-x=0\\8x-4=0\end{cases}< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}}\)
\(\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)=x^2-4\)
\(< =>\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\)
\(< =>\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1-x-2\right)=0\)
\(< =>-1\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(< =>2-x=0< =>x=2\)
\(2x^3+3x^2-32x=48\)
\(< =>x^2\left(2x+3\right)-16\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(x^2-16\right)\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(< =>\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(< =>\hept{\begin{cases}x=4\\x=-4\\x=-\frac{3}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Tính f(x) + g(x) với:
f(x) = x5 – 3x2 + x3 – x2 – 2x + 5
g(x) = x2 – 3x + 1 + x2 – x4 + x5
Thu gọn, sắp xếp đa thức theo lũy thừa giảm của biến:
* Ta có: f(x) = x5 – 3x2 + x3 – x2 – 2x + 5
= x5 – (3x2 + x2 ) + x3 - 2x + 5
= x5 – 4x2 + x3 – 2x + 5
= x5 + x3 – 4x2 – 2x + 5
Và g(x) = x2 – 3x + 1 + x2 – x4 + x5
= (x2 + x2 ) – 3x + 1 – x4 + x5
= 2x2 – 3x + 1 – x4 + x5
= x5 – x4 + 2x2 – 3x + 1
* f(x) + g(x):
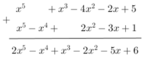
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)





























