tìm x
2.(x-1)=4/3
(x-1)^2=4
2.|x+1|=3

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Tìm x :
b )(x-1) . ( x2 +x +1) -x.(x-3) . (x+3 )=8
c)( X2 + 2 ) . (x-4 ) - ( X+2 ). ( x2 +4x +4=-16
b) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=8\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3-1-x\left(x^2-9\right)=8\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3-1-x^3+9x=8\)
\(\Rightarrow9x=9\Rightarrow x=1\)
c) \(\left(x^2+2\right)\left(x-4\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2+4x+4\right)=-16\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3-4x^2+2x-8-\left(x+2\right)\left(x+2\right)^2=-16\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3-4x^2+2x-8-\left(x+2\right)^3=-16\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3-4x^2+2x-8-\left(x^3+6x^2+12x+8\right)=-16\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3-4x^2+2x-8-x^3-6x^2-12x-8=-16\)
\(\Rightarrow-10x^2-10x-16=-16\)
\(\Rightarrow10x^2+10x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow10x\left(x+1\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Bài 1: Tìm x:
1) (x-3)3 -( x-3)(x2+ 3x+9) +6( x+1)2+ 3x2 = -33
2) (X-3)( X2+ 3X+9) - X(X-2)( 2+X) = 1
3) (X+2)(X2 - 2X+4) – X(X-3)(X+3) = 26
a: Ta có: \(\left(x-3\right)^3-\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+3x+9\right)+6\left(x+1\right)^2+3x^2=-33\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-9x^2+27x-27-x^3+27+6x^2+12x+1+3x^2=-33\)
\(\Leftrightarrow39x=-34\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{34}{39}\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+3x+9\right)-x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-27-x^3+4x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=28\)
hay x=7
c: Ta có: \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=26\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+8-x^3+9x=26\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
1/Rút gọn các biểu thức: a)(x+1)2-(x-1)2-3(x+1)(x-1)
b)5(x+2)(x-2)-(2x-3)2-x2+17
c)(x-3)3-(x-3)(x2+3x+9)+6(x+1)2
2/ Tìm x a) (x+4)2-(x+1)(x-1)=16
b) (x+2)(x2-2x+4)-x(x2+2)=15
Tìm x, biết:a)
(
x
+
3
)
2
+ (4 - x)(x + 4) 1;b)
(2 - x)
3
+(3 +x)(9 - 3x +
x
2
) + 6x(1 - x) 17;c)
x
4
- 2
x
2
+1 0.
Đọc tiếp
Tìm x, biết:
a) ( x + 3 ) 2 + (4 - x)(x + 4) = 1;
b) (2 - x) 3 +(3 +x)(9 - 3x + x 2 ) + 6x(1 - x) = 17;
c) x 4 - 2 x 2 +1 = 0.
a) Tìm được x = -4.
b) Tìm được x = 3.
c) Tìm được x = ±1.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Rút gọn biểu thức:
a) (x + 2)(x – 2) – (x + 1)2
b) (2x – 1)(4x2 + 2x + 1) – (2x + 1)( 4x2 – 2x + 1)
3. Tìm x biết:
a) (x + 2)(x2 – 2x + 4) – x(x2 – 2) = 15
b) (x – 1)3 – x(x2 – 3x – 4) = 13
thanks
\(a,=x^2-4-x^2-2x-1=-2x-5\\ b,=8x^3-1-8x^3-1=-2\\ 3,\\ a,\Rightarrow x^3+8-x^3+2x=15\\ \Rightarrow2x=7\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\ b,\Rightarrow x^3-3x^2+3x-1-x^3+3x^2+4x=13\\ \Rightarrow7x=14\Rightarrow x=2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 2:
a) \(=x^2-4-x^2-2x-1=-2x-5\)
b) \(=8x^3-1-8x^3-1=-2\)
Bài 3:
a) \(\Rightarrow x^3+8-x^3+2x=15\)
\(\Rightarrow2x=7\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{2}\)
b) \(\Rightarrow x^3-3x^2+3x-1-x^3+3x^2+4x=13\)
\(\Rightarrow7x=14\Rightarrow x=2\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 2: (2 điểm) Tìm x, biết:
a) (3x + 4)2 – (3x – 1)(3x + 1) = 49
b) x2 – 4x + 4 = 9(x – 2)
c) x2 – 25 = 3x - 15
d) (x – 1)3 + 3(x + 1)2 = (x2 – 2x + 4)(x + 2)
a) \(\Rightarrow9x^2+24x+16-9x^2+1=49\)
\(\Rightarrow24x=32\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
b) \(\Rightarrow x^2-13x+22=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-11\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=11\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(\Rightarrow x^2-3x-10=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Giải các phương trình:
a
x
-
3
2
+
x
+
4
2
23
−
3
x...
Đọc tiếp
Giải các phương trình:
a x - 3 2 + x + 4 2 = 23 − 3 x b ) x 3 + 2 x 2 − x - 3 2 = ( x − 1 ) x 2 − 2 c ) x - 1 3 + 0 , 5 x 2 = x x 2 + 1 , 5 d ) x ( x − 7 ) 3 − 1 = x 2 − x − 4 3 e ) 14 x 2 − 9 = 1 − 1 3 − x f ) $ 2 x x + 1 = x 2 − x + 8 ( x + 1 ) ( x − 4 )
a)
( x − 3 ) 2 + ( x + 4 ) 2 = 23 − 3 x ⇔ x 2 − 6 x + 9 + x 2 + 8 x + 16 = 23 − 3 x ⇔ x 2 − 6 x + 9 + x 2 + 8 x + 16 + 3 x − 23 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 + 5 x + 2 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 5; c = 2 ⇒ Δ = 5 2 – 4 . 2 . 2 = 9 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
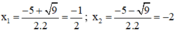
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 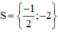
b)
x 3 + 2 x 2 − ( x − 3 ) 2 = ( x − 1 ) x 2 − 2 ⇔ x 3 + 2 x 2 − x 2 − 6 x + 9 = x 3 − x 2 − 2 x + 2 ⇔ x 3 + 2 x 2 − x 2 + 6 x − 9 − x 3 + x 2 + 2 x − 2 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 + 8 x − 11 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 8; c = -11 ⇒ Δ ’ = 4 2 – 2 . ( - 11 ) = 38 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
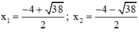
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 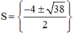
c)
( x − 1 ) 3 + 0 , 5 x 2 = x x 2 + 1 , 5 ⇔ x 3 − 3 x 2 + 3 x − 1 + 0 , 5 x 2 = x 3 + 1 , 5 x ⇔ x 3 + 1 , 5 x − x 3 + 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 − 0 , 5 x 2 = 0 ⇔ 2 , 5 x 2 − 1 , 5 x + 1 = 0
Có a = 2,5; b = -1,5; c = 1
⇒ Δ = ( - 1 , 5 ) 2 – 4 . 2 , 5 . 1 = - 7 , 75 < 0
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.
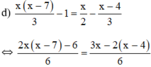
⇔ 2 x ( x − 7 ) − 6 = 3 x − 2 ( x − 4 ) ⇔ 2 x 2 − 14 x − 6 = 3 x − 2 x + 8 ⇔ 2 x 2 − 14 x − 6 − 3 x + 2 x − 8 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 − 15 x − 14 = 0
Có a = 2; b = -15; c = -14
⇒ Δ = ( - 15 ) 2 – 4 . 2 . ( - 14 ) = 337 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
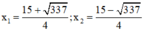
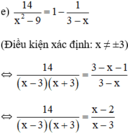
⇔ 14 = ( x - 2 ) ( x + 3 ) ⇔ 14 = x 2 - 2 x + 3 x - 6 ⇔ x 2 + x - 20 = 0
Có a = 1; b = 1; c = -20
⇒ Δ = 1 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 20 ) = 81 > 0
Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
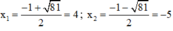
Cả hai nghiệm đều thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-5; 4}.
f) Điều kiện: x≠-1;x≠4

Ta có: a= 1, b = -7, c = - 8
∆ = ( - 7 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 8 ) = 81
=> Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
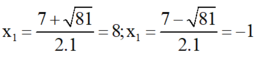
Kết hợp với diều kiện, nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là x = 8
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
tìm x:
a)3(2x-3)+2(2-x)=-3
b)2x(x2-2)+x2(1-2x)-x2=-12
c)3x(2x+3)-(2x+5)(3x-2)=8
d)4x(x - 1) - 3(x2-5)-x2=(x-3)-(x+4)
e)2(3x-1)(2x+5)-6(2x-1)(x+2)=-6
a: Ta có: \(3\left(2x-3\right)+2\left(2-x\right)=-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-9+4-2x=-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=2\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (1)
Bài 1. Tìm x, biết
a) (x+4)2-x2(x+12)=16
c) (x+3)3-x(3x+1)2+(2x+1)(4x2-2x+1)=28
d) (x-2)3-(x+5)(x2-5x+25)-6x2=11
Bài 2. Rút gọn các biểu thức sau:
A = (x+1)3+(x-1)3
B = (x-3)3-(x+3)(x2-3x+9)+(3x-1)(3x+1)
Bài 2:
a: Ta có: \(A=\left(x+1\right)^3+\left(x-1\right)^3\)
\(=x^3+3x^2+3x+1+x^3-3x^2+3x-1\)
\(=2x^3+6x\)
b: Ta có: \(B=\left(x-3\right)^3-\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2-3x+9\right)+\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)\)
\(=x^3-9x^2+27x-27-x^3-27+9x^2-1\)
\(=27x-55\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)


















