Jupiter spins faster than....planet A.any others B.any another C.any D.any other Lm+gthich hộ vs ạ

Những câu hỏi liên quan
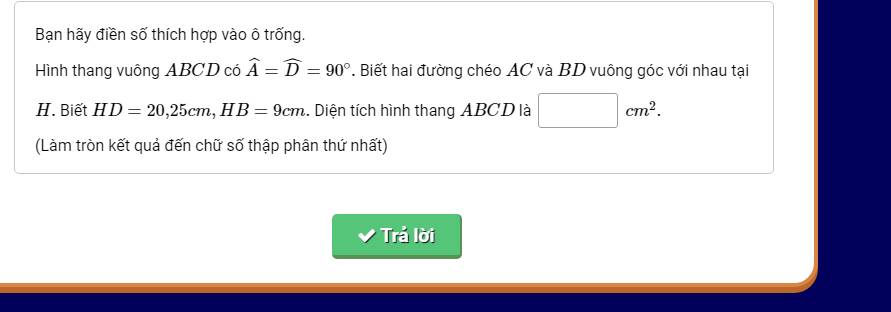
lm vs gthich hộ ạ?
Xét ΔABD vuông tại A có AH là đường cao
nên \(AH^2=HD\cdot HB\)
=>\(AH=\sqrt{20,25\cdot9}=13,5\left(cm\right)\)
Xét ΔDAC vuông tại D có DH là đường cao
nên \(DH^2=AH\cdot HC\)
=>\(HC=\dfrac{20.25^2}{13.5}=30,375\left(cm\right)\)
BD=BH+DH=9+20,25=29,25(cm)
AC=AH+HC=13,5+30,375=43,875(cm)
Vì AC\(\perp\)BD tại H
nên \(S_{ABCD}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot AC\cdot BD=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot29,25\cdot43,875\simeq641,7\left(cm^2\right)\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
I. Chose the best answer to complete each of the following sentences
1.Theres still ..........wine in the bottle.
A.some B.any C.a D.an
2.Ive got hardly ..............money.
A.a B.an C.any D.some
3. ............people find this more difficult than others.
A,A B.An C.Any D.Some
4........... guests are there in the living room?
A.How much B.How many C.How long D.How far
5.There is ...........university opposite to the supermarket
A.some B.any C.a D.an
6. It was with......... surprise th...
Đọc tiếp
I. Chose the best answer to complete each of the following sentences
1.There's still ..........wine in the bottle.
A.some B.any C.a D.an
2.I've got hardly ..............money.
A.a B.an C.any D.some
3. ............people find this more difficult than others.
A,A B.An C.Any D.Some
4........... guests are there in the living room?
A.How much B.How many C.How long D.How far
5.There is ...........university opposite to the supermarket
A.some B.any C.a D.an
6. It was with......... surprise that I heard the news.
A.some B.any C.all D.an
7. She asked if we had ............questions.
A.some B.any C.a D.an
8.Doctors take care of............. patients.
A.No article B.a C.an D.some
9.I don't expect we'll have.......... more trouble from him.
A.any B.some C.a D.an
10. ............powder do you need to make that cake?
A.How often B.How far C.How much D.How many
I. Chose the best answer to complete each of the following sentences
1.There's still ..........wine in the bottle.
A.some B.any C.a D.an
2.I've got hardly ..............money.
A.a B.an C.any D.some
3. ............people find this more difficult than others.
A,A B.An C.Any D.Some
4........... guests are there in the living room?
A.How much B.How many C.How long D.How far
5.There is ...........university opposite to the supermarket
A.some B.any C.a D.an
6. It was with......... surprise that I heard the news.
A.some B.any C.all D.an
7. She asked if we had ............questions.
A.some B.any C.a D.an
8.Doctors take care of............. patients.
A.No article B.a C.an D.some
9.I don't expect we'll have.......... more trouble from him.
A.any B.some C.a D.an
10. ............powder do you need to make that cake?
A.How often B.How far C.How much D.How many
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
I. Chose the best answer to complete each of the following sentences
1.Theres still wine in the bottle.
A.some B.any C.a D.an
2.Ive got hardly money.
A.a B.an C.any D.some
3. people find this more difficult than others.
A,A B.An C.Any D.Some
4. guests are there in the living room?
A.How much B.How many C.How long D.How far
5.There is university opposite to the super...
Đọc tiếp
I. Chose the best answer to complete each of the following sentences
1.There's still wine in the bottle.
A.some B.any C.a D.an
2.I've got hardly money.
A.a B.an C.any D.some
3. people find this more difficult than others.
A,A B.An C.Any D.Some
4. guests are there in the living room?
A.How much B.How many C.How long D.How far
5.There is university opposite to the supermarket
A.some B.any C.a D.an
6. It was with surprise that I heard the news.
A.some B.any C.all D.an
7. She asked if we had questions.
A.some B.any C.a D.an
8.Doctors take care of patients.
A.No article B.a C.an D.some
9.I don't expect we'll have more trouble from him.
A.any B.some C.a D.an
10. powder do you need to make that cake?
A.How often B.How far C.How much D.How many
1. A.
2. D.
3. D.
4. B.
5. C.
6. A.
7. A.
8. A.
9. A.
10. C.
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
I. Chose the best answer to complete each of the following sentences
1.Theres still wine in the bottle.
A.some B.any C.a D.an
2.Ive got hardly money.
A.a B.an C.any D.some
3. people find this more difficult than others.
A,A B.An C.Any D.Some
4. guests are there in the living room?
A.How much B.How many C.How long D.How far
5.There is university opposite to the supermarket
A.some B.any C.a...
Đọc tiếp
I. Chose the best answer to complete each of the following sentences
1.There's still wine in the bottle.
A.some B.any C.a D.an
2.I've got hardly money.
A.a B.an C.any D.some
3. people find this more difficult than others.
A,A B.An C.Any D.Some
4. guests are there in the living room?
A.How much B.How many C.How long D.How far
5.There is university opposite to the supermarket
A.some B.any C.a D.an
6. It was with surprise that I heard the news.
A.some B.any C.all D.an
7. She asked if we had questions.
A.some B.any C.a D.an
8.Doctors take care of patients.
A.No article B.a C.an D.some
9.I don't expect we'll have more trouble from him.
A.any B.some C.a D.an
10. powder do you need to make that cake?
A.How often B.How far C.How much D.How many
Làm+gthich hộ vs ạ:(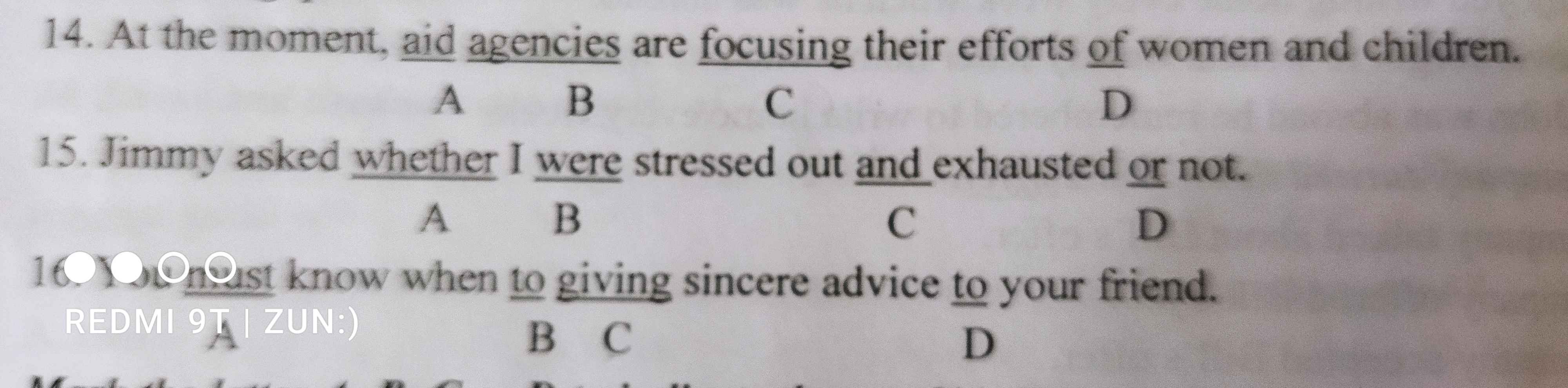
1 D => on
focus st on sb : tập trung cái gì vào ai
2 B => was
tobe đi với I là am ở hiện tại trong câu gián tiếp chuyển sang quá khứ là was
3 C => give
when to V : khi nào làm
Đúng 1
Bình luận (2)
Read the text and answer the following questions.
SATURN
Saturn is the second-largest planet and is a gas giant like Jupiter. Under clouds of methane, hydrogen, and helium, the sky slowly turns into a giant ocean of liquid chemicals. Saturn is the least dense planet in our solar system; it is made mostly of hydrogen and helium. Because it is so lightweight and spins so quickly, Saturn is not perfectly round like the other planets. Saturn is surrounded by thousands of small rings made of rocks...
Đọc tiếp
Read the text and answer the following questions.
SATURN
Saturn is the second-largest planet and is a gas giant like Jupiter. Under clouds of methane, hydrogen, and helium, the sky slowly turns into a giant ocean of liquid chemicals. Saturn is the least dense planet in our solar system; it is made mostly of hydrogen and helium. Because it is so lightweight and spins so quickly, Saturn is not perfectly round like the other planets. Saturn is surrounded by thousands of small rings made of rocks and ice. It also has 140 natural satellites, like moons and pieces of debris.
1. How is Saturn similar to Jupiter?
2. What are the clouds made of?
3. Describe the surface of Saturn.
4. Why is Saturn not perfectly round?
5. Describe some of the things surrounding Saturn.
1. It is a gas giant Jupiter.
2. Clouds are made of methane, hydrogen, and helium.
3. Saturn is the least dense planet in our solar system and is made mostly of hydrogen and helium.
4. Because it is so lightweight and spins so quickly.
5. Saturn is surrounded by thousands of small rings made of rocks and rice.
1 It is a gas giant like Jupiter.
2 Clouds are made of methane, hydrogen, and helium.
3 Saturn is the least dense planet in our solar system and is made mostly of hydrogen and helium.
4 Because it is so lightweight and spins so quickly.
5 Saturn is surrounded by thousands of small rings made of rocks and rice.
1. It is a gas giant like Jupiter.
2. Clouds are made of methane, hydrogen, and helium.
3. Saturn is the least dense planet in our solar system and is made mostly of hydrogen and helium.
4. Because it is so lightweight and spins so quickly.
5. Saturn is surrounded by thousands of small rings made of rocks and rice.
Xem thêm câu trả lời
Talk about life on another planet.
giúp e vs ạ!!
em sắp thi nói rùi:((
Bạn tk:
The gas giant Jupiter, the next planet beyond Mars in the solar system, is inhospitable to life in any currently imaginable form. But its icy moons – especially Europa – have potential. A number of missions have flown past Jupiter and its moons on route to other places, but Nasa’s Galileo mission was the first designed to specifically orbit the planet and study its moons. It collected images and data in the Jovian system from 1995 to 2003, passing Europa 12 times.
Jupiter’s moon Europa is one of the most likely places to harbour life outside Earth, with its liquid oceans and gravitational energy sources
Pictures and data collected by this spacecraft suggest that Europa has a layered structure like Earth: an iron-rich core, a rocky mantle and a crust of ice. Magnetic field measurements found an electric current inside, consistent with a salty liquid ocean beneath the thick crust of ice around the whole planet. Photographs showing huge cracks in the ice, taken by the same mission, support this idea.
Europa’s surface resembles Earth’s sea ice in Antarctica, explains François Poulet from the Institute of Space Astrophysics at the Université Paris-Sud in France: ‘It indicates that the ice is geologically pretty young and it could be proof of its interaction with a reservoir of liquid water.’ In December 2012, the Hubble Space Telescope also detected water vapour above Europa’s South Pole and it was proposed this came from erupting water plumes. Spacecraft have not yet seen these plumes, however, so if they do exist they must be intermittent.
So, Europa probably has water. But what about the other two necessary components to be habitable? It has a source of heat energy coming from the friction of being pulled towards Jupiter’s gravitational field by different amounts during different stages of its elliptical orbit. There is also plenty of radiation around Jupiter to potentially start chemical reactions (strong enough to also very quickly destroy any organic compound formed). But whether it has the correct raw chemical ingredients isn’t yet known; modelling suggests that it might, but more hard data is needed.
In 2022, both the European Space Agency (ESA) and Nasa plan to launch spacecraft that will get up close and personal with Europa. ESA’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice) will take over seven years to reach the Jovian system. ‘We will arrive at the end of 2029 and start operation during 2030,’ says Poulet, a member of the team developing the visible and infrared spectrometer onboard called Majis (Moons and Jupiter Imaging Spectrometer). The main target of the Juice mission is Ganymede, another of Jupiter’s moons, but Europa will receive two flybys. Majis will characterise the surface composition of this moon and – together with the UV spectrometer onboard – determine the composition of Europa’s very thin atmosphere. Other cameras and spectrometers will also help build understanding of this icy world’s interior and crust.
For Nasa’s Europa Clipper mission, Europa is the star of the show. While the seemingly obvious mission would be to orbit Europa for a few years, any spacecraft doing this would be exposed to life-shortening radiation from Jupiter. Instead, Europa clipper will orbit Jupiter, dipping in and out of its radiation belt. It will carry out at least 45 close flybys of Europa over three and a half years. A mixture of cameras and spectrometers will examine the moon and its tenuous atmosphere. If the water plumes above the South Pole do exist, it will also be able to fly through these and therefore directly measure the chemical composition of the moon’s ocean. If the Europa Clipper launches in 2022, there are two possible arrival times for it: 2025, if Nasa’s new Space Launch System (SLS) that is currently in development is used, or January 2030, if a traditional rocket is used.
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
1.I was sitting in the back row of the theatre so I could hardly see the ...
A.painter B.musician C.composer D.writter
2.I havent got ... bread left for breakfast.
A.a B.an C.any D.some
3.There ... bottles of mineral water in the fridge.
A.arent some B.are any C.are some D.is some
4.Shes got ... nice photo of her class.
A.an B.a C.some...
Đọc tiếp
1.I was sitting in the back row of the theatre so I could hardly see the ...
A.painter B.musician C.composer D.writter
2.I haven't got ... bread left for breakfast.
A.a B.an C.any D.some
3.There ... bottles of mineral water in the fridge.
A.aren't some B.are any C.are some D.is some
4.She's got ... nice photo of her class.
A.an B.a C.some D.any
5.Would you like ... yoghurt and cold water.
A.any B.a C.an D.some
1.I was sitting in the back row of the theatre so I could hardly see the ...
A.painter B.musician C.composer D.writter
2.I haven't got ... bread left for breakfast.
A.a B.an C.any D.some
3.There ... bottles of mineral water in the fridge.
A.aren't some B.are any C.are some D.is some
4.She's got ... nice photo of her class.
A.an B.a C.some D.any
5.Would you like ... yoghurt and cold water.
A.any B.a C.an D.some
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1.I was sitting in the back row of the theatre so I could hardly see the ...
A.painter B.musician C.composer D.writter
2.I haven't got ... bread left for breakfast.
A.a B.an C.any D.some
3.There ... bottles of mineral water in the fridge.
A.aren't some B.are any C.are some D.is some
4.She's got ... nice photo of her class.
A.an B.a C.some D.any
5.Would you like ... yoghurt and cold water.
A.any B.a C.an D.some
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
1.I was sitting in the back row of the theatre so I could hardly see the ...
A.painter B.musician C.composer D.writter
2.I haven't got ... bread left for breakfast.
A.a B.an C.any D.some
3.There ... bottles of mineral water in the fridge.
A.aren't some B.are any C.are some D.is some
4.She's got ... nice photo of her class.
A.an B.a C.some D.any
5.Would you like ... yoghurt and cold water.
A.any B.a C.an D.some
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Read the following passage and mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word or phrase that best fits each of the numbered blanks. The Planets of Jupiter The largest of the giant gas planets, Jupiter, with a volume 1,300 times greater than Earth’s, contains more than twice the mass of all the other planets combined. It is thought to be a gaseous and fluid planet without solid surfaces, Had it been somewhat more massive, Jupiter might have attained internal temperatures...
Đọc tiếp
Read the following passage and mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word or phrase that best fits each of the numbered blanks.
The Planets of Jupiter
The largest of the giant gas planets, Jupiter, with a volume 1,300 times greater than Earth’s, contains more than twice the mass of all the other planets combined. It is thought to be a gaseous and fluid planet without solid surfaces, Had it been somewhat more massive, Jupiter might have attained internal temperatures as high as the ignition point for nuclear reactions, and it would have flamed as a star in its own right. Jupiter and the other giant planets are of a low-density type quite distinct from the terrestrial planets: they are composed predominantly of such substances as hydrogen, helium, ammonia, and methane, unlike terrestrial planets. Much of Jupiter’s interior might be in the form of liquid, metallic hydrogen, Normally, hydrogen is a gas, but under pressures of millions of kilograms per square centimeter, which exist in the deep interior of Jupiter, the hydrogen atoms might lock together to form a liquid with the properties of a metal. Some scientists believe that the innermost core of Jupiter might be rocky, or metallic like the core of Earth.
Jupiter rotates very fast, once every 9.8 hours. As a result, its clouds, which are composed largely of frozen and liquid ammonia, have been whipped into alternating dark and bright bands that circle the planet at different speeds in different latitudes. Jupiter’s puzzling Great Red Spot changes size as it hovers in the Southern Hemisphere. Scientists speculate it might be a gigantic hurricane, which because of its large size (the Earth could easily fit inside it), lasts for hundreds of years.
Jupiter gives off twice as much heat as it receives from the Sun. Perhaps this is primeval heat or beat generated by the continued gravitational contraction of the planet. Another star like characteristic of Jupiter is its sixteen natural satellites, which, like a miniature model of the Solar System, decrease in density with distance from rocky moons close to Jupiter to icy moons farther away. If Jupiter were about 70 times more massive, it would have become a star, Jupiter is the best-preserved sample of the early solar nebula, and with its satellites, might contain the most important clues about the origin of the Solar System.
According to the passage, some scientists believe Jupiter and Earth are similar in that they both have__________.
A. solid surfaces
B. similar masses
C. similar atmospheres
D. metallic cores

























