Giúp mik với ạ :D

Giúp mik câu c,d,e với ạ mik đag cần gấp ạ
\(c,\Rightarrow\left|x-\dfrac{1}{9}\right|=-\dfrac{4}{5}\\ \Rightarrow x\in\varnothing\left(\left|x-\dfrac{1}{9}\right|\ge0>-\dfrac{4}{5}\right)\\ d,\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-2=0\\4y-7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\y=\dfrac{7}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\\ e,\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\x-y=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x=y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
 giúp mik với ạ (đang cần gấp ạ ) phần b , c, d,e
giúp mik với ạ (đang cần gấp ạ ) phần b , c, d,e
Ai giúp mik bài 5 câu d với ạ
5:
d: \(A=\dfrac{9\left(x_1+x_2\right)+10-3m}{18\left(x_1x_2+2\right)^2+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{9\cdot\dfrac{m-2}{3}+10-3m}{18\cdot\left(\dfrac{m-6}{3}+2\right)^2+1}=\dfrac{3m-6+10-3m}{18\cdot\left(\dfrac{m-6+6}{3}\right)^2+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{4}{18\cdot\dfrac{m^2}{9}+1}=\dfrac{4}{2m^2+1}< =\dfrac{4}{1}=4\)
Dấu = xảy ra khi m=0

GIÚP MIK CÂU C,D,E,H VỚI Ạ
Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt thì:
\(\Delta>0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(-5\right)^2-4.1.\left(m+4\right)>0\\ \Leftrightarrow25-4m-16>0\\\Leftrightarrow9-4m>0\\ \Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{9}{4}\)
Theo viét:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=5\\x_1x_2=m+4\end{matrix}\right.\)
c,
\(\left|x_1-x_2\right|=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow x_1^2-2x_1x_2+x_2^2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow5^2-4\left(m+4\right)=9\\ \Leftrightarrow25-4m-16=9\\ \Leftrightarrow m=0\left(nhận\right)\)
d.
\(\left|x_1\right|+\left|x_2\right|=4\\ \)
Xét trường hợp 1: hai nghiệm đều dương:
ta có:
\(x_1+x_2=4\)
5 = 4 (vô lý)
Loại trường hợp này.
Xét trường hợp 2: hai nghiệm đều âm, tương tự ta loại trường hợp này.
Xét trường hợp 3:
\(x_1< 0< x_2\)
=> \(x_2-x_1=4\)
<=> \(x_2+x_1-2x_1=4\)
=> \(5-2x_1=4\)
=> \(x_1=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(x_2< 0< x_1\)
\(x_1-x_2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x_1+x_2-2x_2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow5-2x_2=4\\ \Rightarrow x_2=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Có: \(x_1x_2=m+4\\\)
<=> \(\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{1}{2}=m+4\)
=> m = -3,75 (nhận)
e.
Theo viét và theo đề ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x_1+4x_2=6\left(1\right)\\x_1+x_2=5\left(2\right)\\x_1x_2=m+4\left(3\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Từ (1) có \(x_1=\dfrac{6-4x_2}{3}=2-\dfrac{4}{3}x_2\) (x)
Thế (x) vào (2) được \(2-\dfrac{4}{3}x_2+x_2=5\)
=> \(x_2=-9\) (xx)
Thế (xx) vào (1) được \(3x_1+4.\left(-9\right)=6\)
=> \(x_1=14\) (xxx)
Thế (xx) và (xxx) vào (3) được:
\(14.\left(-9\right)=m+4\)
=> m = -130 (nhận)
h.
\(x_1\left(1-3x_2\right)+x_2\left(1-3x_1\right)=m^2-23\)
<=> \(x_1-3x_1x_2+x_2-3x_1x_2=m^2-23\)
<=> \(x_1+x_2-6x_1x_2=m^2-23\)
<=> \(5-6.\left(m+4\right)=m^2-23\)
<=> \(5-6m-20-m^2+23=0\)
<=> \(-m^2-6m+8=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-6\right)^2-4.\left(-1\right).8=68\)
\(m_1=\dfrac{6+\sqrt{68}}{2.\left(-1\right)}=-3-\sqrt{17}\left(nhận\right)\)
\(m_2=\dfrac{6-\sqrt{68}}{2.\left(-1\right)}=-3+\sqrt{17}\left(nhận\right)\)
☕T.Lam
Mình không chắc chắn ở câu d, mình lên đây để ôn bài thi tiện thể giúp được bạn phần nào.
Giúp mik giải bài 2 câu d nhanh với ạ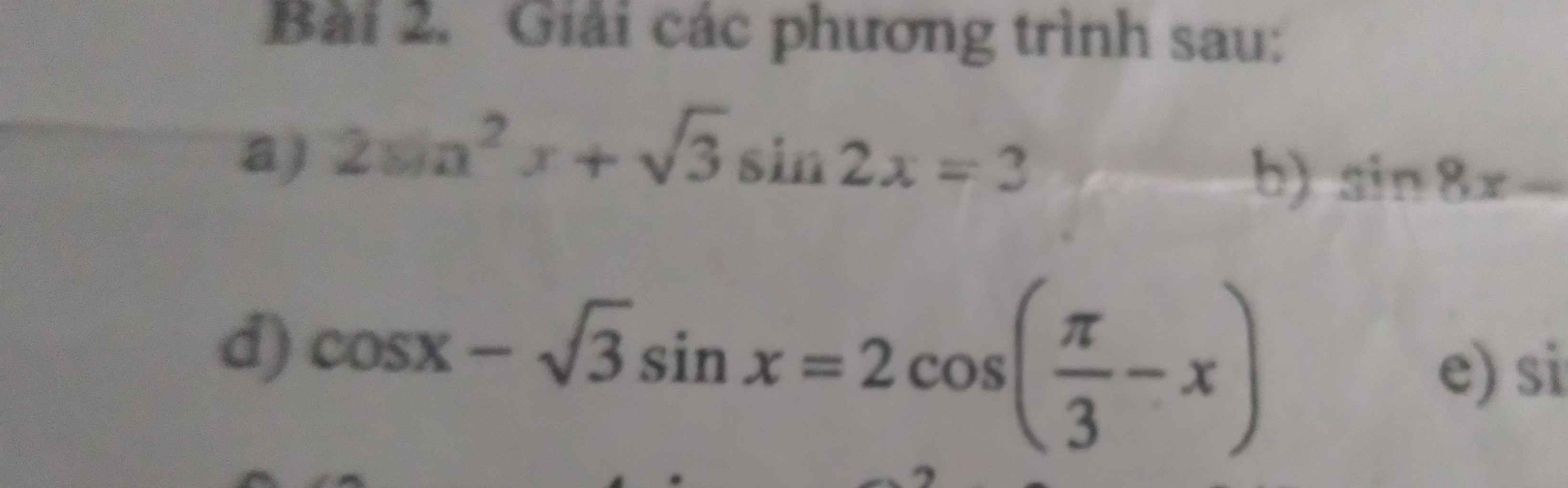
a, \(2sin^2x+\sqrt{3}sin2x=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(1-2sin^2x\right)+\sqrt{3}sin2x=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{3}sin2x-cos2x=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sin2x-\dfrac{1}{2}cos2x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\)
d, \(cosx-\sqrt{3}sinx=2cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}cosx-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx=cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2sin\dfrac{\pi}{3}.sinx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sinx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=k\pi\)
d, cosx - \(\sqrt{3}\)sinx = 2cos\(\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-x\right)\)
⇔ \(2cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=2cos\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)\)
⇔ \(cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)-cos\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)\) = 0
⇔ \(-2sinx.sin\dfrac{\pi}{3}=0\)
⇔ sinx = 0
⇔ x = kπ , k ∈ Z
Sử dụng các công thức sau :
\(cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=cosx.cos\dfrac{\pi}{3}-sinx.sin\dfrac{\pi}{3}=\dfrac{1}{2}cosx-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx\)
\(cosa-cosb=-2sin\dfrac{a+b}{2}.sin\dfrac{a-b}{2}\)
Ai giúp mik giải bài này với ;-;
△DMP có góc D=55 độ; góc 2M=góc3P
Giải giúp với ạ![]()
Từ giả thiết, suy ra: \(\hat{M}=\dfrac{3}{2}\hat{P}\).
Ta có: \(\hat{D}+\hat{M}+\hat{P}=180^o\) (tổng 3 góc trong một tam giác)
\(\Leftrightarrow55^o+\dfrac{3}{2}\hat{P}+\hat{P}=180^o\Leftrightarrow\hat{P}=50^o\)
\(\Rightarrow\hat{M}=\dfrac{3}{2}\hat{P}=\dfrac{3}{2}\cdot50^o=75^o\)
Mọi người giúp mik câu d,e,f,j với ạ 
d) \(\dfrac{5x+2}{6}\) +\(\dfrac{3-4x}{2}\) = 2-\(\dfrac{x+7}{3}\)
=>5x+2+3(3-4x)=12-2(x+7)
5x+2+9-12x=12-2x-14
-5x=-13
x=\(\dfrac{13}{5}\)
e) \(\dfrac{-20}{9}x +4=\dfrac{8}{3}x-40\)
=>-20x+36=24x-360
-44x=-396
x=9
f) 3x(2x-5)-4X+10=0
6X2 -15X-4X+10=0
2x(3x-2)-5(3x-2)=0
(3x-2)(2x-5)=0
\(\left[\begin{array}{} Biểu thức (3x-2=0)\\ Biểu thức (2x-5=0) \end{array} \right.\)\(\left[\begin{array}{} (x=\dfrac{2}{3})\\ (x=\dfrac{5}{2}) \end{array} \right.\)
j) \(\dfrac{x-45}{55}+\dfrac{x-47}{53}=\dfrac{x-55}{45}+\dfrac{x-53}{47}\)
\(\dfrac{x-45}{55}-1+\dfrac{x-47}{53}-1=\dfrac{x-55}{45}-1+\dfrac{x-53}{47}-1\)
\(\dfrac{x-100}{55}+\dfrac{x-100}{53}=\dfrac{x-100}{45}+\dfrac{x-100}{47}\)
\(\dfrac{x-100}{55}+\dfrac{x-100}{53}-\dfrac{x-100}{45}-\dfrac{x-100}{47}=0\)
(x-100)(\(\dfrac{1}{55}+\dfrac{1}{53}-\dfrac{1}{45}-\dfrac{1}{47}\))=0
=> x-100=0(\(\dfrac{1}{55}+\dfrac{1}{53}-\dfrac{1}{45}-\dfrac{1}{47}\) >0)
=> x= 100
GIÚP MIK VỚI Ạ! MIK ĐANG CẦN GẤP!!
GIÚP MIK TỪ CÂU 3 VỚI Ạ!!
Giải giúp mik câu đại với ạ , giúp mik vẽ hình bài hình luoon đc ko ạ !! Giúp mik với mik cần gấp lắm !! Các bạn giải chi tiết giúp mik
Câu 3:
a: \(BD=\sqrt{BC^2-DC^2}=4\left(cm\right)\)
b: \(\widehat{A}=180^0-2\cdot70^0=40^0< \widehat{B}\)
nên BC<AC=AB
c: Xét ΔEBC vuông tại E và ΔDCB vuông tại D có
BC chung
\(\widehat{EBC}=\widehat{DCB}\)
Do đó:ΔEBC=ΔDCB
d: Xét ΔOBC có \(\widehat{OBC}=\widehat{OCB}\)
nên ΔOBC cân tại O
Câu 2
a) Thay y = -2 vào biểu thức đã cho ta được:
2.(-2) + 3 = -1
Vậy giá trị của biểu thức đã cho tại y = -2 là -1
b) Thay x = -5 vào biểu thức đã cho ta được:
2.[(-5)² - 5] = 2.(25 - 5) = 2.20 = 40
Vậy giá trị của biểu thức đã cho tại x = -5 là 40